Value of turbo spin-echo diffusion-weighted imaging sequence in the diagnosis of nasal cavity and paranasal sinus diseases
-
摘要:
目的 前瞻性比较快速自旋回波弥散加权成像(TSE-DWI)与平面回波弥散加权成像(EP-DWI)对鼻腔鼻窦病变图像质量差异,探讨TSE-DWI及EP-DWI的表观扩散系数(ADC)值鉴别鼻腔鼻窦良恶性病变的诊断价值。 方法 前瞻性选取2022年10月~2023年8月在我院诊治鼻腔鼻窦病变的93例患者作为研究对象,采用Philips 1.5T磁共振扫描仪进行扫描,所有患者行常规鼻腔鼻窦磁共振平扫后均行TSE-DWI及EP-DWI成像,通过2位医师对TSE-DWI与EP-DWI图像进行主观评价及客观评价来对比图像质量,评价2位医师间的一致性、两种DWI序列ADC值一致性及Pearson相关系数,比较鼻腔鼻窦良恶性病变ADC值的差异并使用ROC曲线计算ADC值鉴别鼻腔鼻窦良恶性病变的诊断效能。 结果 TSE-DWI图像的各项主观评分值、信噪比均值和对比噪声比均值均高于EP-DWI(P < 0.05),TSE-DWI图像的变形率较EP-DWI降低(P < 0.05);对于图像主观评分,两医师间的一致性较好(Kappa>0.4);对于ADC值测量,两医师间的一致性极好(ICC>0.74);两种DWI序列ADC值一致性极好(ICC> 0.74)并且呈极强正相关(Pearson相关系数>0.8);良恶性病变的ADC值差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),两种DWI序列的ADC值鉴别鼻腔鼻窦良恶性病变的敏感度、特异性、阳性预测值、阴性预测值及准确率相同,分别为90.1%、90.9%、97.0%、74.1%、90.3%。 结论 磁共振TSE-DWI序列可有效提高鼻腔鼻窦部位图像质量,适用于临床广泛应用;ADC值在鉴别鼻腔鼻窦良恶性病变中具有很高的诊断效能。 Abstract:Objective To prospectively compare the difference in image quality between turbo spin-echo diffusion- weighted imaging (TSE- DWI) and planar echo diffusion- weighted imaging (EP-DWI) for nasal sinus lesions. To investigate the diagnostic value of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of TSE-DWI and EP- DWI in identifying benign and malignant nasal sinus lesions. Methods Ninety-three patients with nasal sinus lesions seen in our hospital from October 2022 to August 2023 were prospectively selected for the study. A Philips 1.5T MRI scanner was used for scanning, and all patients underwent TSE-DWI and EP-DWI imaging after routine nasal sinus MRI plain scanning. Image quality was compared through subjective and objective evaluation of TSE-DWI and EP-DWI images by two physicians. The agreement between the two physicians, the agreement between the ADC values of the two DWI sequences, and the Pearson correlation coefficient were evaluated. The differences in ADC values of benign and malignant nasal sinus lesions were compared and the diagnostic efficacy of ADC values for identifying benign and malignant nasal sinus lesions was calculated using ROC curves. Results The mean values of all subjective scores, signal-to-noise ratios and contrast-to-noise ratios of TSE-DWI images were higher than those of EP-DWI (P < 0.05), and the distortion rate of TSE-DWI images was lower than that of EP-DWI (P < 0.05). Regarding subjective scoring of images, the agreement between the two physicians was good (Kappa>0.4). For ADC value measurement, the agreement between two physicians was excellent (ICC>0.74). The agreement between the ADC values of the two DWI sequences was excellent (ICC>0.74) and showed a very strong positive correlation (Pearson's correlation coefficient>0.8). The difference in ADC values for benign and malignant lesions was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The ADC values of the two DWI sequences had the same sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy in identifying benign and malignant lesions of the nasal sinuses, which were 90.1%, 90.9%, 97.0%, 74.1%, 90.3%, respectively. Conclusion The magnetic resonance TSE-DWI sequence can effectively improve the image quality of nasal sinus sites and is suitable for a wide range of clinical applications. The ADC value has high diagnostic efficacy in identifying benign and malignant nasal sinus lesions. -
Key words:
- nasal sinus lesions /
- TSE-DWI /
- EP-DWI /
- image quality /
- benign and malignant lesions /
- apparent diffusion coefficient
-
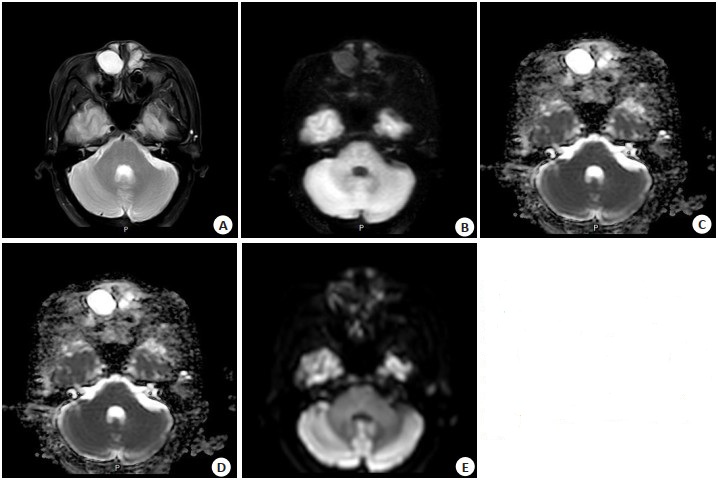
图 4 右侧鼻前庭囊肿1例
Figure 4. One case of nasal vestibular cyst on the right. A: T2WI; B: TSE-DWI(b= 800 s/mm2); C: Fusion of T2WI and TSE- DWI; D: EP- DWI (b=800 s/mm2); E: Fusion of T2WI and EP-DWI. The fusion image of T2WI and TSE-DWI showed that TSE-DWI and T2WI were completely matched (C). The fusion image of T2WI and EP- DWI showed the distortion and displacement of the lesion(E).
表 1 患者疾病类型
Table 1. Type of disease of patients (n)
Type of disease Male Female Total Benign Sinusitis 18 15 33 Maxillary sinus cyst 1 5 6 Nasal polyps 13 4 17 Inverted papilloma 11 4 15 Malignant Adenoid cystic carcinoma 1 1 2 Inflammatory myofibroblastoma 3 0 3 Olfactory neuroblastoma 2 0 2 Melanoma 2 0 2 Squamous cell carcinoma 4 3 7 Lymphoma 2 4 6 表 2 鼻腔鼻窦TSE-DWI、EP-DWI及T2WI扫描参数
Table 2. TSE-DWI, EP-DWI and T2WI scanning parameters of nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses
Sequence TSE-DWI EP-DWI T2WI TR(ms) 4881 5922 2600 TE(ms) 70 62 92 FOV(mm×mm) 270×277 240×240 260×281 b (s/mm2) 0, 800 0, 800 - NSA 4 2 1.3 Layer thickness (mm) 6 5 6 Number of layers 24 24 24 Interlayer spacing(mm) 1 1 1 Matrix 136×112 80×74 324×275 Voxel 2×2.5×6 3×3.29×5 0.8×1.02×6 Scan time(s) 273 160 172 DWI: Diffusion weighted imaging; TSE: Turbo spin-echo; EP: Echo pla-nar; TR: Repetition time; TE: Echo time; FOV: Field of view; NSA: Number of signal average. 表 3 图像质量评分标准
Table 3. Image quality scoring standard
Parameter 1 2 3 4 5 Focus definition Very bad Bad Medium Good Very good Image artifact Very serious Serious Medium Slight Negligible Image distortion Very serious Serious Medium Slight Negligible Overall image quality Very bad Bad Medium Good Very good 表 4 TSE-DWI和EP-DWI视觉评估结果及两医师间的一致性
Table 4. The results of TSE-DWI and EP-DWI visual assessment and the consistency between the two physicians
Parameter Doctor A Doctor B Kappa test TSE-DWI[M(P25, P75)] EP-DWI[M(P25, P75)] P TSE-DWI[M(P25, P75)] EP-DWI[M(P25, P75)] P TSE-DWI EP-DWI Focus definition 5(5, 5) 4(4, 5) <0.001 5(5, 5) 4(4, 5) <0.001 0.72 0.75 Image artifact 5(4, 5) 4(3, 4) <0.001 5(4, 5) 4(3, 4) <0.001 0.71 0.76 Image distortion 5(4, 5) 4(3, 4) <0.001 5(4, 5) 4(3, 4) <0.001 0.84 0.80 Overall image quality 5(4, 5) 4(3, 4) <0.001 5(4, 5) 4(3, 4) <0.001 0.76 0.73 表 5 SNR、CNR和DR的配对t检验
Table 5. Paired t-test of SNR, CNR and DR
Parameter Difference average value Difference standard deviation t P SNR 7.874 6.074 12.500 <0.001 CNR 31.074 34.411 8.708 <0.001 DR -0.093 0.030 -29.374 <0.001 SNR: Signal to noise ratio; CNR: Contrast-to-noise ratio; DR: Distortion ratio. 表 6 2位医师在两种DWI序列上测量的病变及小脑的ADC值(×10-3 mm2 /s)、两种DWI序列ADC值的ICC及Pearson相关系数结果
Table 6. ADC values (×10-3 mm2 /s) of lesions and cerebellum measured by two physicians on two DWI sequences, results of ICC and Pearson correlation coefficient for ADC values of two DWI sequences
Group Doctor A Doctor B Lesion Cerebellum Lesion Cerebellum TSE-DWI [M(P25, P75)] 1.85(0.84, 2.04) 0.69(0.67, 0.72) 1.84(0.86, 2.04) 0.68(0.66, 0.71) EP-DWI [M(P25, P75)] 1.81(0.86, 2.07) 0.71(0.67, 0.74) 1.82(0.86, 2.09) 0.70(0.67, 0.74) TSE-DWI and EP-DWI ICC 0.996 0.812 0.998 0.843 TSE-DWI and EP-DWI pearson correlationcoefficient 0.996 0.820 0.998 0.846 ICC: Interclass correlation efficient. 表 7 良恶性病变的ADC值(×10-3 mm2 /s)比较
Table 7. Comparison of ADC values (×10-3 mm2 /s) for benign and malignant lesions [M(P25, P75)]
ADC value Benign Malignant Z P TSE-DWI 1.95(1.57,2.14) 0.71(0.58,0.88) -3.85 <0.001 EP-DWI 1.96(1.52,2.14) 0.71(0.55,0.85) -3.88 <0.001 表 8 两种DWI序列ADC值鉴别良恶性病变的诊断效能
Table 8. Diagnostic efficiency of ADC value in differentiating benign and malignant lesions
Index TSE-DWI EP-DWI True positive (n) 64 64 False positive (n) 2 2 True negative (n) 20 20 False negative (n) 7 7 Sensitivity (%) 90.1 90.1 Specificity (%) 90.9 90.9 Positive predictive value (%) 97 97 Negative predictive value (%) 74.1 74.1 Accuracy (%) 90.3 90.3 AUC(95% CI) 0.936(0.887-0.985) 0.944(0.900-0.987) -
[1] Kumari S, Pandey S, Verma M, et al. Clinicopathological challenges in tumors of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: our experience [J]. Cureus, 2022, 14(9): e29128. [2] Singh SG, Qureshi S, Jain L, et al. Presentation of lesions of nose and paranasal sinuses at a tertiary care center in central India[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2018, 70(2): 284-9. doi: 10.1007/s12070-018-1246-2 [3] 王晓磊, 李微, 冯长国, 等. 儿童鼻腔鼻窦占位病变的临床研究[J]. 中国医学创新, 2016, 13(1): 130-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2016.01.038 [4] Drake- Pérez M, Boto J, Fitsiori A, et al. Clinical applications of diffusion weighted imaging in neuroradiology[J]. Insights Imag, 2018, 9(4): 535-47. doi: 10.1007/s13244-018-0624-3 [5] Hirata K, Nakaura T, Okuaki T, et al. Comparison of the image quality of turbo spin echo-and echo-planar diffusion-weighted images of the oral cavity[J]. Medicine, 2018, 97(19): e0447. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010447 [6] Yoshizako T, Yoshida R, Asou H, et al. Comparison between turbo spin- echo and echo planar diffusion-weighted imaging of the female pelvis with 3T MRI[J]. Acta Radiol Open, 2021, 10(2): 2058460121994737. [7] Pokorney AL, Miller JH, Hu HH. Comparison of 2D single- shot turbo- spin- echo and spin- echo echo- planar diffusion weighted brain MRI at 3.0 Tesla: preliminary experience in children[J]. Clin Imag, 2017, 42: 152-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2016.12.005 [8] Kamimura K, Nakajo M, Fukukura Y, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion in normal pituitary gland: initial study with turbo spin-echo diffusion-weighted imaging[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2016, 37 (12): 2328-33. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4930 [9] 刘一帆, 郭效宾, 罗玥媛, 等. 磁共振TSE-DWI序列在鼻咽癌检查中的应用价值[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2021, 31(11): 1849-54. [10] Wan Q, Lei Q, Wang P, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging of lung cancer: comparison between turbo spin- echo and echo-planar imaging[J]. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 2020, 44: 334-40. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000001004 [11] 许文辉, 林晓玲, 李可. 医用磁共振成像系统质量控制图像信噪比检测方法的研究[J]. 中国医学装备, 2022, 19(3): 28-33. [12] 康立丽, 余晓锷. MRI图像信噪比影响因素分析[J]. 放射学实践, 2001, 16(6): 404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0313.2001.06.034 [13] Ji B, Hosseini Z, Wang LY, et al. Spectral Wavelet-feature Analysis and Classification Assisted Denoising for enhancing magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. NMR Biomed, 2021, 34(6): e4497. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4497 [14] 康立丽, 卢广文. 部分MR参数对信噪比影响实验研究[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2003(11): 971-3. [15] 张晓槟, 金宝荣, 苏丽娟. MR图像质量与成像参数的相关性及控制对策[J]. 数理医药学杂志, 2006, 19(1): 73-5. [16] 郭红梅, 王振祥, 于集虹. 低场磁共振成像的参数优化[J]. 新疆医学, 2009, 39(8): 15-9. [17] Mori N, Mugikura S, Miyashita M, et al. Turbo spin- echo diffusion-weighted imaging compared with single-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging: image quality and diagnostic performance when differentiating between ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma[J]. Magn Reson Med Sci, 2021, 20 (1): 60-8. doi: 10.2463/mrms.mp.2019-0195 [18] Huang WH, Liu J, Zhang B, et al. Potential value of non- echoplanar diffusion-weighted imaging of the nasopharynx: a primary study for differential diagnosis between recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma and post-chemoradiation fibrosis[J]. Acta Radiol, 2019, 60(10): 1265-72. doi: 10.1177/0284185118822635 [19] Suzuki M, Morita S, Goto Y, et al. Artifact- robust diffusionweighted whole-body imaging with background suppression at 3 T using improved turbo spin-echo diffusion-weighted imaging[J]. Br J Radiol, 2019, 92(1094): 20180489. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180489 [20] 刘怀军. 3T MRI基础与临床第二讲基本参数及其影响因素[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2008, 23(8): 157-60. [21] 陈心莲. 3T人体磁共振成像系统射频场关键科学问题研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2022. [22] Chang MS. Comparison of Distortion in TSE-DWI and EPI-DWI [C]. European Congress of Radiology, 2020. [23] Lavdas I, Miquel ME, McRobbie DW, et al. Comparison between diffusion-weighted MRI (DW-MRI) at 1.5 and 3 tesla: a phantom study[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2014, 40(3): 682-90. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24397 [24] Hiwatashi A, Togao O, Yamashita K, et al. Diffusivity of intraorbital lymphoma vs. inflammation: comparison of single shot turbo spin echo and multishot echo planar imaging techniques[J]. Eur Radiol, 2018, 28(1): 325-30. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-4995-5 [25] 王凯, 张倩文, 张鹏. DWI序列ADC值鉴别前列腺良恶性局灶性病变的价值[J]. 河北医学, 2023, 29(7): 1126-30. [26] 刘雪芬, 张国福, 金俊, 等. 磁共振成像在上皮型卵巢癌分型中的鉴别价值及表观弥散系数值与CA-125和Ki-67表达及预后的关系[J]. 复旦学报: 医学版, 2020, 47(4): 567-73. [27] Tsvetkova S, Doykova K, Vasilska A, et al. Differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions using ADC values and ADC ratio in breast MRI[J]. Diagnostics, 2022, 12(2): 332. -







 下载:
下载: