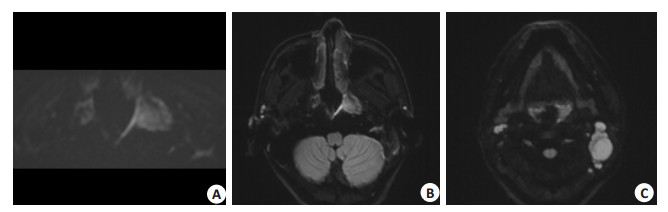
Evaluation of nasopharyngeal image quality from the ZOOMit DWI and RESOLVE DWI techniques
-
摘要:
目的 对3.0 T MR的RESOLVE DWI和小视野ZOOMit DWI技术在鼻咽部的图像质量进行比较。 方法 回顾性分析2021年1~10月在医院行3.0 T MR鼻咽部扫描的40例患者。同时扫描ZOOMit DWI和RESOLVE DWI两种不同扩散成像序列扫描,并对这两种扩散加权成像进行定量分析和主观评分。 结果 两种不同扩散成像序列图像清晰度、伪影和失真的主观评分之间的差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。ZOOMit DWI序列的清晰度最好,失真和伪影最少。两种不同扩散加权序列的信噪比、对比噪声比(b=50 s/mm2)无明显差异。ZOOMitDWI的信噪比、对比噪声比(b=800、1000 s/mm2)优于RESOLVE DWI。 结论 与RESOLVE DWI相比,ZOOMit DWI序列扫描的图像质量更好,适合作为鼻咽部MRI扩散成像的首选序列。 Abstract:Objective To compare the nasopharyngeal image quality with RESOLVE DWI and ZOOMit DWI in 3.0 T MR. Methods Forty patients who underwent 3.0 T MR nasopharyngeal scan in hospital from January to October 2021 were retrospectively analyzed. Two different diffusion imaging sequences, ZOOMit DWI and RESOLVE DWI, were scanned simultaneously, and the two diffusion weighted images were quantitatively analyzed and subjectively scored. Results The subjective scores of image sharpness, artifact and distortion were significantly different between two different diffusion imaging sequences (P < 0.05). ZOOMit DWI sequences had a better sharpness and less distortion and artifacts. SNR and CNR (b=50 s/mm2) of the two diffusion-weighted sequences showed no significant difference. The SNR and CNR (b=800 and b=1000 s/mm2) of ZOOMit DWI were better than that of RESOLVE DWI. Conclusion ZOOMit DWI sequence has better image quality than RESOLVE DWI sequence and it is suitable for MRI diffusion imaging of nasopharynx. -
Key words:
- nasopharynx /
- magnetic resonance imaging /
- diffusion imaging
-
表 1 MRI扫描序列及参数
Table 1. MRI scan sequence and parameters
参数 TR(ms) TE(ms) TA(min) FOV(mm) 矩阵 层数 层厚(mm) 体素 ZOOMit DWI 4200 80 3:11 18×54 134×134 20 4 0.7×0.7×4 RESOLVE DWI 2850 55 5:25 23×230 160×160 20 4 1.0×1.0×4 表 2 两种不同扩散加权序列的主观评分比较
Table 2. Comparison of subjective scores between two diffusion-weighted sequences (n=40, Mean±SD)
评价指标 ZOOMit DWI RESOLVE DWI F P 清晰度 3.51±0.47 3.07±0.49 1.09 < 0.001 失真 3.37±0.52 3.03±0.53 1.04 0.003 伪影 3.19±0.54 3.01±0.51 1.12 0.065 -
[1] 徐金鹏, 任瑞美, 刘希光, 等. 扩散加权成像在鼻咽癌诊断和治疗中的应用[J]. 国际肿瘤学杂志, 2017, 44(10): 771-4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-422X.2017.10.012 [2] 陈竺. 全国第三次死因回顾抽样调查报告[M]. 北京: 中国协和医科大学出版社, 2008: 1-214. [3] 白守民, 刘宜敏, 薛卫平, 等. MRI检测对鼻咽癌颅底侵犯的诊断价值[J]. 中国临床实用医学, 2010, 4(2): 130-1. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZLL200809020.htm [4] 谢传淼, 梁碧玲, 吴沛宏, 等. 螺旋CT与MRI评价鼻咽癌颅底侵犯[J]. 癌症, 2003, 22(7): 729-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AIZH200307015.htm [5] 王颖, 王国杰, 叶颖, 等. 鼻咽癌高分辨率扩散加权成像特征分析[J]. 中华医学杂志2017, 97(17): 1303-6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.17.006 [6] 东强, 徐青, 郭溪, 等. ZOOMit DWI与常规DWI技术在胃癌评估中的初步比较[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2021, 40(3): 511-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS202103022.htm [7] 罗潇, 何永胜, 戚轩, 等. T2*mapping和ZOOMit IVIM序列鉴别诊断甲状腺良恶性结节的价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2021, 55(7): 729-33. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112149-20200617-00827 [8] 王德志, 方元勋. 14例新生儿柯萨奇病毒B3暴发感染的脏器损害特点[J]. 急诊医学, 2000, 9(3): 183-4. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1671-0282.2000.03.018 [9] 但汉丽, 谭钰川, 杨露, 等. MR不同弥散加权序列前列腺图像质量评价研究[J]. 磁共振成像, 2021, 12(3): 54-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGZC202103013.htm [10] Sim KC, Park BJ, Han NY, et al. Efficacy of ZOOMit coronal diffusion-weighted imaging and MR texture analysis for differentiating between benign and malignant distal bile duct strictures[J]. Abdom Radiol: NY, 2020, 45(8): 2418-29. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02625-0 [11] 李敏, 王飚, 刘潇, 等. 高分辨率磁共振成像对女性压力性尿失禁盆底解剖结构评估[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2020, 39(5): 936-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS202005025.htm [12] Seeger A, Batra M, Süsskind D, et al. Assessment of uveal melanomas using advanced diffusion-weighted imaging techniques: value of reduced field of view DWI ("zoomed DWI") and readoutsegmented DWI (RESOLVE)[J]. Acta Radiol Stock Swed, 2019, 60 (8): 977-84. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040887201610_3d6f.html [13] Samson RS, Lévy S, Schneider T, et al. ZOOM or non-ZOOM? assessing spinal cord diffusion tensor imaging protocols for multicentre studies[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(5): e0155557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155557 [14] Sim KC, Park BJ, Han NY, et al. Efficacy of ZOOMit coronal diffusion-weighted imaging and MR texture analysis for differentiating between benign and malignant distal bile duct strictures[J]. Abdom Radiol: NY, 2020, 45(8): 2418-29. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02625-0 [15] 何珍珍, 周清清, 余玉盛, 等. 基于常规DWI和ZOOMit DWI技术对甲状腺图像质量的对比评估[J]. 中国医学计算机成像杂志, 2020, 26 (4): 324-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5741.2020.04.005 [16] 苏昭凤, 李勇刚, 邢建明. 甲状腺病变IVIM、高分辨DWI及常规DWI图像质量优化及诊断价值探讨[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2019, 38(1): 184-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS201901044.htm [17] Hu L, Zhou DW, Fu CX, et al. Advanced zoomed diffusion-weighted imaging vs. full-field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging in prostate cancer detection: a radiomic features study[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(3): 1760-9. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07227-4 -







 下载:
下载: