Clinical characteristics and MRI manifestations of Langerhans cell histiocytosis in children
-
摘要:
目的 探讨小儿垂体朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症(LCH)的临床特征和MRI表现。 方法 回顾性分析2014年11月~2023年8月经病理证实的23例垂体LCH患儿MRI资料, 其中男12例, 女11例, 年龄1岁~12岁6月(6.72±3.33岁)。观察病变部位、垂体高度、神经垂体是否存在、垂体柄形态、大小、垂体强化方式、垂体/松果伴随病变等, 并总结、归纳垂体LCH的MRI表现。 结果 首次就诊原因主要为尿崩症, 其它就诊症状为顶部包块2例, 顶部压痛1例, 颈部包块1例。垂体单系统受累16例, 其余均为多系统受累, 垂体外常累及颅面骨, 少见受累部位为肺部、肋骨等。腺垂体明显凹陷、变薄1例, 饱满/隆起4例; 神经垂体高信号均未见; 垂体柄增粗13例, 细小2例, 另有1例漏斗部线样狭窄、上段结节状增粗, 无明显增粗/细小7例; 增强后垂体均明显均匀强化; 伴随Rathke囊肿/残腔3例, 松果体囊肿2例。 结论 小儿垂体LCH磁共振表现具有一定特征性, 有助于诊断。 -
关键词:
- 垂体 /
- 朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症 /
- 磁共振成像
Abstract:Objective To investigate the MRI and clinical characteristics of Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) of pituitary gland in children. Methods We conducted a retrospective analysis the MRI data of the 23 children with pituitary LCH confirmed by pathological from November 2014 to August 2023, including 12 males and 11 females with an average age of 1 year to 12 years 6 months (6.72±3.33 years old). The lesion location, pituitary height, presence of neurohypophysis, pituitary stalk shape, size, pituitary reinforcement, and pituitary/pineal concomitant lesions were observed. The MRI findings of pituitary LCH were summarized. Results The main reason for the first visit was diabetes insipidus, and other symptoms were head mass in 2 cases, head tenderness in 1 case and neck mass in 1 case. Only pituitary was involved in 16 cases, and the rest were multisystem involved. Craniofacial bones were often involved outside the pituitary, and lungs and ribs were rarely involved. The adenohypophyseal was significantly depressed and thin in 1 case and full/bulging in 4 cases. No neurohypophysial hypersignal was found in all cases. The adenohypophyseal was significantly depressed and thin in 1 case and full/bulging in 4 cases. No neurohypophysial hypersignal was found in all cases. There were 13 cases of pituitary stalk thickening, 2 cases of fine, 1 case of funnel line stenosis, the upper segment nodular thickening, 7 cases without obvious thickening/fine. The pituitary was enhanced uniformly after enhancement. There were 3 cases with rathke cyst/remnant cavity and 2 cases with pineal cyst. Conclusion The MRI manifestations of pituitary LCH in children have certain characteristics, which is helpful for diagnosis. -
Key words:
- pituitary /
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis /
- magnetic resonance imaging
-
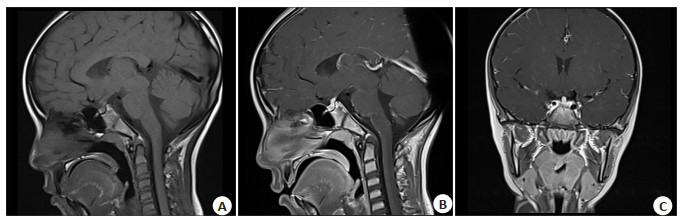
图 1 垂体单系统受累LCH
Figure 1. Pituitary single systemic disease (SS-LCH). Female, 7 years and 3 months old, polyuria for more than 8 months. A: Sagittal MRI plain scan showed that normal posterior pituitary T1WI high signal disappeared, pituitary stalk slightly thickened; Coronal (B) and sagittal (C) MRI showed uniform enhancement of pituitary gland and thickening of pituitary stalk. Later, he was transferred to a superior hospital for diagnosis and treatment, and pathology confirmed that the pituitary single systemic disease (SS-LCH).
图 2 垂体多系统受累LCH:患者1
Figure 2. Pituitary multisystemic disease (MS-LCH): patients 1. Male, 3 years and 3 months old, masses were found on the left top for more than 5 months. A: Sagittal MRI plain scan showed that normal posterior pituitary T1WI high signal disappeared, pituitary stalk slightly smaller; Sagittal (B) MRI showed obvious uniform enhancement of pituitary gland with slightly smaller stalk; Axial CT bone window (C) and axial CT skull VR reconstruction (D) showed multiple bone destruction in the skull. Pituitary multisystemic disease (MS-LCH) was confirmed by pathology.
图 3 垂体多系统受累LCH:患者2
Figure 3. Pituitary multisystemic disease (MS-LCH): patients 2. Male, 5 years and 1 month old, polydipsia and polyuria for more than 1 month. A: Sagittal MRI plain scan showed that normal posterior pituitary T1WI high signal disappeared, and the pituitary stalk showed obvious nodular thickening; The sagittal (B) and coronal (C) MRI enhancement showed obvious nodular thickening and enhancement of the pituitary stalk, which was located on the left side of the sella; D: Thin layer axial MRI showed obvious abnormal enhancement in the soft tissue of the right frontal scalp, and a few lamellar enhancement in the adjacent frontal bone; E: Sagittal MRI enhancement showed obvious uniform enhancement of the adenohypophysial gland, which showed a circular area without enhancement, indicating a Rathke cyst. Pituitary multisystemic disease (MS-LCH) was confirmed by pathology.
-
[1] Tan HW, Yu K, Yu YR, et al. Isolated hypothalamic-pituitary Langerhans'cell Histiocytosis in female adult: a case report[J]. Medicine, 2019, 98(2): e13853. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013853 [2] Zhou W, Rao J, Li C. Isolated Langerhans cell histiocytosis in the hypothalamic-pituitary region: a case report[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2019, 19(1): 143. doi: 10.1186/s12902-019-0474-0 [3] 王志成, 邓侃, 张毅, 等. 内镜下扩大经鼻蝶入路鞍上垂体柄占位性病变活检术临床价值初探[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2019, 19(3): 177-83. [4] Yang IC, Lee GJ, Han MS, et al. Langerhans cell Histiocytosis involving second cervical vertebra and the hypothalamus and pituitary in an adult[J]. World Neurosurg, 2020, 142: 142-6. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.06.200 [5] 龙庆玲, 李长钢. 儿童朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症的诊治新进展[J]. 安徽医药, 2019, 23(6): 1065-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6469.2019.06.002 [6] 黄文献, 曾洪武, 张龚巍, 等. 儿童孤立性垂体柄朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症的MRI表现[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2016, 24(4): 245-7, 252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2016.04.002 [7] 王志成, 朱建宇, 张毅, 等. 鞍区朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症临床特点分析[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2020, 20(7): 625-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2020.07.012 [8] 雷霆, 刘锐, 吴陈兴, 等. 鞍区朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症疾病特征的初步观察[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2021, 37(12): 1246-50. [9] 黄娟, 付雨菲. 朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症的分型及影像学表现[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2022, 41(10): 1977-81. [10] 廖雪莲, 蒋慧, 陆正华, 等. 儿童朗格罕细胞组织细胞增生症45例临床分析[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2017, 32(15): 1145-8. [11] Brys ADH, Vermeersch S, Forsyth R, et al. Central diabetes insipidus: beware of Langerhans cell Histiocytosis![J]. Neth J Med, 2018, 76(10): 445-9. [12] 崔蕾, 张莉, 廉红云, 等. 儿童朗格罕细胞组织细胞增生症BRAFV600E突变对预后的影响[J]. 中国循证儿科杂志, 2020, 15(2): 102-7. [13] 邢菲, 孙娜娜, 刘希胜. 朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症的影像学诊断及病理学特征[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2019, 35(8): 1294-8. [14] 张莉, 廉红云, 马宏浩, 等. 单器官受累朗格罕细胞组织细胞增生症112例[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2016, 31(15): 1172-4. [15] Bärtschi P, Luna E, González-López P, et al. A very rare case of right insular lobe Langerhans cell Histiocytosis (CD1+) mimicking glioblastoma multiforme in a young adult[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 121: 4-11. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.09.093 [16] 王斐, 全会标, 陈道雄, 等. 朗格汉斯组织细胞增生症合并高血糖高渗状态一例[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2020, 59(3): 232-4. [17] Moszczyńska E, Baszyńska-Wilk M, Zasada K, et al. Pituitary stalk thickening in patients under 18 years of age the most common causes and diagnostic procedures[J]. Pedm, 2022, 28(3): 213-27. doi: 10.5114/pedm.2022.115202 [18] 张水花, 张景, 韩佩, 等. PET/MRI观察朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2021, 37(11): 1604-8. [19] 乐颖, 王元阳, 彭全洲, 等. 累及垂体和甲状腺的成人朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症1例[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2022, 61(3): 327-30. [20] 徐加利, 冯逢, 有慧, 等. 48例垂体柄增粗MRI表现[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2017, 25(2): 98-100. [21] 史红媛, 建方方, 卞留贯, 等. 垂体柄病变的MRI影像与临床特征分析[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2023, 33(2): 181-5. [22] Elżbieta M, Karolina K, Marta BW, et al. Pituitary stalk thickening: causes and consequences. the children's memorial health institute experience and literature review[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: : 868558. [23] 邹珍, 赵康艳. 朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症累及中枢神经系统1例[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2021, 32(4): 291-3. [24] Bianco D, Napoli F, Morana G, et al. Endocrine outcomes in central diabetes insipidus: the predictive value of neuroimaging 'mismatch pattern'[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2020, 105(11): 540. [25] Li N, Cui L, Ma HH, et al. Osteopontin is highly secreted in the cerebrospinal fluid of patient with posterior pituitary involvement in Langerhans cell Histiocytosis[J]. Int J Lab Hematol, 2020, 42(6): 788-95. [26] 方凯弘, 徐倩玥, 余红. 儿童朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症病因和治疗进展[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2019, 37(3): 228-32. -







 下载:
下载: