Clinical application of vascular ultrasound in the diagnosis of lower limb venous thrombosis during perioperative period of joint replacement surgery
-
摘要:
目的 分析血管超声在诊断关节置换围手术期下肢静脉血栓中的临床应用。 方法 回顾性收集2021年1月~2023年6月行初次单侧髋、膝关节置换的868例患者作为研究组,另选取同期医院体检的868例健康受检者作为对照组。研究组手术患者均接受抗凝药物、小腿静脉气压泵、加强踝泵和早期下地,以及减少围手术期脱水等多模式血栓预防措施。研究组术前、术后第3~5天和对照组均采用彩色多普勒超声检查双侧下肢静脉血管情况。分析下肢静脉血栓患者的检出准确率,并对比两组人群的血管超声所示股浅静脉、内侧腓肠静脉、胫后静脉的静脉直径差异。 结果 研究组中152例术后发现下肢深静脉血栓(DVT),总发生率为17.5%,均为无症状性DVT。其中发生于手术同侧的DVT为138例,双侧14例,周边型110例,中心型22例,混合型20例。对照组中,26例检出周边型下肢血栓。研究组DVT患者和对照组受试者的下肢静脉直径对比显示,研究组股浅静脉、内侧腓肠静脉、胫后静脉直径均长于对照组(P < 0.05)。 结论 采取血管超声检查可准确诊断关节置换术后患者下肢静脉血栓,且可显示出不同的影像学特点,有利于判断疾病状况,为早期治疗提供一定的临床证据。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the clinical application of vascular ultrasound in the diagnosis of lower limb venous thrombosis during perioperative period of joint replacement surgery. Methods A retrospective study was conducted on 868 patients who underwent initial unilateral hip or knee arthroplasty from January 2021 to June 2023 as the observation group. The group under observation was contrasted with 868 healthy volunteers who had hospital physical examinations within the same period, forming the control group. The observation group was subject to multimodal thrombus prevention measures including anticoagulants, calf venous pressure pump, strengthened ankle pump, early mobilization, and reduction of perioperative dehydration. The observation group underwent color doppler ultrasound examination of bilateral lower limb venous vessels pre- surgery and 3- 5 d post- surgery. The detection accuracy for lower limb venous thrombosis and the differences in vein diameter of the superficial femoral vein, medial sural vein, and posterior tibial vein between both groups were analyzed. Results 152 patients in the observation group were reported to have deep vein thrombosis (DVT) after surgery with an incidence rate of 17.5%. All cases were asymptomatic DVTs. The breakdown was as follows: 138 cases were on the side of the surgery, 14 cases on both sides, 110 cases of peripheral venous embolization, 22 cases of central venous embolization and 20 cases of mixed venous embolization. In the control group, 26 cases of peripheral lower limb thrombosis were found. Comparatively, the diameters of the superficial femoral vein, medial sural vein, and posterior tibial vein in the observation group were significantly larger than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Vascular ultrasound examination can accurately diagnose lower limb venous thrombosis in patients post joint replacement surgery. It can display various imaging characteristics, which is beneficial for disease status assessment and provides clinical evidence for early treatment. -
Key words:
- vascular ultrasound /
- joint replacement /
- lower limb deep vein thrombosis
-
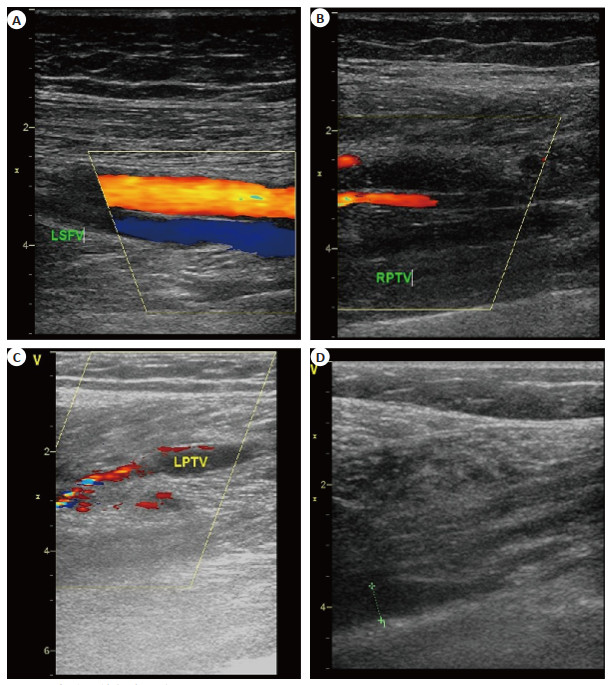
图 1 代表性血管超声图像
Figure 1. Representative vascular ultrasound images. A: Color Doppler ultrasound image of normal lower limb blood vessels, LSFV: Left superficial femoral vein; B: Deep branch of posterior tibial vein completely occlusioned, RPTV: Right posterior tibial vein; C: Incomplete embolized posterior tibial vein image, LPTV: Left posterior tibial vein; D: Representative acute thrombus image.
表 1 不同关节置换手术方式DVT发生情况的比较
Table 1. Comparison of DVT incidence among different joint replacement surgery
Surgery type n DVT counts [n(%)] TKA 635 134 (21.1) HHA 8 2 (25.0) THA 225 16 (7.1) χ2 0.102 P < 0.001 TKA: Total knee arthroplasty; HHA: Hemi-hip arthroplasty; THA: Total hip arthroplasty; DVT: Deep vein thrombosis. 表 2 两组静脉直径比较
Table 2. Comparison of vein diameters between the two groups (n=152, mm, Mean±SD)
Group SFV MGV PTV Experiment group 7.51±0.90 7.17±1.13 6.27±0.63 Control group 5.33±0.45 3.36±0.45 4.49±0.44 t 26.71 38.62 28.56 P < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 SFV: Superficial femoral vein; MGV: Medial sural vein; PTV: Posterior tibial vein. -
[1] Lieberman JR, Cheng V, Cote MP. Pulmonary embolism rates following total hip arthroplasty with prophylactic anticoagulation: some pulmonary emboli cannot be avoided[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2017, 32(3): 980-6. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2016.09.006 [2] Gharaibeh L, Albsoul-Younes A, Younes N. Evaluation of VTE prophylaxis in an educational hospital[J]. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, 2016, 22(7): 627-32. doi: 10.1177/1076029615575344 [3] Barbar S, Noventa F, Rossetto V, et al. A risk assessment model for the identification of hospitalized medical patients at risk for venous thromboembolism: the Padua Prediction Score[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2010, 8(11): 2450-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04044.x [4] 尚萍. 采用血管超声诊断下肢静脉血栓对提高诊断准确率的临床价值探讨[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2020, 4(15): 147-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXYY202015099.htm [5] 王志刚. 彩色多普勒超声在诊断下肢深静脉血栓中的临床价值分析[J]. 基层医学论坛, 2019, 23(34): 4979-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXLT201934058.htm [6] Wilbur J, Shian B. Diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2012, 86(10): 913-9. [7] Nash K, Hafeez A, Hou SS. Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency [J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2002, 39(5): 930-6. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2002.32766 [8] Fazel R, Krumholz HM, Wang YF, et al. Exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation from medical imaging procedures[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 361(9): 849-57. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0901249 [9] Zierler BK. Screening for acute DVT: optimal utilization of the vascular diagnostic laboratory[J]. Semin Vasc Surg, 2001, 14(3): 206-14. doi: 10.1053/svas.2001.25492 [10] Grady-Benson JC, Oishi CS, Hanson PB, et al. Routine postoperative duplex ultrasonography screening and monitoring for the detection of deep vein thrombosis. A survey of 110 total hip arthroplasties[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1994(307): 130-41. [11] Lensing AA, Prandoni P, Brandjes D, et al. Detection of deep-vein thrombosis by real-time B-mode ultrasonography[J]. N Engl J Med, 1989, 320(6): 342-5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200602 [12] Mont MA, Jacobs J. AAOS clinical practice guideline: preventing venous thromboembolic disease in patients undergoing elective hip and knee arthroplasty[J]. J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 2011, 19(12): 777-8. doi: 10.5435/00124635-201112000-00008 [13] Schwarcz TH, Matthews MR, Hartford JM, et al. Surveillance venous duplex is not clinically useful after total joint arthroplasty when effective deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis is used[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2004, 18(2): 193-8. doi: 10.1007/s10016-004-0009-6 [14] Zhang HJ, Mao P, Wang C, et al. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) after total hip or knee arthroplasty[J]. Blood Coagul Fibrin, 2017, 28(2): 126-33. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000000556 [15] Colwell Clifford W. The ACCP guidelines for thromboprophylaxis in total hip and knee arthroplasty[J]. Orthopedics, 2009, 32(12 Suppl): 67-73. [16] Migita K, Bito S, Nakamura M, et al. Venous thromboembolism after total joint arthroplasty: results from a Japanese multicenter cohort study[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2014, 16(4): R154. doi: 10.1186/ar4616 [17] Wong KL, Daguman R, Lim K, et al. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis following total hip arthroplasty: a Doppler ultrasonographic study[J]. J Orthop Surg, 2011, 19(1): 50-3. doi: 10.1177/230949901101900111 [18] 苏艳秋. 血管超声诊断下肢静脉血栓的临床价值探讨[J]. 双足与保健, 2019, 28(13): 129-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZBJ201913075.htm [19] 尚利敏. 彩色多普勒超声在诊断下肢深静脉血栓中的临床价值分析[J]. 中国疗养医学, 2019, 28(2): 168-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGLX201902026.htm [20] 曲燕. 血管超声诊断下肢静脉血栓的临床应用价值分析[J]. 心理月刊, 2018, 13(6): 85-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLYK201806062.htm -







 下载:
下载: