The diagnostic value of MR for calf muscle injury of professional football players
-
摘要:
目的 探讨MR在男性职业足球运动员小腿肌肉损伤的诊断价值。 方法 收集2010年12月~2022年9月在南方医科大学第三附属医院就诊的16位男性职业足球运动员资料,年龄29.3±3.4岁,均于受伤后3 d内进行MR检查,共获得28例小腿损伤的资料。由2位经验丰富的放射医师共同阅读MR图像,评估肌肉损伤,包括肌肉损伤的位置、程度、信号异常区的形态,及有无肌筋膜损伤、浅筋膜渗出、肌间束渗出、肌间积液、断端积液、出血等。 结果 共40肌或肌腱损伤,主要包括比目鱼肌损伤21例,腓肠肌损伤10例等,主要损伤腱腹移行区(36肌),其中Ⅰ度损伤35肌,Ⅱ度5肌,损伤的肌肉呈“正羽”或“绒羽”状及片状改变,并见肌腱膜损伤7例、浅筋膜渗出18例、肌间积液21例、出血3例。 结论 男性职业足球运动员小腿肌肉受伤常累及比目鱼肌,MR可显示受伤肌肉的影像学表现特点,明确损伤部位、损伤程度,可为运动损伤的治疗提供影像学信息。 Abstract:Objective To explore the diagnostic value of MR in male professional football players with calf muscle injuries. Methods Sixteen male professional football players, with an average age of 29.3±3.4 years, underwent MR examinations within 3 days after injury in the Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University from December 2010 to September 2022. MR data of 28 cases of calf muscle injuries were obtained. Two experienced radiologists read the MR images together to evaluate muscle injuries, including the location and degree of injured muscle, the shape of abnormal signal intensity, and whether there was muscle fascia injury, superficial fascia exudation, intermuscular bundle exudation, intermuscular effusion, effusion of broken muscles, or hemorrhage. Results A total of 40 muscles affected, mainly including soleus muscle injury in 21 cases, gastrocnemius muscle injury in 10 cases. The injury mainly involved the tendon belly transition zone (36 muscles), including 35 muscles in grade Ⅰ injuries and 5 muscles in grade Ⅱ injury. The injured muscles demonstrated contour feathery or downy feathery like and lamellar patterns. There were 7 cases of muscle aponeurosis injury, 18 cases of superficial fascia exudation, 21 cases of intramuscular effusion and 3 cases of hemorrhage. Conclusion Calf muscle injuries in male professional football players often involve the gastrocnemius muscle, and MR can show the imaging features of the injured muscles, clarify the location and degree of injury, and provide imaging information for treatment for athletic injury. -
Key words:
- football /
- muscle injury /
- calf /
- magnetic resonance imaging
-
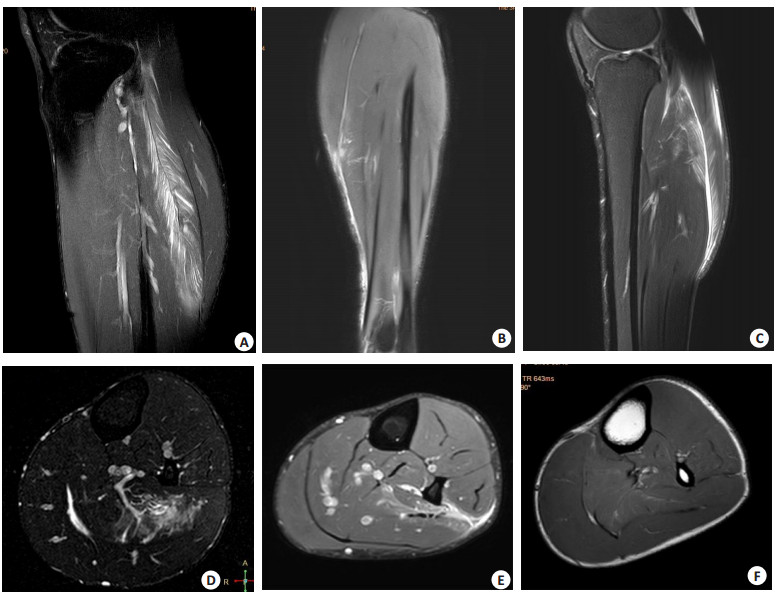
图 1 小腿肌肉损伤的MR表现
Figure 1. MR findings of calf muscle injury. A: The sagittal PDWI-FS showed a grade I muscle injury to the left soleus muscle, with low signal muscle fibers presenting regular appearance with no interruption. The proximal low signal tendon formed a " feather handle, " and the middle muscle fascia formed a " feather axis, " with low signal muscle fibers and high signal liquid exudation forming a " feather twig" -like structure, presenting a typical " feather-like" pattern. Additionally, the middle muscle fascia appeared wave-like and twisted; B: The coronal PDWI-FS showed a Ⅱ degree muscle injury to the left medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle, with local interruption of muscle fibers in the tibial tendon belly transition zone and effusion of broken muscles. In addition, superficial fascia exudation can be seen on the inside; C: The sagittal PDWI-FS showed a " feather" or " contour feather" patterns in the left gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, with the high- signal fluid between the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles to forming the central " shaft" of the " feather". The lower half of the gastrocnemius showed a " half- feather" pattern; D: The axial T2WI-FS showed a " down feather" pattern in the left soleus muscle, with patchy high-signal liquid leakage forming an irregular " feather smaller branch", and the deep vessels forming a " feather axis", which resembled a down feather; E: The axial PDWI-FS showed a disrupted muscular fascia between the left soleus and muscle flexor digitorum longus, as well as fluid accumulation between the soleus and fibularis longus muscles and superficial fascia leakage; F: The axial T1WI showed a faint T1 high-signal lesion in the left soleus muscle, and the pathy high-signal fluid between the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles.
-
[1] Martínez-Rodríguez R, Galán- del- Río F, Cantalapiedra JA, et al. Reliability and discriminative validity of real-time ultrasound elastography in the assessment of tissue stiffness after calf muscle injury[J]. J Bodyw Mov Ther, 2021, 28: 463-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2021.06.019 [2] Brennan JH, Bell C, Brooks K, et al. Correlating clinical assessment and MRI findings in diagnosing calf injuries in elite maleAustralian rules footballers[J]. Skeletal Radiol, 2020, 49(4): 563-70. doi: 10.1007/s00256-019-03318-6 [3] 廖红莉, 代立松, 周红梅, 等. 急性肌肉拉伤的MRI应用进展[J]. 磁共振成像, 2021, 12(1): 121-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGZC202101032.htm [4] 刘春华, 谢宜, 毛锐利, 等. MRI在腘绳肌损伤中的应用价值[J]. 放射学实践, 2022, 37(8): 1023-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSXS202208016.htm [5] Gronwald T, Klein C, Hoenig T, et al. Infographic. Video analysis of match hamstring injury patterns in professional male football (soccer) teaches us about the need for demand- specific multicomponent exercise-based risk reduction programmes[J]. Br J Sports Med, 2022, 56(20): 1194-5. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2022-105600 [6] Aitken D, Balogun S, Foong YC, et al. Clinical relevance of MRI knee abnormalities in Australian rules football players: a longitudinal study[J]. BMJ open sport & exercise medicine, 2021, 7(3): e001097. [7] Cheng Y, Yang HL, Sun ZY, et al. Surgical treatment of gastrocnemius muscle ruptures[J]. Orthop Surg, 2012, 4(4): 253-7. doi: 10.1111/os.12008 [8] 陈垍航, 毕擎, 项海青, 等. 近15年来历届夏季奥运会运动损伤特点分析[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2022, 41(2): 89-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YDYX202202002.htm [9] Orchard J, Orchard J, et al. Fifteen- week window for recurrent muscle strains in football: a prospective cohort of 3600 muscle strains over 23 years in professional Australian rules football[J]. Br J Sports Med, 2020, 54: 1103-7. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2019-100755 [10] 王军辉, 张国庆, 刘玉珂, 等. 网球腿的MRI诊断价值及临床意义[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2021, 32(1): 44-6, 51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYX202101014.htm [11] 代孟, 杨炼, 刘晓庆, 等. 网球腿的MRI表现及发病机制探究[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2019, 53(7): 579-82. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGZP201908005091.htm [12] Silvers-Granelli HJ, Cohen M, Espregueira-Mendes J, et al. Hamstring muscle injury in the athlete: state of the art[J]. J ISAKOS, 2021, 6(3): 170-81. [13] 张睿, 王晓昱, 徐佳, 等. 网球腿发病机制与诊断治疗研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2022, 43(1): 45-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWGK202201011.htm [14] 房立柱, 李志强, 崔立刚, 等. 急诊超声在网球腿诊断中的应用价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2020, 36(8): 738-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCY202008024.htm [15] 陈萍, 马湘乔, 潘诗农. 小腿三头肌运动损伤MRI表现及其诊断价值研究[J]. 徐州医科大学学报, 2020, 40(3): 215-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZYX202003015.htm [16] Green B, Lin M, Schache AG, et al. Calf muscle strain injuries in elite Australian Football players: a descriptive epidemiological evaluation[J]. Scand J Med Sci Sports, 2020, 30(1): 174-84. [17] Ekstrand J, Krutsch W, Spreco A, et al. Time before return to play for the most common injuries in professional football: a 16-year follow-up of the UEFA Elite Club Injury Study[J]. Br J Sports Med, 2019, 54: 421-426. [18] Bordalo M, Arnaiz J, Yamashiro E, et al. Imaging of muscle injuries[J]. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am, 2023, 31(2): 163-79. [19] Kho JSB, Botchu R, Rushton A, et al. MRI features of ERSA (exercise-related signal abnormality) lesions in professional soccer players[J]. Skeletal Radiol, 2022, 51(3): 557-64. [20] Geldenhuys AG, Burgess T, Roche S, et al. Return to play protocols for musculoskeletal upper and lower limb injuries in tackle-collision team sports: a systematic review[J]. Eur J Sport Sci, 2022, 22(11): 1743-56. [21] 张伟, 韩雪, 回瑾, 等. 成人下胫腓联合韧带断层解剖及损伤的磁共振成像表现[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2022, 50(9): 1113-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLYS202209030.htm -







 下载:
下载: