Clinical value of a deep learn-based mammography assisted diagnosis system for breast calcification detection and benign and malignant classification
-
摘要:
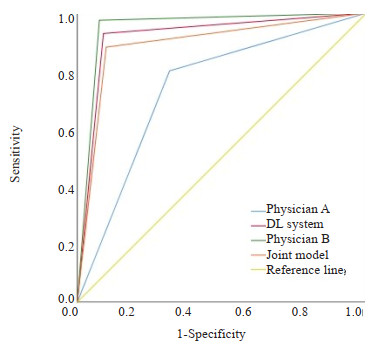
目的 探讨基于深度学习的乳腺X线辅助诊断(DL)系统对乳腺钙化检出和良恶性分类的临床价值。 方法 回顾性分析在2020年1月~2022年12月在徐州市中心医院接受双侧乳腺X线检查的400例患者的头尾位和内外斜位影像资料。以2位具有15年以上乳腺X线诊断经验的副主任医师对乳腺钙化的一致判断作为标准组,由1位低年资住院医师、1位高年资主治医师和DL系统分别盲法独立阅片,经过4周洗脱期后,由联合模型(低年资医师+DL系统)再次盲法独立阅片。结合双向表χ2检验,评价不同乳腺ACR类型、钙化形态和分布、BI-RADS分类对钙化检出的影响,并采用ROC曲线下面积(AUC)评价低年资住院医师、高年资主治医师、DL系统和联合模型(低年资住院医师+DL系统)对可疑钙化检出的性能差异。 结果 1600幅图像(400例患者)共检出BI-RADS 3级及以上可疑钙化975处。低年资住院医师A,高年资主治医师B、DL系统和联合模型对钙化检出的敏感度分别为81.95%、96.62%、93.03%、96.41%。高年资主治医师B、DL系统和联合模型对钙化检出的敏感度不受乳腺ACR类型、钙化形态和分布、BI-RADS分类影响,而低年资住院医师A对钙化检出的敏感度受其影响。联合模型(低年资住院医师+DL系统)在预测钙化良恶性方面具有良好的AUC值、敏感度和特异性,分别为0.891、90.0%和88.2%,和低年资住院医师之间存在差异(P < 0.01)。在DL系统帮助下,低年资住院医师的诊断性能得到明显改善,AUC值由0.740提升到0.891。 结论 DL系统对BI-RADS 3级及以上可疑钙化检出敏感度高且具有较高的良恶性钙化分类性能,与高年资主治医师相当。在DL系统的帮助下,低年资医师可以减少钙化漏诊、误诊,提高乳腺癌筛查和诊断的准确性。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the clinical value of the deep learning-based mammography-assisted diagnosis (DL) system for breast calcification detection and benign and malignant classification. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on the craniocaudal and internal and external oblique imaging data of 400 patients who underwent bilateral mammography in Xuzhou Central Hospital from January 2020 to December 2022. The unanimous judgment of two associate chief physicians with more than 15 years of experience in mammography diagnosis was used as the standard group, the images were blinded and independently reviewed by 1 junior resident, 1 senior attending physician, and the DL system, respectively. After a 4-week washout period, the images were blinded and independently reviewed by the combined model (junior resident+DL system) again. Combined with two- way table chi- square test, the effects of different ACR types, morphology and distribution of calcification, and BI-RADS classification on the detection of calcification were evaluated. The area under the curve (AUC) was used to evaluate the difference in the detection of suspicious calcification among junior residents, senior attending physician, DL system and combined model (junior resident +DL system). Results A total of 975 suspicious calcifications of BI-RADS3 grade and above were detected in 1600 images (400 patients). The sensitivities of junior resident A, senior attending physician B, DL system and combined model were 81.95%, 96.62%, 93.03% and 96.41%, respectively. The sensitivity of senior attending physician B, DL system and combined model to calcification detection was not affected by breast ACR type, morphology and distribution of calcification, and BI- RADS classification, while the sensitivity of junior resident A was affected by it. The combined model (junior resident + DL system) had high AUC value, sensitivity and specificity in predicting the benign and malignant nature of calcifications, with 0.891, 90.0% and 88.2%, respectively, which differed from that of the junior resident (P < 0.01). With the help of the DL system, the diagnostic performance of the junior resident was significantly improved, and the AUC value increased from 0.740 to 0.891. Conclusion The DL system is highly sensitive to the detection of suspicious calcifications of BI-RADS 3 grade and above, and has a high classification performance of benign and malignant calcifications, which is comparable to that of senior attending physician. With the help of the DL system, the junior resident can reduce the missed diagnosis of calcification and misdiagnosis, and improve the accuracy of breast cancer screening and diagnosis. -
Key words:
- mammography /
- suspicious calcification /
- deep learning /
- breast cancer /
- artificial intelligence
-
表 1 不同ACR乳腺构成的钙化检出比较
Table 1. Comparison of calcification in different ACR breast compositions [n(%)]
Models ACR Total a b c d Standardized group (n) 47 346 466 116 975 Physician A 47(100.00) 281(81.21) 385(76.82) 86(51.81) 799(81.95) Physician B 47(100.00) 308(89.02) 456(97.85) 110(94.83) 942(96.62) DL system 47(100.00) 326(94.22) 445(95.49) 107(92.24) 907(93.03) Joint model 47(100.00) 327(94.51) 454(97.42) 108(93.10) 940(96.41) 表 2 不同分布可疑钙化钙化检出比较
Table 2. Comparison of the detection of suspicious calcifications with different distributions of calcifications [n(%)]
Models Distribution of calcification Total Regional distribution Cluster distribution Diffuse distribution Linear distribution Segment distribution Standardized group (n) 183 269 171 214 138 975 Physician A 133(72.68) 195(72.49) 170(99.42) 193(90.19) 108(78.26) 799(81.95) Physician B 178(97.27) 256(95.17) 171(100.00) 208(97.20) 126(91.30) 942(96.62) DL System 169(92.35) 240(89.22) 171(100.00)) 205(95.79) 132(95.65) 907(93.03) Joint model 173(94.54) 252(93.68) 171(100.00) 207(96.73) 133(96.38) 940(96.41) 表 3 不同形态可疑钙化钙化检出比较
Table 3. Comparison of the detection of different forms of suspicious calcification calcifications [n(%)]
Models Calcification morphology Total Roughness heterogeneity Indeterminate fuzzy Small pleomorphic Linear branching Punctate Standardized group (n) 271 256 189 176 83 975 Physician A 241(88.93) 187(73.05) 142(75.13) 151(85.80) 78(93.98) 799(81.95) Physician B 263(97.05) 245(95.70) 176(93.12) 174(98.86) 81(97.59) 942(96.62) DL System 264(97.42) 234(91.41) 167(88.36) 167(94.89) 78(93.98) 907(93.03) Joint model 265(97.79) 245(95.70) 179(94.71) 171(97.16) 80(96.39) 940(96.41) 表 4 不同BI-RADS分级可疑钙化钙化检出比较
Table 4. Comparison of different BI-RADS grading of suspicious calcifications for calcification detection [n(%)]
Models BI-RADS grading Total 3 4A 4B 4C 5 Standardized group (n) 54 385 326 154 56 975 Physician A 47(87.04) 316(82.08) 259(79.45) 125(81.17) 52(92.86) 799(81.95) Physician B 52(96.30) 373(96.89) 310(95.09) 148(96.10) 56(100.00) 942(96.62) DL System 47(87.04) 352(91.43) 312(95.71) 143(92.86) 53(94.64) 907(93.03) Joint model 52(96.30) 365(94.81) 316(96.93) 147(95.45) 56(100.00) 940(96.41) 表 5 联合模型、医师B、DL系统和医师A之间的比较
Table 5. Comparison between the joint model, physician B, DL system and physician A
Models Sensitivity
(%)Specificity
(%)Positive predictive value(%) Negative predictive value(%) AUC(95% CI) P vs joint model Joint model 90.0(189/210) 88.2(675/765) 67.7(189/279) 97.0(675/696) 0.891(0.864-0.918) N/A Physician B 92.4(194/210) 97.5(746/765) 91.1(194/213) 97.9(746/762) 0.949(0.928-0.971) < 0.001 DL system 91.0(191/210) 92.9(711/765) 78.0(191/245) 97.4(711/730) 0.919(0.895-0.944) < 0.001 Physician A 68.1(143/210) 80.0(612/765) 48.3(143/296) 90.1(612/679) 0.740(0.700-0.781) < 0.001 -
[1] Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA A Cancer J Clinicians, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492 [2] Harbeck N, Gnant M. Breast cancer[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10074): 1134-50. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31891-8 [3] Son J, Lee SE, Kim EK, et al. Prediction of breast cancer molecular subtypes using radiomics signatures of synthetic mammography from digital breast tomosynthesis[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 21566. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78681-9 [4] 金征宇. 人工智能医学影像应用: 现实与挑战[J]. 放射学实践, 2018, 33(10): 989-91. [5] 王小琦, 刘鹏, 陈赜, 等. 基于深度学习的乳腺X线摄影钙化检测系统对乳腺可疑钙化的检出效能[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2019, 35(12): 1784-8. [6] Fenton JJ, Taplin SH, Carney PA, et al. Influence of computer-aided detection on performance of screening mammography[J]. N Engl J Med, 2007, 356(14): 1399-409. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa066099 [7] Niu SH, Huang JH, Li J, et al. Application of ultrasound artificial intelligence in the differential diagnosis between benign and malignant breast lesions of BI-RADS 4A[J]. BMC Cancer, 2020, 20(1): 959. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07413-z [8] 李欣, 梁森, 黄正南, 等. 乳腺X线AI智能病灶检测[J]. 放射学实践, 2018, 33(10): 1029-32. [9] 周娟, 王婷婷, 李明, 等. 基于深度学习的乳腺X线摄影钙化检出系统评估[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2019, 53(11): 6. [10] 哈婷婷, 潘俊, 王洪光, 等. 基于深度学习的乳腺X线摄影病灶检出系统的临床价值[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2019, 35(12): 1789-93. [11] 中华医学会放射学分会乳腺学组. 乳腺X线摄影检查和诊断共识[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2014, 48(9): 711-7. [12] Oliver A, Freixenet J, Martí J, et al. A review of automatic mass detection and segmentation in mammographic images[J]. Med Image Anal, 2010, 14(2): 87-110. [13] Liu HH, Chen YH, Zhang YZ, et al. A deep learning model integrating mammography and clinical factors facilitates the malignancy prediction of BI‑RADS 4 microcalcifications in breast cancer screening[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(8): 5902-12. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07659-y [14] Lotter W, Diab AR, Haslam B, et al. Robust breast cancer detection in mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis using an annotation-efficient deep learning approach[J]. Nat Med, 2021, 27(2): 244-9. [15] Zhang F, Wu SD, Zhang C, et al. Multi-domain features for reducing false positives in automated detection of clustered microcalcifications in digital breast tomosynthesis[J]. Med Phys, 2019, 46(3): 1300-8. [16] Lei CQ, Wei W, Liu ZY, et al. Mammography-based radiomic analysis for predicting benign BI-RADS category 4 calcifications[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2019, 121: 108711. [17] Lehman CD, Arao RF, Sprague BL, et al. National performance benchmarks for modern screening digital mammography: update from the breast cancer surveillance consortium[J]. Radiology, 2017, 283(1): 49-58. [18] 彭芳芳, 沈坤炜. 中西方女性乳腺密度与乳腺癌发病关系的研究进展[J]. 中国癌症防治杂志, 2020, 12(4): 469-74. [19] 徐泽园, 秦耿耿, 陈卫国. 致密型乳腺影像筛查技术及研究进展[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志, 2019, 42(3): 312-6. -







 下载:
下载: