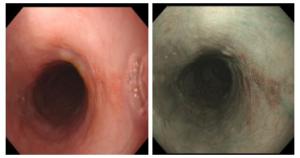
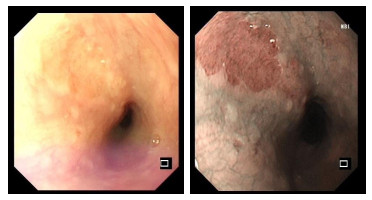
Clinical value of I-Scan combined with magnifying endoscopy in the diagnosis of early cancer and precancerous lesions of the esophagus
-
摘要:
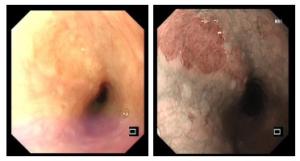
目的探讨高清智能电子染色内镜(i-Scan)联合放大内镜对食管早癌、癌前病变的诊断价值。 方法选取我院经病理学检查证实为食管早癌患者100例(早癌组)、200例发生食管癌癌前病变(癌前病变组)的患者的内镜检查资料进行数据分析,以病理学结果作为金标准,计算i-Scan联合放大内镜下、白光内镜单独及联合应用时诊断食管早癌及癌前病变的检出率及诊断指标。 结果i-Scan对食管早癌的诊断检出率为88.00%,癌前病变检出率为82.50%,轻度不典型增生检出率为28.00%,中度不典型增生检出率29.00%;白光内镜对食管早癌的诊断检出率为57.00%,癌前病变检出率为56.00%,轻度不典型增生检出率为16.00%,中度不典型增生检出率为17.00%;i-Scan对上述病变的检出率均高于白光内镜,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。i-Scan对食管黏膜重度不典型增生检出率(25.50%)与白光内镜(22.50%)比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);i-Scan联合放大内镜检查对100例食管早癌患者、200例食管癌前病变患者诊断的IPCL分型与病理类型对比,结果显示:100例食管早癌患者中有12例诊断为A型、将中度不典型增生患者中的2例诊断为B1型,将重度不典型增生患者中的4例诊断为B1型;白光内镜鉴别诊断食管早癌、食管癌癌前病变的敏感度为57.00%,特异性为56.00%;i-Scan鉴别诊断食管早癌、食管癌癌前病变的敏感度为88.00%,特异性为82.50%;i-Scan联合放大内镜检查鉴别诊断食管早癌、食管癌癌前病变的敏感度为88.00%,特异性为97.00%。 结论iScan联合放大内镜对食管早癌、癌前病变的鉴别诊断具有较高的敏感度和特异性。 -
关键词:
- 高清智能电子染色内镜 /
- 放大内镜 /
- 食管早癌 /
- 癌前病变
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the value of high-definition intelligent electronic staining endoscopy (i-Scan) combined with magnifying endoscopy in the diagnosis of early cancer and precancerous lesions of the esophagus. MethodsWe selected the endoscopy data of 100 patients with early esophageal cancer (early cancer group) and 200 patients with esophageal precancerous lesions (precancerous lesions group) confirmed by pathological examination in our hospital. The pathological results was treated as the gold standard. The detection rate and diagnostic indicators for the diagnosis of early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions under i-Scan combined with magnifying endoscopy and white light endoscopy alone and in combination were calculated. Resultsi-Scan had a diagnostic detection rate of 88.00% for early esophageal cancer, 82.50% for precancerous lesions, 28.00% for mild dysplasia, 29.00% for moderate dysplasia, white light endoscopy. The diagnosis and detection rate of early cancer of the esophagus was 57.00%, the detection rate of precancerous lesions was 56.00%, the detection rate of mild dysplasia was 16.00%, and the detection rate of moderate dysplasia was 17.00%. The detection rate of I-Scan was higher than that of white light endoscopy and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The detection rate of I-Scan for severe esophageal mucosal dysplasia was 25.50% compared with 22.50% of white light endoscopy, with no significant difference (P>0.05). 100 patients with early esophageal cancer Twelve cases were diagnosed as type A, 2 of patients with moderate dysplasia were diagnosed as type B1, and 4 of patients with severe dysplasia were diagnosed as type B1. White light endoscopy differential diagnosis of early esophageal cancer, esophageal cancer. The sensitivity of precancerous lesions was 57.00%, and the specificity was 56.00%. The sensitivity of I-Scan for differential diagnosis of early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions of esophagus was 88.00%, and the specificity was 82.50%. The sensitivity for diagnosing early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions of esophagus was 88.00%, and the specificity was 97.00%. Conclusioni-Scan combined with magnifying endoscopy has high sensitivity and specificity in the differential diagnosis of early cancer and precancerous lesions of the esophagus. -
表 1 一般资料比较
Table 1. General information comparison
因素 早癌组(n=100) 癌前病变组(n=200) t/χ2 P 年龄(岁, Mean±SD) 56.8±7.8 58.0±8.3 -1.204 0.230 BMI(kg/m2) 23.6±2.6 23.3±2.1 1.075 0.283 性别[n(%)] 0.545 0.460 男 58 (58.00) 107 (53.50) 女 42 (42.00) 93 (46.50) 病变部位[n(%)] 0.493 0.782 上段 11 (11.00) 17 (8.50) 中段 69 (69.00) 142 (71.00) 下段 20 (20.00) 41 (20.50) 吸烟[n(%)] 1.365 0.243 是 35 (35.00) 84 (42.00) 否 65 (65.00) 116 (58.00) 饮酒[n(%)] 0.706 0.783 是 26 (26.00) 55 (27.50) 否 74 (74.00) 145 (72.50) 表 2 I-Scan、白光内镜诊断不同病理学类型食管病变的检出率比较
Table 2. Comparison of the detection rate of I-Scan and white light endoscopy in the diagnosis of different pathological types of esophageal lesions [n(%)]
病理类型 白光内镜 i-Scan χ2 P 食管早癌 57 (57.00) 88 (88.00) 44.806 0.000 癌前病变 112 (56.00) 165 (82.50) 32.978 0.000 轻度不典型增生 32 (16.00) 56 (28.00) 8.392 0.004 中度不典型增生 35 (17.50) 58 (29.00) 7.411 0.006 重度不典型增生 45 (22.50) 51 (25.50) 0.493 0.482 表 3 IPCL分级与病理结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of IPCL grade and pathological results
病理类型 IPCL分型 合计 A型 B1型 B2型 B3型 食管早癌 12 32 40 16 100 轻度不典型增生 69 0 0 0 69 中度不典型增生 72 2 0 0 74 重度不典型增生 53 4 0 0 57 表 4 i-Scan鉴别诊断食管早癌、食管癌癌前病变
Table 4. i-Scan differential diagnosis of early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions of esophageal cancer
i-Scan 病理学结果 合计 阳性 阴性 阳性 88 35 123 阴性 12 165 177 合计 100 200 300 表 5 白光内镜鉴别诊断食管早癌、食管癌癌前病变
Table 5. White light endoscopy in differential diagnosis of early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions of esophageal cancer
白光内镜 病理学结果 合计 阴性 阳性 阳性 57 88 145 阴性 43 112 155 合计 100 200 300 表 6 i-Scan联合放大内镜鉴别诊断食管早癌、食管癌癌前病变
Table 6. i-Scan combined with magnifying endoscopy in differential diagnosis of early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions of esophagus
i-Scan联合放大内镜 病理学结果 合计 阳性 阴性 阳性 88 6 94 阴性 12 194 206 合计 100 200 300 表 7 i-Scan、白光内镜、i-Scan联合放大内镜鉴别诊断食管早癌、食管癌癌前病变的价值
Table 7. The value of i-Scan, white light endoscopy, and i-Scan combined with magnifying endoscopy in the differential diagnosis of early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions of esophagus (%)
诊断方法 敏感度 特异性 漏诊率 误诊率 i-Scan 88.00 82.50 12.00 17.50 白光内镜 57.00 56.00 43.00 44.00 i-Scan联合放大内镜 88.00 97.00 12.00 3.00 -
[1] 刘小玉. 窄带成像放大内镜结合卢戈氏染色对食管癌癌前病变及早期癌诊断的应用价值[J]. 陕西医学杂志, 2020, 49(9): 1185-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7377.2020.09.034 [2] 姜菊英, 张玉华. 常规内镜、NBI电子染色放大内镜及内镜下色素染色对早期大肠肿瘤性病变诊断的研究[J]. 中国社区医师, 2020, 36(16): 107-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2020.16.064 [3] 麦文杰, 吉凯, 苏林杰, 等. 人工智能电子染色及白光模式诊断食管病变的临床对照研究[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗, 2019, 24(10): 1180-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2159.2019.10.026 [4] Dan X, Lv XH, San ZJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of multiband mucosectomy versus cap-assisted endoscopic resection for early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech, 2019, 29(5): 313-20. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000711 [5] 练键勤, 凌威, 赵以谦. 高清染色内镜(i-Scan)技术在鼻咽癌早期诊断中的价值分析[J]. 当代医学, 2020, 26(12): 163-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2020.12.071 [6] Li Y, Yangjin CR, Shi YY, et al. The significance of a pale area via flexible spectral imaging color enhancement in the diagnosis of esophageal precancerous lesions and early-stage squamous cancer [J]J Clin Gastroenterol, 2019, 53(9): e400-4. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30829906 [7] 中国抗癌协会食管癌专业委员会. 食管癌规范化诊疗指南[M]. 北京: 中国协和医科大学出版社, 2013. [8] 陈远博, 赵妙, 晏洁影, 等. 窄带成像技术联合超声内镜对早期食管癌及癌前病变的诊治价值[J]. 中国临床研究, 2015, 28(8): 996-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCK201508007.htm [9] 陈晓琼, 陈雅华, 郑晓玲, 等. 日本食管协会分型中AB分型在早期食管鳞癌T分期的应用价值[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志, 2016, 33(9): 621-4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-5232.2016.09.012 [10] 庄小端, 白杨. 表浅食管鳞状细胞癌内镜下诊断进展[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志, 2019, 36(4): 299-304. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-5232.2019.04.019 [11] 夏佳薇, 何松. 消化道早癌筛查技术的研究进展[J]. 重庆医学, 2019, 48(6): 1014-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2019.06.030 [12] 邱云峰, 初春梅, 李长锋. 窄带成像结合放大内镜对大肠侧向发育型肿瘤的诊断价值[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2018, 22(9): 1553-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2018.09.021 [13] Sun YW, Zhang T, Wu WJ, et al. Risk factors associated with precancerous lesions of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a screening study in a high risk Chinese population[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(14): 3284-90. doi: 10.7150/jca.29979 [14] 刘云霞, 吴华清, 房贤村. 内镜下卢戈氏液染色在早期食管癌诊断中的应用分析[J]. 临床医药文献电子杂志, 2020, 7(14): 132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWX202014120.htm [15] 马瑞军, 汪嵘, 陈星, 等. 人工智能电子染色技术在声带白斑及食管病变诊断中的临床应用[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志, 2018, 35(9): 656. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-5232.2018.09.011 [16] Chen R, Ma SR, Guan CT, et al. The national cohort of esophageal cancer-prospective cohort study of esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions based on high-risk population in China (NCECHRP): study protocol [J]. BMJ Open, 2019, 9(4): e027360. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027360 [17] 舒梅铃, 荆晓娟, 杨彬, 等. 碘液染色在食管早期癌症及癌前病变内镜检查中的应用[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2020, 36(11): 1690-2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2020.11.026 [18] 王东悦. 早期食管癌及癌前病变患者诊治中的内镜下食管碘染应用分析[J]. 中国实用医药, 2019, 14(35): 37-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSSA201935017.htm [19] 庞霄君, 林子闻, 丁秋龙, 等. 内镜下碘染色筛查早期食管癌及癌前病变的应用价值[J]. 医药前沿, 2019(18): 233-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYZ201203019.htm [20] Pan D, Su M, Zhang T, et al. A distinct epidemiologic pattern of precancerous lesions of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a high-risk area of Huai'an, Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Cancer Prev Res, 2019, 12(7): 449-62. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-18-0462 [21] 邢洁, 李鹏. 早期食管鳞状细胞癌及癌前病变的诊断与治疗策略[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2020, 59(4): 318-21. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20200210-00061 [22] Li L, Wang W, Yue H, et al. Endoscopic submucosal multi-tunnel dissection for large early esophageal cancer lesions[J]. Acta Gastroenterol Belg, 2019, 82(3): 355-8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31566321 [23] Dumoulin FL, Hildenbrand R, Oyama T, et al. Current trends in endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of early esophageal cancer[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(4): 752. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040752 [24] Guo LJ, Xiao X, Wu CC, et al. Real-time automated diagnosis of precancerous lesions and early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using a deep learning model (with videos)[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2020, 91(1): 41-51. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2019.08.018 [25] Wei YT, Wang XJ, Li MS. Intelligent medical auxiliary diagnosis algorithm based on improved decision tree[J]. J Electr Comput Eng, 2020, 2020: 1-9. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/343955698_Intelligent_Medical_Auxiliary_Diagnosis_Algorithm_Based_on_Improved_Decision_Tree -






 下载:
下载: