Longitudinal distribution characteristics of atherosclerotic plaques in the tortuous basilar artery
-
摘要:
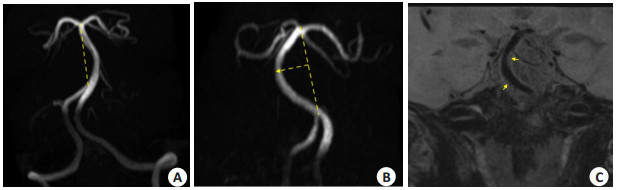
目的 采用高分辨MRI分析迂曲的基底动脉斑块的纵轴分布特征,为预测后循环缺血性脑卒中的发生提供帮助。 方法 回顾性分析我院神经内科住院并接受高分辨MRI检查的患者60例,基底动脉检测到斑块共90个。依据斑块与迂曲弧顶的关系,将所有患者分为:分叉组(n=19)、近端组(n=43)和远端组(n=28),比较3组患者的一般资料、管壁及斑块特点。将近端组及远端组患者依据迂曲方向分为右迂曲组(n=52)和左迂曲组(n=19),比较基底动脉斑块分布与迂曲方向的关系。 结果 60例患者的斑块最常位于近端组。近端组血管面积大于远端组(P=0.049),近端组管壁面积大于远端组(P=0.010)。3组患者斑块分布的差异有统计学意义(P=0.001),弧顶近端及远端斑块多位于侧壁,分叉处斑块多位于前壁。对于近端组和远端组,左侧壁斑块更常分布在右侧迂曲的患者(10.5% vs 42.3%,P=0.012);右侧壁斑块更常分布在左侧迂曲的患者(25.0% vs 57.9%,P=0.009)。 结论 迂曲的基底动脉斑块最常位于弧顶近端,基底动脉迂曲弧顶周围的斑块多位于侧壁及迂曲弧内壁。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the longitudinal distribution characteristics of atherosclerotic plaques in the tortuous basilar artery using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging, for predicting the occurrence of posterior circulation ischemic stroke. Methods We involved the retrospective analysis of 60 patients who underwent high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging exams at our hospital's neurology department, and 90 plaques were detected. All patients were divided into three groups based on the relationship between the plaque's location and the tortuous arc top: bifurcation (n=19), proximal (n=43) and distal (n=28). The characteristics of the vessel wall, plaque, and general data were compared between the three groups. All patients in the proximal group and the distal group were divided into the right tortuosity group (n=52) and the left tortuosity group (n=19) based on the direction of basilar artery convexity. The relationship between the distribution of plaque and the direction of basilar artery convexity was compared. Results Among 60 patients, plaques were mostly located in the proximal group. The vessel area in the proximal group was larger than that in the distal group (P=0.049), and the vessel wall area in the proximal group was larger than that in the distal group (P=0.010). There was a statistically significant difference in the distribution of plaques among the three groups (P=0.001). The plaques at the proximal and the distal groups were mostly located in the lateral wall, and the plaques at the bifurcation group were mostly located in the anterior wall. For both the proximal and the distal groups, the plaque distribution in the left wall was more frequent in patients with right convex basilar artery(10.5% vs 42.3%, P=0.012), the plaque distribution in the right wall was more frequent in patients with left convex basilar arter (25.0% vs 57.9%, P=0.009). Conclusion Plaques in the tortuous basilar artery were mostly located at the proximal of the arc top, and plaques at the arc top's proximal and distal ends were mostly located in the tortuous arc's lateral and inner walls. -
表 1 三组患者的一般资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of clinical data among the three groups [n(%)]
Characteristics Bifurcation (n=19) Proximal (n=43) Distal (n=28) P Age (years, Mean±SD) 64.11±8.76 62.49±9.41 61.86±9.16 0.707 Male 13(68.4) 30(69.8) 22(78.6) 0.661 Hypertension 17(89.5) 38(88.4) 26(92.9) 0.902 Diabetes mellitus 8(42.1) 19(44.2) 13(46.4) 0.957 Hyperlipidemia 5(26.3) 15(34.9) 13(46.4) 0.353 Smoking 7(36.8) 15(34.9) 7(25.0) 0.608 Posterior circulation cerebral infarction 2(10.5) 11(25.6) 9(32.1) 0.232 表 2 斑块及管壁特点的组间比较
Table 2. Comparison of plaque and wall characteristics between groups
Characteristics Bifurcation(n=19) Proximal(n=43) Distal(n=28) P Intraplaque hemorrhage[n(%)] 2(10.5) 11(25.6) 6(21.4) 0.407 Lumen area(mm2, Mean±SD) 8.35±5.85 6.94±4.91 6.07±3.93 0.254 Vessel area(mm2, Mean±SD) 30.93±10.01 30.18±9.63 26.00±7.68 0.028 Wall area(mm2, Mean±SD) 22.58±5.30 23.24±5.70 19.93±4.46 0.011 Plaque area(mm2, Mean±SD) 3.55±2.12 4.10±3.75 3.07±2.64 0.476 Plaque burden(%, Mean±SD) 12.37±7.01 14.49±11.50 11.90±10.72 0.642 Stenosis ratio(%, Mean±SD) 30.24±13.35 41.97±24.42 34.16±19.50 0.224 Remodeling index(Mean±SD) 1.03±0.11 0.96±0.20 0.95±0.16 0.057 Plaque distribution [n(%)] 0.001 Left wall 0(0) 14(32.6) 10(35.7) Right wall 4(21.1) 13(30.2) 11(39.3) Anterior wall 12(63.2) 8(18.6) 3(10.7) Posterior wall 3(15.8) 8(18.6) 4(14.3) 表 3 基底动脉弧顶近端及远端斑块分布与迂曲方向的关系
Table 3. Relationship between plaque distribution and the direction of tortuosity at proximal and distal basilar arcs [n(%)]
Quadrants Left tortuosity(n=19) Right tortuosity (n=52) P Left wall 2(10.5) 22(42.3) 0.012 Right wall 11(57.9) 13(25.0) 0.009 Anterior wall 3(15.8) 8(15.4) 1.000 Posterior wall 3(15.8) 9(17.3) 1.000 -
[1] Lusis AJ. Atherosclerosis[J]. Nature, 2000, 407(6801): 233-41. doi: 10.1038/35025203 [2] Cecchi E, Giglioli C, Valente S, et al. Role of hemodynamic shear stress in cardiovascular disease[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2011, 214(2): 249-56. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.09.008 [3] Nixon AM, Gunel M, Sumpio BE. The critical role of hemodynam-ics in the development of cerebral vascular disease[J]. J Neurosurg, 2010, 112(6): 1240-53. doi: 10.3171/2009.10.JNS09759 [4] Kobayashi N, Karino T. Flow patterns and velocity distributions in the human vertebrobasilar arterial system. Laboratory investigation [J]. J Neurosurg, 2010, 113(4): 810-9. doi: 10.3171/2010.1.JNS09575 [5] Wake-Buck AK, Gatenby JC, Gore JC. Hemodynamic characteris-tics of the vertebrobasilar system analyzed using MRI-based models [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(12): e51346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051346 [6] Qiao Y, Steinman DA, Qin Q, et al. Intracranial arterial wall imag-ing using three- dimensional high isotropic resolution black blood MRI at 3.0 Tesla[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2011, 34(1): 22-30. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22592 [7] Yu YN, Li ML, Xu YY, et al. Middle cerebral artery geometric features are associated with plaque distribution and stroke[J]. Neurology, 2018, 91(19): e1760-e1769. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006468 [8] Raghuram K, Durgam A, Kohlnhofer J, et al. Relationship between stroke recurrence, infarct pattern, and vascular distribution in pa-tients with symptomatic intracranial stenosis[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2018, 10(12): 1161-3. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2017-013735 [9] Deng SS, Zheng JM, Wu YX, et al. Geometrical characteristics associated with atherosclerotic disease in the basilar artery: a magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging study[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2021, 11(6): 2711-20. doi: 10.21037/qims-20-1291 [10] Kim BJ, Kim HY, Jho W, et al. Asymptomatic basilar artery plaque distribution and vascular geometry[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2019, 26(11): 1007-14. doi: 10.5551/jat.47365 [11] Wang MN, Wu F, Yang YJ, et al. Quantitative assessment of symptomatic intracranial atherosclerosis and lenticulostriate arteries in recent stroke patients using whole-brain high-resolution cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson, 2018, 20(1): 35. doi: 10.1186/s12968-018-0465-8 [12] Turan TN, Bonilha L, Morgan PS, et al. Intraplaque hemorrhage in symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic disease[J]. J Neuroimag-ing, 2011, 21(2): e159-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6569.2009.00442.x [13] Sun JL, Liu GQ, Zhang DY, et al. The longitudinal distribution and stability of curved basilar artery plaque: a study based on HR-MRI [J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2021, 28(12): 1333-9. doi: 10.5551/jat.62448 [14] Lee SH, Hur N, Jeong SK. Geometric analysis and blood flow simulation of basilar artery[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2012, 19(4): 397-401. doi: 10.5551/jat.10694 [15] Davies PF. Hemodynamic shear stress and the endothelium in cardiovascular pathophysiology[J]. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med, 2009, 6(1): 16-26. doi: 10.1038/ncpcardio1397 [16] Chiu JJ, Usami S, Shu CE. Vascular endothelial responses to altered shear stress: Pathologic implications for atherosclerosis[J]. Ann Med, 2009, 41(1): 19-28. doi: 10.1080/07853890802186921 [17] Ravensbergen J, Krijger JK, Verdaasdonk AL, et al. The influence of the blunting of the apex on the flow in a vertebro-basilar junction model[J]. J Biomech Eng, 1997, 119(2): 195-205. doi: 10.1115/1.2796080 [18] Ravensbergen J, Ravensbergen JW, Krijger JK, et al. Localizing role of hemodynamics in atherosclerosis in several human vertebrobasilar junction geometries[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 1998, 18(5): 708-16. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.18.5.708 [19] Chen ZS, Liu AF, Chen HJ, et al. Evaluation of basilar artery atherosclerotic plaque distribution by 3D MR vessel wall imaging [J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2016, 44(6): 1592-9. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25296 [20] Zhou L, Yan YF, Du H, et al. Plaque features and vascular geome-try in basilar artery atherosclerosis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2020, 99(18): e19742. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019742 -







 下载:
下载: