Application of PET/CT tomography in the diagnosis of lesion distal metastasis and evaluation of prognosis in patients with chemoradiotherapy after rectal cancer surgery
-
摘要:
目的 探究PET/CT在直肠癌术后放化疗患者癌灶远端转移诊断及预后评估中的应用效果。 方法 回顾性分析我院2019年3月~2020年3月70例直肠癌手术患者的资料,所有患者术后均进行放化疗辅助治疗,并采用PET/CT检测治疗效果,根据治疗后是否出现复发、转移评估患者预后,以病理学检测为金标准,比较CT、PET/CT对直肠癌患者癌灶远端转移的诊断价值;将复发、转移者纳入复发转移组(n=26),无复发转移者纳入预后良好组(n=44),对比两组的临床资料;采用多因素Logistic回归分析影响直肠癌患者术后放化疗患者预后的相关因素。 结果 70例患者中,术后3年经病理诊断癌灶远端转移阳性21例,阴性49例,CT诊断癌灶远端转移阳性22例,阴性48例,其中漏诊4例,误诊5例,诊断敏感度为80.95%,特异性为88.37%,准确率为87.14%,阳性预测值为77.27%,阴性预测值为91.67%,Kappa值为0.698;PET/CT诊断远端转移阳性23例,阴性47例,其中漏诊2例,误诊4例,诊断敏感度为90.47%,特异性为91.84%,准确率为91.43%,阳性预测值为82.61%,阴性预测值为95.74%,Kappa值为0.801;复发转移组年龄、病灶最大直径、TNM分期、最大标准化摄取值(SUVmax)、最小标准化摄取值(SUVmin)、滞留指数(RI)均高于预后良好组(P<0.05),两组性别、BMI、病理类型比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);多因素Logistic回归分析显示,年龄、病灶最大直径、TNM分期、SUVmax值、SUVmin值、RI值是影响直肠癌患者术后放化疗预后的危险因素(P<0.05)。 结论 PET/CT技术对直肠癌术后放化疗患者癌灶远端转移诊断价值较高,且其诊断参数SUVmax值、SUVmin值、RI值是影响患者术后放化疗预后的危险因素,可用于临床术后复发转移预测。 Abstract:Objective To explore the application effects of PET/CT in the diagnosis of lesion distal metastasis and evaluation of prognosis in patients with chemoradiotherapy after rectal cancer surgery. Methods Retrospective analysis was conducted on the data of 70 patients with rectal cancer surgery in the hospital from March 2019 to March 2020. All patients received adjuvant therapy with chemoradiotherapy after surgery, and PET/CT technology was used to detect the therapeutic effect. The prognosis of patients was evaluated according to whether recurrence or metastasis occurred after treatment. With postoperative pathological detection as the gold standard, the diagnostic value of CT and PET/CT on lesion distal metastasis in patients with rectal cancer was compared. Patients with recurrence and metastasis were included in the recurrence metastasis group (n=26), and those without recurrence and metastasis were included in the good prognosis group (n=44). The clinical data of the two groups were compared. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the related factors affecting prognosis of patients with chemoradiotherapy after rectal cancer surgery. Results Among the 70 patients at 3 year after surgery, distal metastasis was positive in 21 cases and negative in 49 cases by pathological diagnosis, distal metastasis was positive in 22 cases and negative in 48 cases by CT diagnosis, including 4 cases of missed diagnosis and 5 cases of misdiagnosis. The diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, accuracy rate, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and Kappa value were 80.95%, 88.37%, 87.14%, 77.27%. 91.67% and 0.698. PET/CT diagnosis showed 23 cases of positive distal metastasis and 47 negative cases, including 2 cases of missed diagnosis and 4 cases of misdiagnosis, and the diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, accuracy rate, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and Kappa value were 90.47%, 91.84%, 91.43%, 82.61%, 95.74% and 0.801. The age, maximum lesion diameter, TNM stage, maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), minimum standardized uptake value (SUVmin) and retention index (RI) in recurrence metastasis group were significantly higher than those in good prognosis group (P < 0.05). There were no statistical differences in gender, BMI and pathological type between the two groups (P > 0.05). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that age, maximum lesion diameter, TNM stage, SUVmax, SUVmin and RI were risk factors affecting the prognosis of postoperative chemoradiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer (P < 0.05). Conclusion PET/CT has a high diagnostic value on lesion distal metastasis in patients with chemoradiotherapy after rectal cancer surgery. SUVmax, SUVmin and RI are risk factors affecting the prognosis of patients with postoperative chemoradiotherapy. It can be used in clinical prediction of postoperative recurrence and metastasis. -
Key words:
- positron emission tomography /
- rectal cancer /
- chemoradiotherapy /
- metastasis /
- prognosis /
- diagnostic value
-
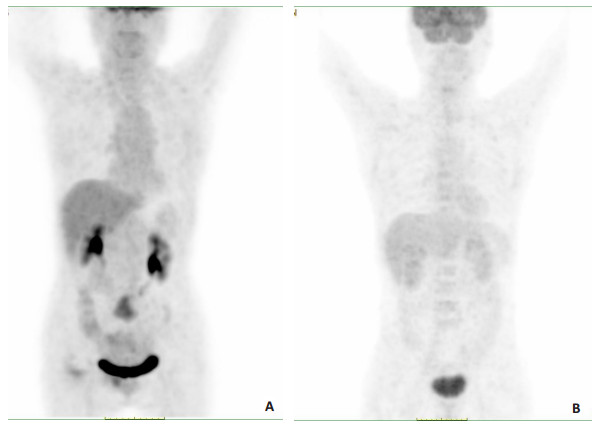
图 1 PET/CT断层显像技术诊断直肠癌术后远端转移图像
Figure 1. Images of PET/CT tomography in the diagnosis of postoperative distal metastasis of rectal cancer. A: PET/CT imaging revealed multiple calcification of the trachea and bronchus. There was a pure ground glass nodule (about 5 mm×6 mm) in the posterior upper lobe of the right lung and a pure ground glass nodule (about 5 mm×5 mm) in the dorsal segment of the lower lobe of the right lung. 3 solid nodules were seen in the posterior basal segment of the left lower lobe, and the larger one was about 6mm×3mm. There were 2 calcified nodules between the dorsal segments of the right lower lobe, and the larger one was about 4 mm×3 mm. There was no thickening of the bilateral pleura, and an irregular soft tissue mass was seen on the right side of the pelvic floor. There was no effusion in the bilateral thoracic cavity and pericardial cavity, and patchy high-density shadow was seen in the aortic wall. No lymph nodes were seen in the brain, head and neck, pharynx, liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and other parts. SUVmax=3.70. B: PET/CT imaging showed a lymph node was found under the left clavicle of the head and neck, with a maximum short diameter of about 12.6 mm. The nodules in the anterior segment of the upper lobe of the lung and the dorsal segment of the lower lobe of the left lung were 13.5 mm×5.5 mm. Irregular low-density shadows were seen in the liver and stomach space. No lymph node metastasis was found in the other lungs, mediastinal hilar lymph nodes, bilateral pleura and esophagus. There was no thickening of the anastomotic stoma and increased 18F uptake. No lymph node metastasis was found in brain, thyroid, pharynx, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and prostate. SUVmax=2.62.
表 1 CT对结肠癌远端转移的诊断价值分析
Table 1. Analysis of diagnostic value of CT on distal metastasis of colon cancer (n)
CT diagnosis Pathological examination Total Positive Negative Positive 17 5 22 Negati 4 44 48 Total 21 49 70 表 2 PET/CT对结肠癌远端转移的诊断价值分析
Table 2. Analysis of diagnostic value of PET/CT on distal metastasis of colon cancer (n)
PET/CT diagnosis Pathological examination Total Positive Negative Positive 19 4 23 Negati 2 45 47 Total 21 49 70 表 3 复发转移组和预后良好组的临床资料比较
Table 3. Comparison of clinical data between recurrence metastasis group and good prognosis group
Influencing factor Recurrence metastasis group(n=26) Good prognosis group(n=44) t/χ2 P Gender [n(%)] 0.150 0.698 Male 16(61.54) 25(56.82) Female 10(38.46) 19(43.18) Age (years, Mean±SD) 53.64±7.82 47.57±8.75 2.914 0.005 BMI (kg/m2, Mean±SD) 24.45±1.83 23.76±1.92 1.478 0.144 Maximum lesion diameter (mm, Mean±SD) 18.31±4.02 14.74±4.53 3.346 0.001 Pathological type [n(%)] 2.605 0.107 Adenocarcinoma 9(34.62) 24(54.55) Mucinous adenocarcinoma 17(65.38) 20(45.45) 9.409 0.009 TNM staging [n(%)] Stage Ⅰ 0 7(15.91) Stage Ⅱ 9(34.62) 23(52.27) Stage Ⅲ 17(65.38) 14(31.82) SUVmax(Mean±SD) 5.43±1.33 1.56±0.42 17.924 <0.001 SUVmin(Mean±SD) 1.86±0.46 0.47±0.14 18.711 <0.001 RI (Mean±SD) 0.74±0.13 0.34±0.08 15.964 <0.001 SUV: Standardized uptake value; RI: Retention index. 表 4 影响直肠癌患者术后放化疗预后的相关因素分析
Table 4. Analysis of related factors affecting prognosis of postoperative chemoradiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer
Variable β S.E Wald χ2 OR P 95% CI Age 0.896 0.287 9.747 2.450 0.002 1.396-4.300 Maximum lesion diameter 0.932 0.256 13.254 2.540 <0.001 1.538-4.194 TNM staging 1.021 0.327 9.749 2.776 0.002 1.462-5.269 SUVmax 1.172 0.331 12.537 3.228 <0.001 1.687-6.177 SUVmin 1.224 0.325 14.254 3.411 <0.001 1.804-6.449 RI 1.131 0.338 11.197 3.099 0.001 1.598-6.010 Independent variable assignment: Actual values of age, maximum lesion diameter, SUVmax, SUVmin and RI; TNM staging: 1=stage Ⅲ; 0=stage Ⅰ-Ⅱ; Dependent variable assignment: 1=recurrence metastasis; 2=good prognosis. -
[1] 李昀昊, 林国乐, 李昌龙, 等. 新辅助放疗和预防性造口对中低位直肠癌根治术后吻合口漏发生率的影响[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2021, 24 (6): 498-504. [2] 周思成, 裴炜, 周海涛, 等. 细胞减灭术联合腹腔热灌注化疗治疗结直肠癌腹膜转移的临床应用与展望[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2022, 44(1): 73-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AZJZ202311025.htm [3] 董备, 黄文起, 林光耀. MRI常规序列结合DWI在诊断直肠癌侧方淋巴结转移中的应用[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2022, 20(1): 171-2, 188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR202201053.htm [4] 胡赢, 韦成江, 龚晗, 等. 结直肠癌肝转移灶的影像学特征与病理微形态学特点的关系[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2022, 38(9): 1109-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LSBL202209018.htm [5] 阮以荣, 唐恬恬, 袁为标, 等. CT增强扫描与MRI对直肠癌术前分期的诊断价值[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2021, 31(11): 1925-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ202111031.htm [6] 张晓洁, 李娜, 杨芳, 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT技术评价T2DM对晚期结直肠癌患者PD-L1治疗疗效的影响[J]. 影像科学与光化学, 2022, 40(2): 237-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GKGH202202006.htm [7] 廖恺, 程刚, 黄颖. 晚期非小细胞肺癌EGFR突变与18F-FDG PET/ CT代谢参数的相关性及其对预后评估的影响[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2021, 48(2): 66-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZL202102004.htm [8] 张旭初, 张建华, 王荣福, 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT联合多种肿瘤标志物在结直肠中分化腺癌术后复发及转移中的应用价值[J]. 北京大学学报: 医学版, 2019, 51(6): 1071-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BYDB202102003.htm [9] 黄荷, 陈婷, 郑丹, 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT联合Ki-67诊断结直肠癌术后复发、转移的价值分析[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2020, 18(12): 135-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR202012043.htm [10] 孙春锋, 谭忠华, 高艳, 等. 结直肠癌腹膜转移的18F-FDG PET/CT影像学表现及其临床意义[J]. 中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2019, 39 (11): 653-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCYX202203012.htm [11] 谭一非, 张捷, 汪晓东, 等. 影像学手段在结直肠癌术前评估中的应用[J]. 华西医学, 2013, 28(3): 481-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYX201303068.htm [12] 徐启兰, 彭传勇, 吴宗山, 等. 高分辨MRI可精准评估直肠癌术前分期及淋巴结转移[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2022, 45(2): 261-4. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2022.02.20 [13] 苏萱, 方长海, 陈华. 结直肠癌肝转移MSCT三期增强扫描影像特征及其诊断价值探讨[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2021, 19(2): 99-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR202102034.htm [14] 张将, 陈亚明, 王蒙, 等. PET-CT SUV值对结直肠癌患者术后复发与转移的诊断价值[J]. 河北医学, 2021, 27(6): 892-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HCYX202106003.htm [15] 柳伟坤, 周旋, 彭李, 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT显像在不明原发癌中的诊断价值[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2020, 43(1): 140-3. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2020.01.29 [16] 杨建峰, 黄亚男, 张雅萍, 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT延迟显像诊断结直肠癌肝转移瘤的价值[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2021, 29(12): 1227-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYZ202112011.htm [17] 何海月, 宋丽萍. PET/CT预测结直肠癌区域淋巴结转移的价值[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2021, 40(11): 2158-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS202111024.htm [18] 周魏薇, 宋丽萍. PET/CT双时相显像在预测宫颈癌淋巴结转移中的价值[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2022, 27(3): 232-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCZL202203007.htm [19] 张伟标, 黄晓红, 智生芳, 等. PET/CT与MRI融合图像诊断直肠癌淋巴结转移的临床价值及影像学分析[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2022, 43(7): 657-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QQHB202207014.htm [20] 华俊, 杨媛媛, 刘影, 等. 18F-前列腺特异性膜抗原-1007PET/CT鉴别正常神经节与前列腺癌淋巴结转移[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2022, 38(9): 1371-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX202209020.htm [21] 黄瑜亮, 黄斌, 严俊. 结直肠癌的早期诊断技术进展[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2019, 42(1): 77-80. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2019.01.18 [22] 郭仲秋, 刘启志, 潘桂霞, 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT相关参数预测结直肠癌切除术预后口价值[J]. 国际放射医学核医学杂志, 2019(4): 295-302. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXZL202319023.htm -







 下载:
下载: