Value of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging sequence in the diagnosis of orbit tumors and tumorlike lesions
-
摘要:
目的 研究磁共振成像分段读出平面回波成像(RS-EPI)序列在诊断眼眶肿瘤及肿瘤样病变中的应用价值。 方法 本研究为回顾性研究,以2016年12月~2018年12月在我院诊断并治疗的眼眶肿瘤及肿瘤样病变患者60例作为研究对象,所有患者均采取3T磁共振扫描仪(MAGNETOM Trio Tim)进行扫描,分别比较RS-EPI以及单次激发平面回波成像(SS-EPI)序列图像质量定性评分、图像质量定量评分的差异。分析RS-EPI序列及SS-EPI序列对于眼眶肿瘤及肿瘤样病变诊断效能之间的差异。 结果 两种方法对观察者组患者脂肪抑制情况之间的差异无统计学意义(P > 0.001),RS-EPI序列诊断方法对于观察者组患者的正常解剖结构的显示能力、伪影情况以及图像综合质量评分高于SS-EPI序列(P < 0.001);两种方法对观察者组患者玻璃体表观扩散系数(ADC)、脑干ADC脂的差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),RS-EPI序列诊断方法对于观察者组患者眼球前后、眼球左右的几何变形情况及信噪比低于SS-EPI序列(P < 0.001);RS-EPI序列对于眼眶肿瘤及肿瘤样病变的诊断敏感度高于SS-EPI序列(P < 0.05);ROC曲线显示,RS-EPI序列对于眼眶肿瘤及肿瘤样病变的曲线下面积高于SS-EPI序列(P < 0.001)。 结论 磁共振成像RS-EPI序列可有效提升眼眶肿瘤及肿瘤样病变的图像质量以及诊断敏感度。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the value of diffusion-weighted MRI using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging (RS-EPI) sequence in the diagnosis of orbit tumors and tumorlike lesions. Methods A retrospective study was performed on 60 patients with orbital tumors or tumorlike lesions in our hospital from December 2016 to December 2018. The patients were imaged on a 3T MRI scanner (MAGNETOM Trio Tim). The RS-EPI and single-shot echo-planar imaging (SS-EPI) sequences were compared in terms of image quality. The diagnostic efficacy between RS-EPI sequence and SS-EPI sequence for orbital tumors and tumorlike lesions were compared. Results Fat suppression in the RS-EPI sequence showed no statistical difference to that in the SS-EPI sequence (P > 0.05), while RS-EPI sequence was was superior to SS-EPI sequence in terms of normal anatomical structure display, ghosting artifact, overall image quality (P < 0.001). The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of vitreous body and brainstem yielded no statistical difference between two methods (P > 0.05). The geometric distortion ratio in both anterior-posterior and right-left direction, as well as signal-to-noise ratio of RS-EPI sequence were all lower than those of SS-EPI sequence (P < 0.001). The diagnostic sensitivity of RS-EPI sequence for orbital tumors and tumorlike lesions was significantly higher than that of SS-EPI sequence (P < 0.05). ROC curve denoted that the area under the curve of RS-EPI sequence in the diagnosis of orbital tumors and tumorlike lesions was significantly larger than that of SS-EPI sequence (P < 0.001). Conclusion MRI using RS-EPI sequence can effectively improve the image quality and diagnostic sensitivity of orbital tumors and tumorlike lesions. -
Key words:
- RS-EPI sequence /
- SS-EPI sequence /
- image quality /
- MRI /
- orbital tumor
-
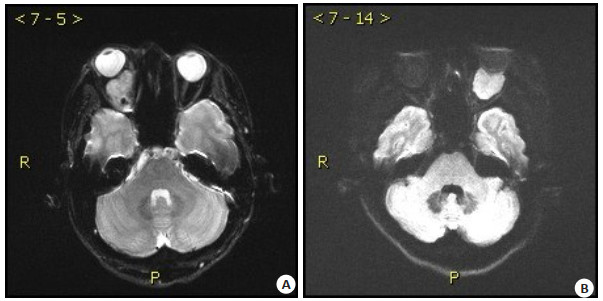
图 1 典型病例图片
Figure 1. Typical case image. A: Isolated orbital fibroma of the right eye (a mass of 28 mm×19 mm×19 mm in the lower part of the vertebrae of the posterior bulbar muscle of the right eye, with local upward displacement of the optic nerve); B: Left orbital musculoconoidal space lymphoma (slightly higher DWI signal, lower ADC, compressed and flattened eyeball, about 2.1 cm×2.4 cm in size).
表 1 两种方法对观察者组患者的图像质量定性评分分析
Table 1. Qualitative score analysis of image quality of patients in the observer group by two methods (n=60, points, Mean±SD)
Diagnostic method Display ability of normal anatomical structures Fat inhibition status Artifacts Comprehensive image quality RS-EPI sequence 3.81±0.81 2.67±0.71 2.36±0.55 2.51±0.57 SS-EPI sequence 2.79±0.94 2.63±0.28 1.58±0.58 1.11±0.21 t 6.367 0.406 7.559 17.852 P < 0.001 0.686 < 0.001 < 0.001 RS-EPI: Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging; SS-EPI: Single-shot echo-planar imaging; ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient. 表 2 两种方法对观察者组患者的图像质量定量评分分析
Table 2. Quantitative score analysis of image quality of patients in the observer group by two methods (n=60, Mean±SD)
Diagnostic method GDRAP(%) GDRRL(%) SNR Vitreous body ADC Brainstem ADC RS-EPI sequence 2.73±0.74 1.66±0.81 1.58±0.54 2.72±0.65 0.89±0.49 SS-EPI sequence 5.23±0.46 4.39±0.73 4.59±0.71 2.82±0.70 0.81±0.74 t 22.225 19.393 26.138 0.811 0.698 P < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.419 0.486 GDR: Geometric distortion ratio; AP: Anterior-posterior direction; RL: Right-left direction. 表 3 两种诊断方法对患者的诊断效能分析
Table 3. Diagnostic efficacy analysis of two diagnostic methods on patients
Diagnostic method True positive cases (n) False positive cases (n) True negative cases (n) False negative cases (n) Accuracy (%) Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) Positive predictive value (%) Negative predictive value (%) RS-EPI sequence 50 11 49 10 82.50 83.33 81.67 81.97 83.05 SS-EPI sequence 45 12 48 15 77.50 75.00 80.00 78.95 76.19 表 4 RS-EPI序列及SS-EPI序列对眼眶肿瘤及肿瘤样病变的ROC曲线分析
Table 4. ROC curve analysis of RS-EPI and SS-EPI sequences on orbital tumors and tumor-like lesions
Diagnostic method SE AUC 95% CI P RS-EPI sequence 0.027 0.878 0.762-0.899 < 0.001 SS-EPI sequence 1.027 0.792 0.762-0.870 < 0.001 -
[1] 马建民, 陈青华, 鲜军舫. 高分辨多模态MRI推进眼眶肿瘤和肿瘤样病变个性化精准诊疗[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2021, 55(10): 1001-3. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112149-20210819-00778 [2] 付珺, 胡俊岭, 刘强, 等. 分段读出序列对眼眶良恶性肿瘤的诊断价值[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2021, 37(2): 203-6, 242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2021.02.008 [3] 首都医科大学眼部肿瘤临床诊疗与研究中心, 中华医学会放射学分会头颈学组. 眼眶肿瘤和肿瘤样病变3.0 T MR检查与诊断专家共识[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2021, 55(10): 1008-23. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112149-20210609-00548 [4] 赵鑫, 胥朵, 李少海, 等. 眼眶肿瘤和瘤样病变MRI检查影像学征象及鉴别诊断研究[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2022, 20(8): 47-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR202208013.htm [5] 齐草源, 鲜军舫. 鼻颅底恶性肿瘤磁共振成像特征及颅底改变特点分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2022, 29(4): 231-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT202204007.htm [6] 杨立娟, 谢小洋, 张晖, 等. MRI特征在鉴别眼眶淋巴瘤与炎性假瘤中的诊断价值[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2021, 37(7): 1056-9, 1135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2021.07.003 [7] 郭明亮. MRI不同序列扩散加权成像在宫颈癌检查中的影像质量比较[J]. 临床医学, 2021, 41(3): 63-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBED202103028.htm [8] 任明玉, 吴一湘, 韩瑞娟, 等. 眼内转移性肿瘤的诊疗分析[J]. 天津医药, 2020, 48(3): 216-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYZ202003013.htm [9] Karthigeyan M, Salunke P, Praneeth K, et al. Convergence weakness with intact medial rectus function in proptosis due to orbital tumors[J]. Neurol India, 2020, 68(4): 840. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.293479 [10] Poflee S, Pawar P, Gaddewar N, et al. Primary yolk sac tumor of orbit: report of a rare case[J]. Indian J Cancer, 2020, 57: 337-9. [11] Mohammad Ahmad A, AboGhadir Ahmed A, Othman Ihab S, et al. Expanded use of transconjunctival orbitotomy in management of different orbital tumors at different locations[J]. Eur J Ophthalmol, 2020, 31(5): 2666-74. [12] Dermarkarian CR, Patel KR, Fuller MY, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the orbit in an 8-month old[J]. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg, 2020, 36(3): e65-8. [13] Barrantes PC, Zhou P, MacDonald S, et al. Granular cell tumor of the orbit: review of the literature and a proposed treatment modality[J]. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg, 2021, 38: 122-31. [14] Khoulali M, Oulali N, Raouzi N, et al. Giant arachnoid cyst associated with an orbital meningocele: a case report and cystoperitoneal shunt management[J]. Pediatr Neurosurg, 2021, 56(1): 50-5. [15] Ouyang BY, Yang QZ, Wang XY, et al. Single-shot T2 mapping via multi-echo-train multiple overlapping-echo detachment planar imaging and multitask deep learning[J]. Med Phys, 2022, 49(11): 7095-107. [16] 梁天齐, 张月强, 朱敬伟, 等. MRI-DWI与DCE-MRI对眼眶肿瘤的诊断价值对比[J]. 西部医学, 2022, 34(8): 1240-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIBU202208029.htm [17] Gallo RA, Shoag J, Johnson TE, et al. Eye-sparing treatment of localized orbital medulloepithelioma with neoadjuvant chemoradiation[J]. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg, 2020, 37(1): e13-6. [18] Chaskes MB, Rabinowitz MR. Orbital Schwannoma[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2020, 81(4): 376-80. [19] Liu Z, Wang Y, Shen F, et al. Radiomics based on readout-segmented echo-planar imaging (RS-EPI) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) for prognostic risk stratification of patients with rectal cancer: a two-centre, machine learning study using the framework of predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine[J]. EPMA J, 2022, 13(4): 633-47. [20] Zhong M, Yang Z, Chen X, et al. Readout-segmented echo-planar diffusion-weighted mr imaging improves the differentiation of breast cancer receptor statuses compared with conventional diffusion-weighted imaging[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2022, 56(3): 691-9. [21] Toledano H, Dotan G, Friedland R, et al. Trametinib for orbital plexiform neurofibromas in young children with neurofibromatosis type 1[J]. Child's Nerv Syst, 2021, 37(6): 1909-15. [22] Dobbs NW, Budak MJ, White RD, et al. MR-eye: high-resolution microscopy coil MRI for the assessment of the orbit and periorbital structures, part 2: clinical applications[J]. AJNR Am J\n Neuroradiol, 2021, 42(7): 1184-9. [23] Oprean CM, Badau LM, Segarceanu NA, et al. Unilateral orbital metastasis as the unique symptom in the onset of breast cancer in a postmenopausal woman: case report and review of the literature[J]. Diagnostics, 2021, 11(4): 725. [24] Guadarrama-Ortiz P, Choreño-Parra JA, Pacheco-Sánchez FJ, et al. The pterional approach for the surgical resection of an orbital cholesteatoma: a case report[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2021, 15(1): 18. -







 下载:
下载: