Consistency of carotid duplex ultrasound and transcranial Doppler with cerebral angiography
-
摘要:
目的探讨颈部血管彩超、经颅多普勒超声(TCD)对颈动脉狭窄、椎-基底动脉狭窄和动脉粥样硬化斑块的诊断价值,分析其与脑血管造影的一致性。 方法选取2019年1月~2020年6月106例动脉粥样硬化性脑梗死患者为观察组,53例无脑梗死的动脉粥样硬化高血压病和(或)高脂血症患者为对照组。比较两组颈部血管彩超和TCD对颈动脉与椎-基底动脉中重度以上狭窄、不稳定型斑块的检出率。以脑血管造影为金标准,分析颈部血管彩超和TCD的诊断一致性。 结果观察组颈动脉与椎-基底动脉中度狭窄、重度狭窄、完全闭塞的检出率均高于对照组(P < 0.05)。观察组颈动脉粥样硬化不稳定型斑块的检出率高于对照组(P < 0.05)。颈部血管彩超联合TCD对中重度以上狭窄检出的敏感度为93.75%,特异性为88.46%,准确率为92.45%,一致性较高(Kappa=0.801);对不稳定型斑块检出的敏感度为87.67%,特异性为87.88%,准确率为87.74%,一致性较高(Kappa= 0.725)。 结论颈部血管彩超和TCD诊断颈动脉狭窄、椎-基底动脉狭窄和动脉粥样硬化斑块准确、无创、便捷,对脑梗死的预防、诊断、病因分析具有重要的参考意义。 Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the value of carotid duplex ultrasound and transcranial Doppler (TCD) in the diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis, vertebro-basilar artery stenosis and atherosclerotic plaque, and analyze their consistencies with cerebral angiography. Methods106 patients with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction who were treated between January 2019 and June 2020 were selected as the observation group. Meanwhile, 53 patients with atherosclerotic hypertension and/or hyperlipidemia and without cerebral infarction were selected as the control group. The detection rates of severer than moderate to severe stenosis of carotid artery and vertebro-basilar artery and unstable plaques by carotid duplex ultrasound and TCD were compared between the 2 groups. Cerebral angiography was taken as the golden standard to analyze the diagnostic consistency of carotid duplex ultrasound and TCD. ResultsThe detection rates of moderate stenosis, severe stenosis and complete occlusion of carotid artery and vertebro-basilar artery, and the detection rate of carotid atherosclerotic unstable plaques in the observation group were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of carotid duplex ultrasound combined with TCD in detection of severer than moderate to severe stenosis were 93.75%, 88.46% and 92.45%, with high consistency (Kappa=0.801). For detection of unstable plaques, the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were 87.67%, 87.88% and 87.74%, with high consistency (Kappa=0.725). ConclusionCarotid duplex ultrasound and TCD are accurate, non-invasive and convenient in the diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis, vertebro-basilar artery stenosis and atherosclerotic plaque, which is of great significance for prevention, diagnosis and cause analysis of cerebral infarction. -
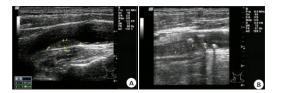
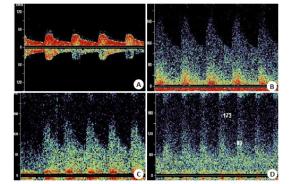
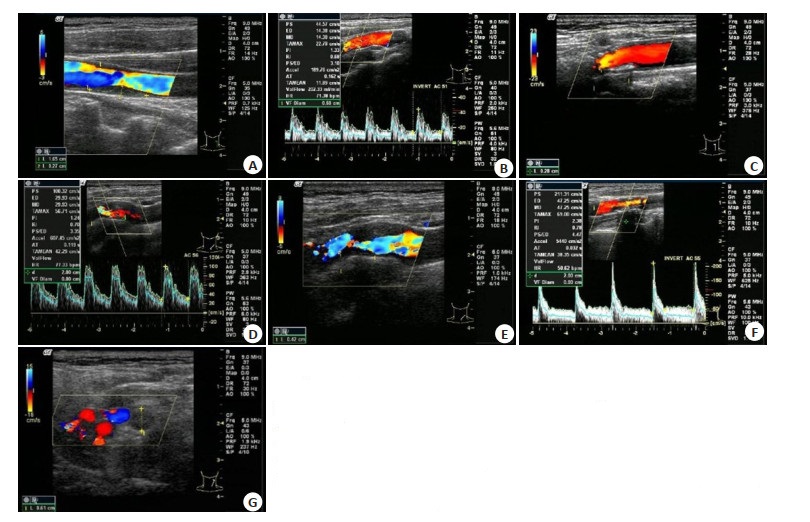
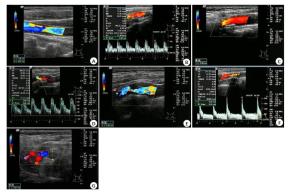
图 1 颈部血管彩超评估颈动脉狭窄
A: 轻度狭窄, 血流束稍微变窄; B: 轻度狭窄, 频谱图显示高阻型血流频谱, 收缩期迅速升高, 舒张期下降呈尖峰状; C: 中度狭窄, 血流速明显增高; D: 中度狭窄, 频谱图显示高阻型血流频谱, 狭窄处血流明显上升, 波形高尖; E: 重度狭窄, 血流明显变细, 信号不等; F: 重度狭窄, 频谱图显示高阻型血流频谱, 波形高尖, 峰值流速大于200 cm/s; G: 完全闭塞, 强回声团块, 血流信号中断, 无法测及频谱.
Figure 1. Evaluation of carotid artery stenosis by carotid duplex ultrasound
表 1 两组患者一般资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of general data between the two groups
组别 性别(n) 年龄(岁, Mean±SD) BMI(kg/m2, Mean±SD) 慢病史(n) 男 女 高血压病 高脂血症 观察组(n=106) 60 46 64.58±6.33 23.76±1.84 72 39 对照组(n=53) 28 25 62.73±6.12 23.81±2.01 40 22 χ2 0.204 1.756 0.157 0.967 0.332 P 0.652 0.081 0.876 0.326 0.564 表 2 两组颈部血管彩超对颈动脉狭窄检出率的比较
Table 2. Comparison of the detection rate of carotid artery stenosis by carotid duplex ultrasound between the two groups [n(%)]
组别 颈动脉狭窄 轻度狭窄 中度狭窄 重度狭窄 完全闭塞 观察组(n=106) 28(26.43) 50(47.17) 18(16.98) 10(9.42) 对照组(n=53) 45(84.91) 8(15.09) 0(0) 0(0) χ2 48.678 15.688 10.149 5.336 P < 0.001 < 0.001 0.001 0.021 注: 轻度狭窄、中度狭窄、重度狭窄和完全闭塞作为等级资料, 视为一个整体, 行秩和检验, Z=50.294, P < 0.001. 表 3 两组颈部血管彩超对颈动脉粥样硬化斑块检出率的比较
Table 3. Comparison of the detection rate of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by carotid duplex ultrasound between the two groups [n (%)]
组别 颈动脉粥样硬化斑块 稳定型斑块 不稳定型斑块 观察组(n=106) 38(35.85) 68(64.15) 对照组(n=53) 30(56.60) 23(43.40) χ2 6.218 P 0.013 表 4 两组TCD对椎-基底动脉狭窄检出率的比较
Table 4. Comparison of the detection rate of vertebrobasilar artery stenosis by TCD between the two groups [n(%)]
组别 椎-基底动脉狭窄 轻度狭窄 中度狭窄 重度狭窄 完全闭塞 观察组(n=106) 31(29.25) 40(37.74) 23(21.70) 12(11.31) 对照组(n=53) 42(79.25) 11(20.75) 0(0) 0(0) χ2 35.571 4.676 13.445 6.490 P < 0.001 0.031 < 0.001 0.011 注: 轻度狭窄、中度狭窄、重度狭窄和完全闭塞作为等级资料, 视为一个整体, 行的秩和检验, Z=39.916, P < 0.001. 表 5 颈部血管彩超联合TCD与脑血管造影对动脉狭窄检出的一致性
Table 5. Consistency of carotid duplex ultrasound with TCD and cerebral angiography in the detection of arterial stenosis
方法 脑血管造影 合计 中重度以上狭窄 轻度狭窄 颈部血管彩超联合TCD 中重度以上狭窄 75 3 78 轻度狭窄 5 23 28 合计 80 26 106 注: 颈动脉、椎基底动脉任意1条及以上动脉存在中重度以上狭窄. 表 6 颈部血管彩超联合TCD与脑血管造影对动脉斑块检出的一致性
Table 6. Consistency of carotid duplex ultrasound with TCD and cerebral angiography in the detection of arterial plaques
方法 脑血管造影 合计 不稳定型斑块 稳定型斑块 颈部血管彩超联合TCD 不稳定型斑块 64 4 68 稳定型斑块 9 29 38 合计 73 33 106 -
[1] Luo L, Zhu ML, Zhou JJ. Association between CTSS gene polymorphism and the risk of acute atherosclerotic cerebral infarction in Chinese population: a case-control study[J]. Biosci Rep, 2018, 38(6): 586. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30341237 [2] Hayashi K, Uekawa K, Kawano T, et al. Cortical venous reddening predicts remote cerebral infarction post superficial temporal arterymiddle cerebral artery bypass in atherosclerotic occlusive cerebrovascular disease[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 127: e864-72. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.03.287 [3] 杨瑞芳, 阴彦龙, 杨敏清, 等. 基质金属蛋白酶与动脉粥样硬化及斑块破裂的关系[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2017, 40(4): 482-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4500.2017.04.25 [4] Li JQ, Wu HQ, Hao Y, et al. Unstable carotid plaque is associated with coagulation function and platelet activity evaluated by thrombelastography[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2019, 28(11): 104336. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.104336 [5] Snelling BM, Sur S, Shah SS, et al. Transradial cerebral angiography: techniques and outcomes[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2018, 10(9): 874- 81. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2017-013584 [6] Alakbarzade V, Pereira AC. Cerebral catheter angiography and its complications[J]. Pract Neurol, 2018, 18(5): 393-8. doi: 10.1136/practneurol-2018-001986 [7] Yılmaz C, Gorgulu FF, Oksuzler FY, et al. Color Doppler ultrasonography is a reliable diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of extracranial vertebral artery dissections[J]. J Med Ultrason: 2001, 2019, 46(1): 153-8. doi: 10.1007/s10396-018-0901-2 [8] Blanco P, Abdo-Cuza A. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound in neurocritical care[J]. J Ultrasound, 2018, 21(1): 1-16. doi: 10.1007/s40477-018-0282-9 [9] 高长玉, 吴成翰, 赵建国, 等. 中国脑梗死中西医结合诊治指南(2017) [J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2018, 38(2): 136-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXJ201802003.htm [10] Dharmakidari S, Bhattacharya P, Chaturvedi S. Carotid artery Stenosis: medical therapy, surgery, and stenting[J]. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 2017, 17(10): 77. doi: 10.1007/s11910-017-0786-2 [11] Zhou Y, Wang L, Zhang JR, et al. Angioplasty and stenting for severe symptomatic atherosclerotic Stenosis of intracranial vertebrobasilar artery[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2019, 63: 17-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2019.02.017 [12] Zhang JY, Tang Y, Shi Y, et al. Research progress of low/high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and carotid artery unstable plaque[J]. Chin J Neur, 2019, 18(2): 189-93. [13] Wang F, Hu XY, Wang T, et al. Clinical and imaging features of vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia combined with posterior circulation infarction: a retrospective case series study[J]. Medicine, 2018, 97 (48): e13166. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013166 [14] 王淑清, 龚丽娜, 颜明. 彩色多普勒及经颅多普勒在颈动脉粥样硬化与脑梗死相关性研究中的联合应用[J]. 中国医学装备, 2018, 15 (12): 85-9. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2018.12.022 [15] 赵月晨. 颈部血管彩超联合DSA对动脉粥样硬化性脑梗死的诊断价值[J]]. 慢性病学杂志, 2019, 20(9): 1413-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSO201909051.htm [16] 臧艳芳, 袁振林, 董军见, 等. 超声、CT血管造影在诊断颈动脉粥样硬化斑块中的应用价值[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2020, 18(5): 92-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2020.05.029 [17] 翟江玉, 陆青卫. 经颅彩色多普勒超声血流参数对短暂性脑缺血发作患者颈动脉狭窄的诊断价值[J]. 影像科学与光化学, 2020, 38(4): 632-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GKGH202004007.htm [18] Spence JD. Transcranial Doppler emboli identifies asymptomatic carotid patients at high stroke risk: why this technique should be used more widely[J]. Angiology, 2017, 68(8): 657-60. doi: 10.1177/0003319716651525 [19] Chi HY, Chen KW, Hsu CF, et al. Ultrasound findings disclose the mutual impact of vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia and vertebral artery hypoplasia[J]. J Ultrasound Med, 2019, 38(11): 3037-42. doi: 10.1002/jum.15011 [20] Gunabushanam G, Kummant L, Scoutt LM. Vertebral artery ultrasound[J]. Radiol Clin NorthAm, 2019, 57(3): 519-33. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2019.01.011 [21] Magenta A, Sileno S, D'Agostino M, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque instability in carotid arteries: miR-200c as a promising biomarker [J]. Clin Sci: Lond, 2018, 132(22): 2423-36. doi: 10.1042/CS20180684 -






 下载:
下载: