Application value of liver transient elastography and ultrasound diagnostic parameters in the diagnosis of fatty liver and the evaluation of disease severity
-
摘要:
目的 探究肝脏瞬时弹性成像和超声诊断参数在脂肪肝诊断及病情程度评估中的应用价值。 方法 选择2019年1月1日~ 2021年3月1日于我院确诊为脂肪肝的120例患者作为观察组,并选取同时期健康体检者50例作为对照组,均行肝脏彩色多普勒超声及瞬时弹性成像检查。根据肝脏常规检查(肝脏大小、肝实质回声)结果对观察组患者进行病情程度评估,将患者分为轻度组(n=54)、中度组(n=44)和重度组(n=24),分别比较4组BMI、皮下脂肪层厚度、肝组织声速值、肝脏硬度值,采用Kappa一致性检验分析肝脏瞬时弹性成像与彩色多普勒超声诊断脂肪肝结果一致性,线性趋势卡方检验分析肝脏瞬时弹性成像与彩色多普勒超声诊断脂肪肝的相关性。 结果 对照组、轻度组、中度组、重度组患者BMI、皮下脂肪层厚度、肝脏硬度值依次增加,中度组、重度组患者肝组织声速值依次降低(P < 0.05),对照组、轻度组、中度组患者肝组织声速值差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);肝脏瞬时弹性成像与彩色多普勒超声诊断脂肪肝结果一致性良好(Kappa=0.67,P < 0.05);肝脏瞬时弹性成像与彩色多普勒超声诊断脂肪肝相关性有统计学意义,且肝脏瞬时弹性成像对于轻、中度脂肪肝区分度高于彩色多普勒超声(总变异χ2=298.25,线性回归分量χ2=203.47,偏离线性回归分量χ2=91.43,P < 0.05)。 结论 肝脏瞬时弹性成像和超声诊断脂肪肝一致性良好,但肝脏瞬时弹性成像可更精细区分病情程度。 Abstract:Objective To explore the application value of liver transient elastography and ultrasound diagnostic parameters in fatty liver diagnosis and disease severity evaluation. Methods A total of 120 patients with fatty liver in our hospital between January 1, 2019 and March 1, 2021 were enrolled as observation group. Fifty healthy subjects with physical examination during the same period were treated as control group. All patients underwent liver color Doppler ultrasound and transient elastography. According to the results of liver routine examination (liver size, liver parenchymal echo), the patients in observation group were given disease severity evaluation, and then divided into mild group (n=54), moderate group (n=44) and severe group (n=24). BMI, subcutaneous fat layer thickness, liver tissue sound velocity and liver stiffness value were compared among control group, mild fatty liver group, moderate fatty liver and severe fatty liver group, respectively. Kappa consistency test was used to analyze the consistency of liver transient elastography and color Doppler ultrasound in diagnosing fatty liver. Linear trend chi-square test was applied to analyze the correlation between liver transient elastography and color Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis of fatty liver. Results The BMI, subcutaneous fat layer thickness and liver stiffness value of control group, mild group, moderate group and severe group and the liver tissue sound velocity of moderate group and severe group were increased (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in liver tissue sound velocity among control group, mild group and moderate group (P>0.05). Liver transient elastography and color Doppler ultrasound showed good consistency in the diagnosis of fatty liver (Kappa=0.67, P < 0.05). Chi-square test showed that the liver transient elastography and color Doppler ultrasound were significantly relevant in diagnosing fatty liver. The liver transient elastography was more discriminating than color Doppler ultrasound for mild-to-moderate fatty liver (total variation χ2= 298.25, linear regression component χ2=203.47, deviation from linear regression component χ2=91.43, P < 0.05). Conclusion Liver transient elastography and ultrasound are consistent in the diagnosis of fatty liver, but liver transient elastography can distinguish the severity of the disease more finely. -
Key words:
- transient elastography /
- ultrasound diagnosis /
- fatty liver /
- disease severity
-
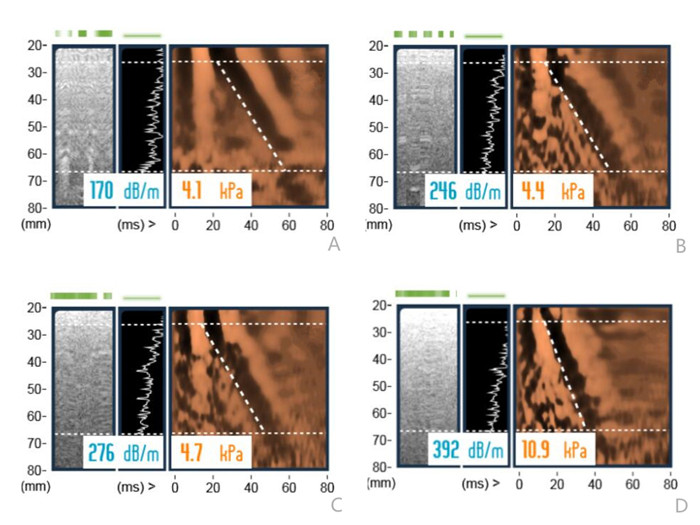
表 1 4组BMI、皮下脂肪层厚度、肝组织声速值、CAP比较
Table 1. Comparison of BMI, subcutaneous fat layer thickness, liver tissue sound velocity and CAP among the four groups (Mean±SD)
组別 BM(kg/m2) 皮下脂肪层厚度(cm) 声速值(m/s) CAP(db/m) 重度组(n=24) 28.47±0.92abc 2.17±0.15abc 1472.57±11.06abc 259.79±9.14abc 中度组(n=44) 27.14±1.09ab 1.96±0.21ab 1520.52±13.13 250.50±10.10ab 轻度组(n=54) 23.11±1.20a 1.47±0.24a 1521.51±12.04 241.42±11.15a 对照组(n=50) 21.62±1.15 1.29±0.20 1522.24±11.73 211.13±11.28 F 384.791 180.598 181.343 178.518 P < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 aP < 0.05 vs对照组;bP < 0.05 vs轻度组;cP < 0.05 vs中度组. CAP: 肝脏硬度值. 表 2 肝脏瞬时弹性成像与彩色多普勒超声诊断脂肪肝结果一致性分析
Table 2. Consistency analysis of liver transient elastography and color Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis of fatty liver (n)
肝脏瞬时弹性成像诊断 彩色多普勒超声诊断 总计 Kappap系数 P 脂肪肝 非脂肪肝 脂肪肝 109 12 121 0.67 < 0.05 非脂肪肝 11 38 49 总计 120 50 170 -
[1] Wong VWS, Petta S, Hiriart JB, et al. Reliability criteria for the diagnosis of fatty liver using controlled attenuation parameter by transient elastography-A multicentre study of 754 patients[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66(1): S67-8. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(17)30396-3 [2] 吴琦琦, 孙红霞, 庄小芳, 等. 脂肪衰减参数联合生化指标对非酒精性脂肪性肝病的诊断价值[J]. 肝脏, 2018, 23(9): 818-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2018.09.025 [3] Chakraborty S, Ganie MA, Masoodi I, et al. Fibroscan as a non-invasive predictor of hepatic steatosis in women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Indian J Med Res, 2020, 151(4): 333-41. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_610_18 [4] 李凤舞, 孙晓慧, 何琼, 等. 脂肪衰减参数评估不同程度脂肪肝的临床初步研究[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2019, 35(8): 702-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2019.08.011 [5] 中国研究型医院学会肝病专业委员会, 中国医师协会脂肪性肝病专家委员会, 中华医学会肝病学分会脂肪肝与酒精性肝病学组, 等. 中国脂肪性肝病诊疗规范化的专家建议(2019年修订版)[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2019, 27(10): 748-53. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.10.003 [6] 杨秀珍, 肖丽, 咸建春, 等. 瞬时弹性成像技术对非酒精性脂肪性肝病的诊断及相关因素分析[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2018, 17 (7): 548-50. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2018.07.013 [7] 周锦纹, 王营忠. 瞬时弹性成像在评估非酒精性脂肪肝中的应用[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2017, 14(1): 146-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2017.01.060 [8] 宋旭光, 何玉冰. 瞬时弹性成像在NAFLD患者肝纤维化和脂肪变性检测中的临床应用[J]. 肝脏, 2020, 25(5): 536-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2020.05.030 [9] 邵玥明, 温晓玉. 在多囊卵巢综合征和健康女性中腹型肥胖是通过超声和瞬时弹性成像评估非酒精性脂肪性肝病的预测因素[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(2): 441. [10] Liu SY, Wong VW, Wong SK, et al. A prospective 5-year study on the use of transient elastography to monitor the improvement of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease following bariatric surgery[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 5416. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83782-0 [11] Cardoso AC, Cravo C, Calçado FL, et al. The performance of M and XL probes of FibroScan for the diagnosis of steatosis and fibrosis on a Brazilian nonalcoholic fatty liver disease cohort[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 32(2): 231-8. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001496 [12] Yilmaz Y, Eren F. Transient elastography for assessing severe hepatic fibrosis in diabetic patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: definitions matter[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 31(12): 1601-2. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31464785 [13] 邵幼林, 张锁才, 吴剑明, 等. 肝脏受控衰减参数与人体脂肪质量和其分布的关系[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2019, 27(10): 754-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.10.004 [14] Song SH, Wong YC, Wu TC, et al. Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease predicted by anthropometric values through transient elastography[J]. Pediatr Int, 2021, 63(2): 183-8. doi: 10.1111/ped.14395 [15] 王慧莲, 王俊平. 瞬时弹性成像系统检测慢性肝病患者的临床价值及影响因素[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2019, 19(13): 2271-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWLC201913068.htm [16] Isoura Y, Cho Y, Fujimoto H, et al. Effects of obesity reduction on transient elastography-based parameters in pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Obes Res Clin Pract, 2020, 14(5): 473-8. doi: 10.1016/j.orcp.2020.08.005 [17] Magrì S, Paduano D, Chicco F, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Beyond the natural history[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(37): 5676-86. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i37.5676 [18] 卢友光, 谢丽平, 林涛发, 等. 肝脏脂肪变性对慢性乙型肝炎患者实时组织弹性成像技术诊断肝纤维化的影响[J]. 肝脏, 2018, 23 (9): 789-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2018.09.014 [19] Shengir M, Krishnamurthy S, Ghali P, et al. Prevalence and predictors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in South Asian women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26 (44): 7046-60. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i44.7046 [20] Mikolasevic I, Delija B, Mijic A, et al. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease diagnosed by transient elastography and liver biopsy[J]. Int J Clin Pract, 2021, 75 (4): e13947. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.13947 [21] Olteanu VA, Bălan GG, Gîlcă Blănariu GE, et al. Biases of Shear Wave vs Transient Elastography in fibrosis assessment of patients with fatty liver disease[J]. Rom Biotechnol Lett, 2020, 25(1): 1289-95. doi: 10.25083/rbl/25.1/1289.1295 [22] 谢晓, 刘婷, 董志霞, 等. FibroTouch检测肝脏受控衰减参数对肝脂肪变的诊断价值分析[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2019, 22(4): 526-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2019.04.019 [23] 陈容容, 林志辉. 瞬时弹性成像技术和超声诊断非酒精性脂肪性肝病的一致性分析[J]. 海峡预防医学杂志, 2019, 25(1): 105-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYF201901046.htm -







 下载:
下载: