The value of color doppler ultrasonography in evaluating the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer
-
摘要:
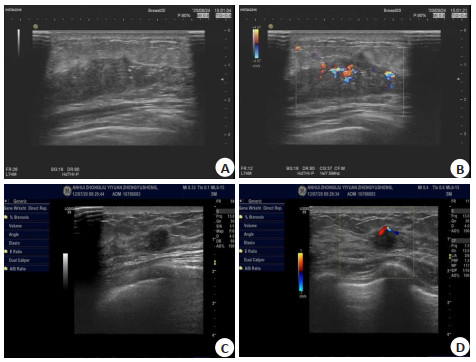
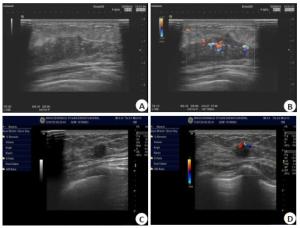
目的探讨彩色多普勒超声检查在评估乳腺癌手术前辅助性化疗效果的价值。 方法选取2015年1月~2021年1月安徽省肿瘤医院术前采取辅助化疗方式治疗的88例乳腺癌患者作为研究对象,根据化疗效果将患者分为有效组(n=60)和无效组(n= 28),对比两组化疗前后的原发病灶大小、病灶内血流分级特征、超声声像特征差异。 结果化疗前,有效组和无效组患者的病灶长、宽、厚、病灶面积、病灶体积测定值差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);化疗后,有效组患者的病灶长、宽、厚、病灶面积、病灶体积测定值均低于无效组(P < 0.05),两组患者的病灶长、宽、厚、病灶面积、病灶体积测定值较化疗前均降低(P < 0.05);化疗前,有效组和无效组患者的病灶形态、边界、强回声带、后方回声构成情况差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);化疗后,有效组患者肿瘤病灶规则形态、边界清晰、后方回声无异常的占比均高于化疗无效组,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05);化疗前,有效组和无效组患者的肿瘤病灶血流分级构成情况差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);化疗后,有效组患者肿瘤病灶血流分级达到(0级+Ⅰ级)占比高于无效组,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论彩色多普勒超声可以从病灶大小、血流分级、声像特征变化3个方面评估乳腺癌术前辅助性化疗效果,对于指导临床治疗及手术具有重要价值。 Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the value of color Doppler ultrasonography (CDFI) in evaluating the effect of adjuvant chemotherapy before breast cancer surgery. MethodsFrom January 2015 to January 2021, 88 patients with breast cancer who were treated with adjuvant chemotherapy before surgery in our Hospital were selected. According to the effect of chemotherapy, the patients were divided into effective group of 60 cases and ineffective group of 28 cases. The two groups of chemotherapy were compared. The size of the primary lesion, the grading characteristics of blood flow in the lesion, and the characteristics of ultrasound imaging before and after were compared. ResultsBefore chemotherapy, the differences of the length, width, thickness, lesion area, and volume of the lesion between two groups were not significant (P>0.05). After chemotherapy, the length and width of the lesion, thickness, lesion area, and lesion volume in effective group were lower than those of ineffective group (P < 0.05). The measured values of lesion length, width, thickness, lesion area, and lesion volume of the two groups were all lower than those before chemotherapy (P < 0.05). Before chemotherapy, the differences of the morphology, border, hyperechoic band, and posterior echo composition between two groups were not significant (P>0.05). After chemotherapy, the tumor lesions in the effective group had regular morphology and borders. The proportions of clear and no abnormal back echoes were higher than those in the chemotherapy-ineffective group(P < 0.05). Before chemotherapy, there was no difference of the blood flow classification of tumor lesions between two groups (P>0.05). After chemotherapy, the proportion of patients in the effective group with tumor lesion blood flow classification (grade 0+Ⅰ) was higher than that in the ineffective group(P < 0.05). ConclusionColor Doppler ultrasonography can evaluate the effect of adjuvant chemotherapy before surgery for breast cancer from three aspects: lesion size, blood flow grade, and changes in acoustic and image characteristics. It is of great value for guiding clinical treatment and surgery. -
Key words:
- color Doppler ultrasound /
- breast cancer /
- adjuvant chemotherapy /
- blood flow grading
-
表 1 两组患者的基线资料分析
Table 1. Baseline data analysis of the two groups of patients[n(%)]
组别 有效组(n=60) 无效组(n=28) t/χ2 P 年龄(岁, Mean±SD) 45.9±6.6 47.2±8.1 -0.799 0.426 BMI(kg/m2, Mean±SD) 23.5±2.2 23.8±2.4 -0.579 0.564 患侧分布 0.933 0.334 左侧 32(53.33) 18(64.29) 右侧 28(46.67) 10(35.71) 临床分期 2.202 0.699 ⅡA 20(33.33) 6(21.43) ⅡB 18(30.00) 8(28.57) ⅢA 11(18.33) 6(21.43) ⅢB 8(13.33) 5(17.86) ⅢC 3(5.00) 3(10.71) 化疗方案 3.262 0.071 T方案 22(36.67) 16(57.14) TP方案 38(63.33) 12(42.86) 表 2 两组患者化疗前后的病灶大小参数变化
Table 2. Changes of lesion size parameters before and after chemotherapy in the two groups (Mean±SD)
病灶参数 有效组(n=60) 无效组(n=28) t P 长(cm) 化疗前 2.84±0.86 2.76±0.93 0.396 0.693 化疗后 1.10±0.36 1.74±0.35 -7.835 < 0.001 宽(cm) 化疗前 2.40±0.81 2.24±0.74 0.886 0.378 化疗后 0.96±0.31 1.52±0.40 -7.179 < 0.001 厚(cm) 化疗前 1.83±0.47 1.75±0.42 0.768 0.444 化疗后 0.90±0.28 1.32±0.33 -6.187 < 0.001 面积(cm2) 化疗前 6.74±1.95 6.29±2.04 0.994 0.323 化疗后 2.86±0.73 4.10±1.55 -5.12 < 0.001 体积(cm3) 化疗前 13.83±3.75 13.05±3.52 0.926 0.357 化疗后 4.62±1.38 8.06±1.90 -9.622 < 0.001 表 3 化疗前两组病灶声像特征参数比较
Table 3. Comparison of the characteristic parameters of the two groups of lesions before chemotherapy[n(%)]
声像特征 有效组(n=60) 无效组(n=28) χ2 P 形态 1.539 0.215 规则 13(21.67) 3(10.71) 不规则 47(78.33) 25(89.29) 边界 0.828 0.363 清晰 11(18.33) 3(10.71) 不清晰 49(81.67) 25(89.29) 强回声带 2.256 0.133 有 9(15.00) 8(28.57) 无 51(85.00) 20(71.43) 后方回声 1.268 0.53 增强 19(31.67) 11(39.29) 衰减 32(53.33) 53.57 无异常 9(15.00) 2(7.14) 表 4 化疗后两组病灶声像特征参数比较
Table 4. Comparison of the characteristic parameters of the two groups of lesions after chemotherapy[n(%)]
声像特征 有效组(n=60) 无效组(n=28) χ2 P 形态 4.477 0.034 规则 40(66.67) 12(42.86) 不规则 20(33.33) 16(57.14) 边界 5.359 0.021 清晰 33(55.00) 8(28.57) 不清晰 27(45.00) 20(71.43) 强回声带 1.719 0.190 有 5(8.33) 5(17.86) 无 55(91.67) 23(82.14) 后方回声 17.180 0.000 增强 6(10.00) 8(28.57) 衰减 9(15.00) 12(42.86) 无异常 45(75.00) 8(28.57) 表 5 两组患者化疗前后的肿瘤病灶血流分级比较
Table 5. Comparison of blood flow grades of tumor lesions before and after chemotherapy in the two groups[n(%)]
化疗时间 有效组(n=60) 无效组(n=28) χ2 P 化疗前 0.003 0.959 0级+Ⅰ级 5(8.33) 2(7.14) Ⅱ级+Ⅲ级 55(91.67) 26(92.86) 化疗后 4.513 0.034 0级+Ⅰ级 36(60.00) 10(35.71) Ⅱ级+Ⅲ级 24(40.00) 18(64.29) -
[1] Ren H, Shen ZP, Shen JR, et al. Diagnostic value of Doppler ultrasound parameters combined with MMP-11 in early breast cancer and benign breast diseases[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 20(2): 1028-32. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11676 [2] 程红莲, 王梦, 余岳, 等. 早期乳腺癌新辅助化疗淋巴结转阴患者术后放疗的价值[J]. 天津医药, 2020, 48(1): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYZ202001011.htm [3] 吴云华, 代前军. 超声造影参数对中晚期乳腺癌新辅助化疗有效性的应用价值[J]. 安徽医药, 2020, 24(7): 1399-402. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6469.2020.07.033 [4] 杨立光, 周倩, 李启霖, 等. 功能成像技术对乳腺癌新辅助化疗后疗效评估的研究进展[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2019, 42(3): 285-9. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2019.03.01 [5] 曹文斌, 陈琴, 罗俊, 等. 超声成像技术对乳腺癌新辅助化疗疗效评估研究进展[J]. 实用医院临床杂志, 2019, 16(3): 250-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2019.03.078 [6] 孙建新, 党笑坤, 张亚雄, 等. 乳腺癌超声影像与病理组织学分型的对照研究[J]. 肿瘤研究与临床, 2009, 21(8): 490-1. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-9801.2009.08.023 [7] Clauser P, Londero V, Como G, et al. Comparison between different imaging techniques in the evaluation of malignant breast lesions: can 3D ultrasound be useful?[J]. La Radiol Med, 2014, 119 (4): 240-8. doi: 10.1007/s11547-013-0338-z [8] 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会. 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌诊治指南与规范(2015版[) J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2015, 25(9): 692-754. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGAZ201509014.htm [9] Yu J, Wu J, Huang O, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics, adjuvant chemotherapy decision and disease outcome in patients with breast cancer with a 21-gene recurrence score of 26-30[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 20(2): 1545-56. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11734 [10] Chen WJ, Tu Q, Shen YF, et al. Sequential vs concurrent adjuvant chemotherapy of anthracycline and taxane for operable breast cancer[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2021, 19(1): 52. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02150-4 [11] Haas BK, Osborne CRC, Vukelja SJ, et al. Effect of exercise during adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37 (15_suppl): 6524. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.6524 [12] Labrosse J, Osdoit M, Hamy AS, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer after preoperative chemotherapy: a propensity score matched analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(6): e0234173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234173 [13] Ayettey Anie HN, Yarney J, Sanuade O, et al. Outcome of treatment after locoregional radiation, neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol, 2020, 108 (3): e418. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360301620339250 [14] Genshin M, Tsunoda-Shimizu H, Mukai RE, et al. Histopathological evaluation of breast cases with positive color Doppler method and negative elastography for malignancy[J]. Jpn J Med Ultrasonics, 2009, 36(1): 33-7. doi: 10.3179/jjmu.36.33 [15] Li M, Li Q, Yin Q, et al. Evaluation of color Doppler ultrasound combined with plasma miR-21 and miR-27a in the diagnosis of breast cancer[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2021, 23(4): 709-17. doi: 10.1007/s12094-020-02501-9 [16] Sehgal CM, Weinstein SP, Arger PH, et al. A review of breast ultrasound[J]. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia, 2006, 11(2): 113- 23. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17082996/ [17] 吴国柱. 瘤体周边滋养血管对乳腺癌的诊断价值及与分子标记物相关性研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2018: 12-13. [18] Park EK, Seo BK, Kwon M, et al. Low-dose perfusion computed tomography for breast cancer to quantify tumor vascularity: correlation with prognostic biomarkers[J]. Invest Radiol, 2019, 54 (5): 273-81. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000538 [19] 邹荣莉, 程冲, 曹伟, 等. CDFI在肿瘤腹腔转移患者腹腔灌注化疗中的应用[C]//中国超声医学工程学会成立30周年暨第十二届全国超声医学学术大会论文集. 西安, 2014: 655. [20] 陈翠香. 二维结合彩色多普勒血流成像对乳腺良恶性肿瘤的诊断价值[J]. 中华医学超声杂志: 电子版, 2010, 7(11): 1815-9. doi: 10.3969/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2010.11.008 [21] 左文思, 金林原, 李芬穗. 超声造影对不同分子分型乳腺癌的诊断价值[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2019, 42(4): 423-9. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2019.04.01 -






 下载:
下载: