Value of C-TIRADS combined with BRAFV600E testing in the differential diagnosis of Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology category Ⅲ thyroid nodules
-
摘要:
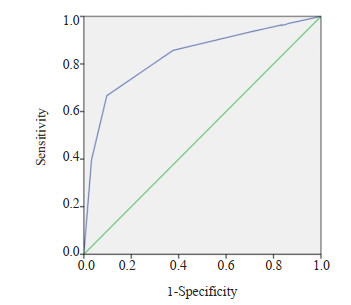
目的 探讨2020年中国超声甲状腺影像报告和数据系统(C-TIRADS)联合BRAFV600E基因检测在甲状腺细胞病理学Bethesda报告系统(BSRTC)Ⅲ类结节良恶性鉴别诊断中的价值。 方法 回顾性分析2020年10月~2022年10月于我院行超声引导甲状腺细针穿刺活检细胞学结果为BSRTC Ⅲ类的124例患者共156个结节, 所有结节均行C-TIRADS分类及BRAFV600E基因检测, 并均经手术病理证实。以手术病理结果为金标准, 比较C-TIRADS、BRAFV600E检测及二者联合在BSRTC Ⅲ类甲状腺结节中的诊断效能。 结果 156个BSRTC Ⅲ类甲状腺结节最终术后病理结果显示良性结节93个, 恶性结节63个; BRAFV600E基因突变阳性48个, 阴性108个。C-TIRADS分类ROC曲线下面积为0.834(95%CI: 0.765~0.902);C-TIRADS分类和BRAFV600E基因检测鉴别诊断BSRTC Ⅲ类甲状腺结节良恶性的敏感度分别为73.0%、76.2%, 特异性分别为88.2%、98.9%, 阳性预测值分别为80.7%、97.9%, 阴性预测值分别为82.8%、85.2%, 准确度分别为82.1%、89.1%。二者联合诊断的敏感度、特异性、阳性预测值、阴性预测值、准确度分别为90.4%、96.8%、95.0%、93.8%、94.2%。与C-TIRADS、BRAFV600E基因检测单独诊断相比, 联合诊断具有较高的敏感度(χ2=6.435, P=0.011; χ2=4.629, P=0.032)和阴性预测值(χ2=5.588, P=0.018; χ2=3.875, P=0.049)。 结论 C-TIRADS超声分类和BRAFV600E基因检测对BSRTC Ⅲ类甲状腺结节均有较高的诊断效能, 两者联合运用可提高诊断的敏感度及阴性预测值, 有助于BSRTC Ⅲ类甲状腺结节的鉴别诊断。 -
关键词:
- 中国超声甲状腺影像报告和数据系统 /
- BRAFV600E基因检测 /
- Bethesda报告系统 /
- 甲状腺结节 /
- 诊断效能
Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of 2020 Chinese Thyroid Imaging Report and Data System (C-TIRADS) combined with BRAFV600E testing in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant category Ⅲ nodules in Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology (BSRTC). Methods A total of 156 thyroid nodules in 124 patients with BSRTC category Ⅲ who underwent ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University from October 2020 to October 2022 were selected.Each nodule underwent C-TIRADS classification and BRAFV600E testing and was confirmed by histopathology.The diagnostic efficacy of C-TIRADS, BRAFV600E testing, and their combination in BSRTC category Ⅲ nodules were assessed according to histopathology findings. Results According to histopathology findings, 93 benign nodules and 63 malignant nodules in 156 nodules, 48 positive and 108 negative for BRAFV600E testing.The area under the ROC curve of C-TIRADS classification was 0.834(95%CI: 0.765-0.902).The sensitivities of C-TIRADS classification and BRAFV600E testing were 73.0% and 76.2%, the specificity were 88.2% and 98.9%, the positive predictive value were 80.7% and 97.9%, the negative predictive value were 82.8% and 85.2%, the accuracy were 82.1% and 89.1%, respectively.The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy of the two combined diagnosis were 90.4%, 96.8%, 95.0%, 93.8% and 94.2%, respectively.The combination of two methods significantly increased the sensitivity (χ2=6.435, P=0.011; χ2=4.629, P=0.032) and negative predictive value (χ2=5.588, P=0.018; χ2=3.875, P=0.049) when compared with C-TIRADS and BRAFV600E testing in BSRTC category Ⅲ nodules. Conclusion C-TIRADS classification and BRAFV600E testing have great diagnostic efficacy in BSRTC category Ⅲ nodules, and the combination of two methods can improve the diagnostic sensitivity and negative predictive value, suggesting the great value in differentiating BSRTC category Ⅲ nodules. -
图 2 C-TIRADS联合BRAFV600E基因检测诊断甲状腺右叶BSRTC Ⅲ类结节
Figure 2. C-TIRADS combined with BRAFV600E testing for diagnosis of nodules with BSRTC category Ⅲ in the right lobe of thyroid gland. A: C-TIRADS classification diagnosed negative (C-TIRADS category 4A: internal clumps of coarse calcification); B: Ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy; C: The cytology of fine needle biopsy was BSRTC Ⅲ (HE staining, ×40); D: BRAFV600E testing showed an obvious amplification signal indicating a positive result (mutant); E: Postoperative pathology confirmed papillary thyroid microcarcinma (HE staining, ×400).
表 1 C-TIRADS分类
Table 1. C-TIRADS category
C-TIRADS category Score Malignancy rate(%) 1:No nodule N/A 0 2:Benign -1 0 3:Probably benign 0 < 2 4A:Low suspicion 1 2~10 4B:Moderate suspicion 2 10~50 4C:High suspicion 3-4 50~90 5:Highly suggestive of malignancy 5 > 90 C-TIRADS: Chinese thyroid imaging report and data system; N/A: Not available. 表 2 术前C-TIRADS超声分类与最终术后病理结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of preoperative C-TIRADS classification and postoperative pathology (n)
Pathology results C-TIRADS 3 C-TIRADS 4A C-TIRADS 4B C-TIRADS 4C C-TIRADS 5 Total Benign 25 31 26 7 4 93 Malignancy 3 5 9 18 28 63 Total 28 36 35 25 32 156 表 3 C-TIRADS、BRAFV600E基因检测和联合诊断对BSRTC Ⅲ类甲状腺结节良恶性的诊断效能
Table 3. The efficacy of C-TIRADS, BRAFV600E testing and combined diagnosis for benign and malignant thyroid nodules with BSRTC category Ⅲ (%)
Diagnostic method Sensitivity Specificity Positive predictive value Negative predictive value Accuracy C-TIRADS 73.0(46/63) 88.2(82/93) 80.7(46/57) 82.8(82/99) 82.1(128/156) BRAFV600E testing 76.2(47/63) 98.9(92/93) 97.9(47/48) 85.2(92/108) 89.1(139/156) Combined diagnosis 90.4a(57/63) 96.8(90/93) 95.0(57/60) 93.8b(90/96) 94.2(147/156) aP < 0.05 vs C-TIRADS, bP < 0.05 vs BRAFV600E testing. -
[1] Durante C, Grani G, Lamartina L, et al. The diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules: a review[J]. JAMA, 2018, 319(9): 914-24. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.0898 [2] Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, et al. 2015 American thyroid association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American thyroid association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid, 2016, 26(1): 1-133. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020 [3] Cibas ES, Ali SZ. The 2017 Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology[J]. Thyroid, 2017, 27(11): 1341-6. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0500 [4] Straccia P, Rossi ED, Bizzarro T, et al. A meta-analytic review of the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: has the rate of malignancy in indeterminate lesions been underestimated?[J]. Cancer Cytopathol, 2015, 123(12): 713-22. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21605 [5] Haugen BR. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: what is new and what has changed?[J]. Cancer, 2017, 123(3): 372-81. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30360 [6] Marin F, Murillo R, Diego C, et al. The impact of repeat fine-needle aspiration in thyroid nodules categorized as atypia of undetermined significance or follicular lesion of undetermined significance: a single center experience[J]. Diagn Cytopathol, 2021, 49(3): 412-7. doi: 10.1002/dc.24676 [7] Zhou JQ, Yin LX, Wei X, et al. 2020 Chinese guidelines for ultrasound malignancy risk stratification of thyroid nodules: the C-TIRADS[J]. Endocrine, 2020, 70(2): 256-79. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02441-y [8] 周建桥, 詹维伟. 2020年中国超声甲状腺影像报告和数据系统(C-TIRADS)指南解读[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2020, 19(4): 350-3. doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2020.04.005 [9] 张卫兵, 陈天奕, 刘华, 等. 五种不同甲状腺结节超声恶性危险分层系统的比较[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2022, 38(2): 132-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2022.02.004 [10] 丁思悦, 丁全全, 王雁, 等. C-TIRADS与ACR TI-RADS在甲状腺结节中的诊断效能对比研究[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2021, 37(9): 964-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2021.09.002 [11] 储荣先, 彭梅. C-TIRADS联合超声弹性成像对甲状腺结节良恶性鉴别的诊断价值分析[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2022, 38(5): 485-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2022.05.002 [12] 王剑翔, 俞飞虹, 叶新华, 等. 超声联合BRAFV600E检测对BSRTCⅢ类甲状腺结节的诊断价值[J]. 中华医学超声杂志: 电子版, 2020, 17(12): 1179-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHCD202012008.htm [13] Kwak JY, Han KH, Yoon JH, et al. Thyroid imaging reporting and data system for US features of nodules: a step in establishing better stratification of cancer risk[J]. Radiology, 2011, 260(3): 892-9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11110206 [14] Tessler FN, Middleton WD, Grant EG, et al. Re: ACR thyroid imaging, reporting and data system (TI-RADS): white paper of the ACR TI-RADS committee[J]. J Am Coll Radiol, 2018, 15(3 Pt A): 381-2. [15] Russ G, Bonnema SJ, Erdogan MF, et al. European thyroid association guidelines for ultrasound malignancy risk stratification of thyroid nodules in adults: the EU-TIRADS[J]. Eur Thyroid J, 2017, 6(5): 225-37. doi: 10.1159/000478927 [16] 林婉玲, 吕国荣, 李伯义, 等. TI-RADS超声分类联合BRAFV600E基因突变在甲状腺结节诊断中的价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2017, 33(3): 193-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCY201703001.htm [17] Na DG, Kim DS, Kim SJ, et al. Thyroid nodules with isolated macrocalcification: malignancy risk and diagnostic efficacy of fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy[J]. Ultrasonography, 2016, 35(3): 212-9. doi: 10.14366/usg.15074 [18] 李萍, 周云, 刘姣. 超声量化评分系统与细针穿刺及BRAF基因检测对甲状腺乳头状癌鉴别诊断价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2019, 35(11): 965-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2019.11.002 [19] 章美武, 张燕, 范晓翔, 等. 甲状腺细针穿刺细胞学联合BRAF基因检测的诊断价值[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2017, 26(7): 622-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2017.07.011 [20] Rodrigues HGC, DE Pontes AAN, Adan LF. Contribution of the BRAF oncogene in the pre-operative phase of thyroid carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2013, 6(1): 191-6. [21] Kim MH, Bae JS, Lim DJ, et al. Quantification of BRAF V600E alleles predicts papillary thyroid cancer progression[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2014, 21(6): 891-902. [22] 张卫兵, 秦爱平, 陈天奕, 等. 超声造影联合C-TIRADS分类诊断FNA细胞学不明确甲状腺结节[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2022, 38(9): 979-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCY202209006.htm [23] 王超君, 秦勇, 程颢, 等. 超声造影联合BRAF V600E基因在甲状腺细针穿刺意义不明确类型结节中的应用[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2019(1): 49-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCCY202309015.htm [24] 骆洁丽, 徐侃伦, 黄封博, 等. BRAF V600E检测联合剪切波弹性成像对Bethesda Ⅲ类甲状腺结节的诊断价值[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2018, 27(6): 496-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ202307009.htm [25] 王剑翔, 俞飞虹, 胡菊萍, 等. TIRADS联合剪切波弹性成像对BSRTCⅢ类结节的诊断价值[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2021, 29(10): 993-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYZ202110008.htm -







 下载:
下载: