Application value of MRI features in growing BI-RADS class 3 breast lesions
-
摘要:
目的 分析MRI在生长型BI-RADS 3类乳腺病变中的应用价值。 方法 选择2021年11月~2022年6月本院确诊BI-RADS 3类乳腺病变的115例患者作为研究对象,分析其MRI影像学特征及其对此类患者病情变化预测价值。 结果 115例患者经乳腺超声随访检查发现87例生长型BI-RADS 3类病变分级下降或者稳定,28例病变分级升级;降级或稳定组与升级组患者形态、边界、内部强化、时间-信号强度曲线(TIC)、表观扩散系数(ADC)值等MIR放射学表现的差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,内部强化、TIC曲线、ADC值是生长型BI-RADS 3类乳腺病变变化影响因素(P < 0.05);ROC曲线显示,内部强化、TIC曲线、ADC值用于预测生长型BI-RADS 3类病变变化曲线下面积分别为0.669、0.582、0.844(P < 0.05)。 结论 生长型BI-RADS 3类乳腺病变患者MRI放射学特征与病变分级升级密切相关,其中内部强化、TIC曲线、ADC值等MRI放射学特征可作为预测BI-RADS 3类病变升级的重要指标,对乳腺病变良恶性诊断及病情进展预测提供可靠依据。 -
关键词:
- 乳腺影像报告和数据系统 /
- 磁共振 /
- 影像学特征
Abstract:Objective To analyze the application value of MRI in growing BI-RADS class 3 breast lesions. Methods A total of 115 patients who diagnosed with growing BI-RADS class 3 lesions in the hospital from November 2021 to June 2022 were selected as the study subjects. The MRI features and their predictive value for condition changes were analyzed. Results Breast ultrasound follow- up found that among the 115 patients, there were 87 patients with decreased grade of BI-RADS class 3 lesions or stable BI-RADS class 3 lesions, and 28 patients with increased grade of BI-RADS 3 lesions. There was statistically significant differences in MRI findings such as morphology, boundary, internal enhancement, time-signal intensity curve (TIC) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value between the decreased grade or stable group and the increased grade group (P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis found that internal enhancement, TIC curve and ADC value were influencing factors of changes in growing BI-RADS class 3 lesions (P < 0.05). ROC curve showed that the area under the curve values of internal enhancement, TIC curve and ADC value to predict changes in growing BI-RADS class 3 lesions were 0.669, 0.582 and 0.844, respectively (P < 0.05). Conclusion MRI features of patients with growing BI-RADS class 3 breast lesions are closely related to the grading and upgrading of lesions. Features such as internal enhancement, tic curve and ADC value can be used as important indicators to predict the upgrading of BI-RADS class 3 lesions, it provides a reliable basis for the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions and the prediction of disease progression. -
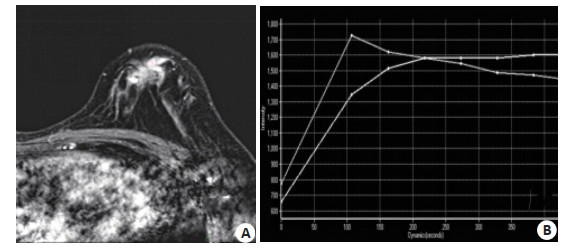
图 1 生长型BI-RADS 3类乳腺病变随访稳定患者病例
Figure 1. Follow-up images of a patient with stable growing BIRADS class 3 breast lesions. The patient was a 51-year-old female with left breast mass of growing BI-RADS class 3. A: MRI showed clear boundary. B: TIC was type III, Follow-up diagnosis showed the condition was stable and the lesion was still BI-RADS class 3.
图 2 生长型BI-RADS 3类乳腺病变随访升级患者
Figure 2. Follow-up images of patients with upgraded growing BI-RADS class 3 breast lesions.The patient was a 42-year-old female with left breast mass of growing BI-RADS class 3. A: MRI showed irregular boundary; B: TIC was type III. Follow-up diagnosis showed upgrading to BI-RADS class 4. Later, the patient was confirmed as breast invasive ductal carcinoma.
表 1 生长型BI-RADS 3类乳腺病变升级与MRI检查放射学表现的关系
Table 1. Relationship between upgrading of growing BI-RADS class 3 breast lesions and MRI findings [n(%)]
MRI findings Downgrading/stable group (n=87) Upgrading group (n=28) t/χ2 P Morphology 4.164 0.041 Irregular (n=32) 20(22.99) 12(42.86) Round/roundish (n=83) 67(77.01) 16(57.14) Boundary 7.332 0.026 Spiculation (n=13) 6(6.90) 7(25.00) Blurry and irregular (n=28) 21(24.14) 7(25.00) Smooth (n=74) 60(68.97) 14(50.00) Composition of breast fibrograndular tissue 0.745 0.863 Inhomogeneous dense type (n=62) 46(52.87) 16(57.14) Extremely dense type (n=34) 26(29.89) 8(28.57) Small amount type (n=11) 8(9.20) 3(10.71) Fat type (n=8) 7(8.05) 1(3.57) Internal enhancement 8.717 0.013 Homogeneous enhancement (n=36) 33(37.93) 3(10.71) Inhomogeneous enhancement (n=57) 41(47.13) 16(57.14) Ring enhancement (n=22) 13(14.94) 9(32.14) Background enhancement of breast parenchyma 0.556 0.907 No enhancement (n=43) 34(39.08) 9(32.14) Mild enhancement (n=38) 28(32.18) 10(35.71) Moderate enhancement (n=25) 18(20.69) 7(25.00) Severe enhancement (n=9) 7(8.05) 2(7.14) TIC 9.534 0.009 Inflow type (n=31) 29(33.33) 2(7.14) Outflow type (n=36) 22(25.29) 14(50.00) Platform type (n=48) 36(41.38) 12(42.38) ADC value(×10-3mm2/s, Mean±SD) 1.96±0.41 1.28±0.24 8.314 <0.001 TIC: Time-signal intensity curve; ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient. 表 2 生长型BI-RADS 3类病变变化影响因素分析
Table 2. Influencing factors of condition changes of growing BI-RADS class 3 lesions
Factors β SE Wald χ2 OR 95% CI P Morphology Irregular 1.000 Round/roundish 0.528 0.327 2.607 1.696 0.893-3.219 0.107 Boundary Boundary 1.000 Blurry and irregular -0.327 0.196 2.783 0.721 0.491-1.059 0.096 Smooth -0.423 0.241 3.081 0.655 0.408-1.051 0.080 Internal enhancement Homogeneous enhancement 1.000 Inhomogeneous enhancement 0.454 0.181 6.292 1.575 1.104-2.245 0.013 Ring enhancement 0.549 0.256 4.599 1.732 1.048-2.860 0.033 TIC Inflow type 1.000 Outflow type 0.495 0.147 11.339 1.640 1.230-2.188 0.001 Platform type 0.324 0.108 9.000 1.383 1.119-1.709 0.003 ADC value (×10-3mm2/s) 0.576 0.216 7.111 1.779 1.165-2.717 0.008 表 3 内部强化、TIC曲线、ADC值对生长型BI-RADS 3类乳腺病变升级的预测价值分析
Table 3. The predictive value of internal enhancement, TIC and ADC value for upgrading of growing BI-RADS class 3 breast lesions
Index AUC Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) 95% CI P Internal enhancement 0.669 89.31 37.92 0.559-0.779 0.007 TIC 0.582 92.88 33.29 0.472-0.691 0.195 ADC value 0.844 96.38 70.08 0.775-0.914 < 0.001 -
[1] Zeng L, Li W, Chen CS. Breast cancer animal models and applications[J]. Zool Res, 2020, 41: 477-494. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2020.095 [2] Berg WA. BI-RADS 3 on screening breast ultrasound: what is it and what is the appropriate management?[J]. J Breast Imaging, 2021, 3(5): 527-38. doi: 10.1093/jbi/wbab060 [3] 陈旭, 宋歌声, 李爱银. 多模态X线影像组学模型对乳腺BI-RADS4类肿块良恶性的辅助诊断价值[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2022, 41(1): 54-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS202201011.htm [4] Eghtedari M, Chong A, Rakow-Penner R, et al. Current status and future of BI-RADS in multimodality imaging, from theAJRSpecial series on radiology reporting and data systems[J]. Am J Roentgenol, 2021, 216(4): 860-73. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.24894 [5] 徐帅娅, 罗芳琼, 巴晨曦, 等. 多模态超声对70例BI-RADS 4类乳腺病变的诊断价值[J]. 山东大学学报: 医学版, 2023, 61(2): 95-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYB202302014.htm [6] 徐金亮, 滕心瑞, 刘宝良, 等. 乳腺X线摄影及动态增强MRI对BIRADS 4-5微钙化病变的诊断价值[J]. 影像科学与光化学, 2020, 38 (5): 815-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GKGH202005010.htm [7] Gao WB, Zhang SQ, Guo JX, et al. Investigation of synthetic relaxometry and diffusion measures in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions as compared to BI-RADS[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2021, 53(4): 1118-27. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27435 [8] 钟兆明, 唐丽娜, 王瑶琴, 等. 常规超声联合超声造影对乳腺BIRADS 4类小结节的诊断价值[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2021, 30 (11): 955-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCCY202302012.htm [9] 孔繁奇, 曹军英. 基于超声量化评分及临床资料对乳腺结节良恶性的预测[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2022, 38(6): 630-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCY202206009.htm [10] Martin E, Boudier J, Salleron J, et al. Synchronous BI-RADS category 3 lesions detected by preoperative breast MRI in patients with breast cancer: may follow- up be adequate?[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(12): 9489-98. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07983-x [11] 丁炎, 周锋盛, 朱巧英, 等. 超声造影与MRI鉴别诊断乳腺钙化性病变良恶性的对比研究[J]. 南京医科大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 42 (1): 103-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJYK202201019.htm [12] 陈铃, 郭俊, 张建兴, 等. 乳腺"第二眼"超声对动态增强MRI额外检出ACR-BI-RADS 4类以上病灶的再评价[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2020, 36(15): 2147-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYZ202015026.htm [13] Ambinder EB, Myers K, Panigrahi B, et al. Breast MRI BI-RADS 3: impact of patient- level factors on compliance with short- term follow-up[J]. J Am Coll Radiol, 2020, 17(3): 377-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2019.09.001 [14] 杨光飞, 常瑞姣, 武雅婷, 等. 超声与MRI对乳腺BI-RADS 3~5类肿物的诊断分类一致性比较[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2022, 30(10): 991-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYZ202210003.htm [15] Lee SE, Lee JH, Han K, et al. BI-RADS category 3, 4, and 5 lesions identified at preoperative breast MRI in patients with breast cancer: implications for management[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(5): 2773-81. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06620-y [16] 杨义文, 胡春洪, 朱默, 等. MRI表观扩散系数联合动态增强TIC类型对肿块型浆细胞性乳腺炎及乳腺癌的鉴别诊断价值[J]. 磁共振成像, 2019, 10(7): 530-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGZC201907013.htm [17] Clauser P, Krug B, Bickel H, et al. Diffusion- weighted Imaging Allows for Downgrading MR BI-RADS 4 Lesions in Contrastenhanced MRI of the Breast to Avoid Unnecessary Biopsy[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 27(7): 1941-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3037 [18] 胡善林, 罗建芳, 聂云凤, 等. DWI表观扩散系数值预测乳腺癌预后的价值[J]. 放射学实践, 2021, 36(5): 601-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSXS202105013.htm [19] 杨一风, 祁章璇, 聂生东. 基于多模态MRI与深度学习的乳腺病变良恶性鉴别[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(4): 401-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PPXZ202204003.htm [20] 吴芳, 胡红杰, 何杰, 等. 最小ADC值对降低乳腺磁共振BIRADS 4类和5类病变活检率的研究[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2022, 41 (7): 1286-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS202207019.htm -







 下载:
下载: