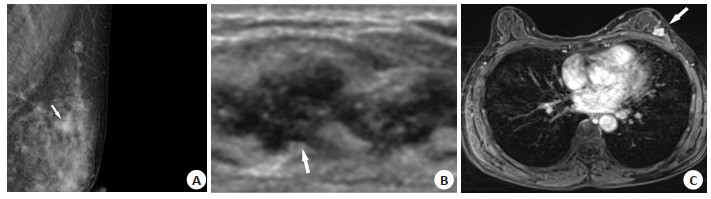
Comparation of diagnosis value of ultrasound, conventional mammography and dynamic in breast lesions with calcification categorized 3-5
-
摘要:
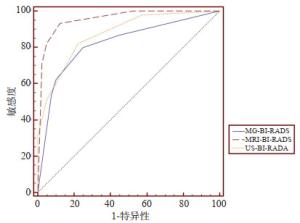
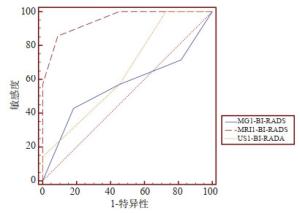
目的比较常规超声、常规乳腺X线摄影(MG)及动态增强磁共振(DCE-MRI)对乳腺BI-RADS 3~5类钙化性病变的诊断效能。 方法回顾性分析2010年1月~2019年2月同时完成超声、MG和MRI的82例患者共85个含钙化原发初治病灶,与病理结果为诊断金标准,计算其敏感度、特异性、准确性、阳性预测值及阴性预测值,比较三者之间的诊断效能;并根据超声和MG BI-RADS评估将病灶分为一致组和不一致组,计算3种乳腺影像学检查方法的曲线下面积,分析总体组和不一致组的诊断效能。 结果MG、超声和DCE-MRI在诊断乳腺BI-RADS 3~5类钙化性病变的敏感性、特异性、准确性、阳性预测值与阴性预测值分别为80.0% vs 82.2% vs 93.3%、75.0% vs 77.5% vs 87.5%、77.6% vs 80.0% vs 90.6%、78.3% vs 80.4% vs 89.4%、77.0% vs 79.5% vs 92.1%,诊断价值差异有统计学意义(P=0.022、0.019)。MG和超声的曲线下面积在总体组和不一致组分别为0.821、0.565和0.872、0.649,而DCE-MRI对应值分别为0.956和0.948,明显优于MG和超声(P < 0.05)。 结论DCE-MRI在鉴别诊断乳腺BI-RDAS 3~5类钙化性病变方面优于MG和超声,尤其是当二者出现不同诊断意见时。 Abstract:ObjectiveTo compare the efficacy of conventional ultrasound (US), conventional mammography (MG) and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) in the diagnosis of breast lesions with calcification categorized 3-5. MethodsBetween January 2010 and February 2019, a total of 85 untreated breast lesions with calcification from 82 patients who underwent US, MG and MRI at the same time were retrospectively analyzed. All the lesions were confirmed by histopathological assessment. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value and negative predictive value were evaluated, and the diagnostic value of the three modalities were compared. Lesions were divided into consistent or inconsistent group on the basis of BI-RADS MG and US assessment. The diagnostic efficacy of three methods in the overall and inconsistent group were assessed by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. ResultsThe sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of MG, US and MRI in the diagnosis of breast lesions with calcification were 80.0% vs 82.2% vs 93.3%、75.0% vs 77.5% vs 87.5%、77.6% vs 80.0% vs 90.6%、78.3% vs 80.4% vs 89.4%、77.0% vs 79.5% vs 92.1%, respectively, with significant difference (P=0.022、0.019). The AUCs of MG and US were 0.821, 0.872 for overall group and 0.565, 0.649 for inconsistent group. The corresponding values of MRI were 0.956 and 0.948, which were significantly prior to those of MG and US (P < 0.05). ConclusionThe DCE-MRI has a better diagnostic efficiency than MG or US alone in the differentiation of the breast lesions with calcification especially when disagreement occurred. -
表 1 三种检查方法对乳腺BI-RADS 3~5类钙化性病变的诊断情况
Table 1. Diagnosis of breast lesions with calcification categorized 3-5 by three methods
检查方法 病理结果 良性 恶性 超声 良性 31 8 恶性 9 37 DCD-MRI 良性 35 3 恶性 5 42 MG 良性 30 9 恶性 10 36 表 2 三种乳腺影像学检查方法的诊断效能
Table 2. Diagnostic performance of the three modalities in differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions with calcification
检查方法 敏感度(%) 特异性(%) 准确率(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) 诊断符合率 总体组AUC 不一致组AUC 一致组 不一致组 MG 80.0 75.0 77.6 78.3 77.0 0.821 0.565 58/67 8/18 超声 82.2 77.5 80.0 80.4 79.5 0.872 0.649 10/18 DCE-MRI 93.3 87.5 90.6 89.4 92.1 0.956 0.948 61/67 16/18 P* - – 0.019 – – 0.0021 0.0108 – – P# - – 0.022 – – 0.0054 0.0079 – – P*: MRI vs MG; P#: MRI vs超声; MG: 常规乳腺X线摄影; DCE-MRI: 动态增强磁共振; AUC: 曲线下面积. 表 3 三种检查方法的BI-RADS分类与病理结果对照
Table 3. Comparison of scores of the three modalities with pathology results
乳腺分级 US-BI-RADS US-BI-RADS US-BI-RADS n 病理结果 符合率(%) n 病理结果 符合率(%) n 病理结果 符合率(%) (-) (+) (-) (+) (-) (+) 3 18 17 1 94.4 19 19 0 100.0 28 22 6 78.6 4A 21 14 7 66.7 19 16 3 84.2 11 8 3 72.7 4B 18 7 11 61.1 8 3 5 62.5 14 6 8 57.1 4C 11 2 9 81.8 6 1 5 83.3 5 1 4 80.0 5 17 0 17 100.0 33 1 32 97.0 27 3 24 88.9 表 4 null致组与不一致组的分布
Table 4. Distribution of consistent and inconsistent results of mammography and conventional US in benign and malignant categories
因素 良性 恶性 MG与超声诊断不一致时 11 7 MG≥4B且超声≤4A 6 3 超声≥4B且MG≤4A 5 4 MG与超声诊断一致时 29 38 BI-RADS≤4A 25 5 BI-RADS≥4B 4 33 -
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590 [2] Tong WJ, Zhang XL, Luo J, et al. Value of multimodality imaging in the diagnosis of breast lesions with calcification: a retrospective study[J]. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc, 2020, 76(1): 85-98. doi: 10.3233/CH-200877 [3] Rao AA, Feneis J, Lalonde C, et al. A pictorial review of changes in the BI-RADS fifth edition[J]. Radiographics, 2016, 36(3): 623-39. doi: 10.1148/rg.2016150178 [4] Xiao XY, Dong LC, Jiang QC, et al. Incorporating contrast-enhanced ultrasound into the BI-RADS scoring system improves accuracy in breast tumor diagnosis: a preliminary study in China[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2016, 42(11): 2630-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2016.07.005 [5] 曲玉虹, 陈倩倩, 曹崑. 对比增强能谱乳腺X线摄影的临床应用及进展[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2019, 35(4): 511-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201904011.htm [6] Li EN, Li J, Song Y, et al. A comparative study of the diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced breast MR imaging and mammography on patients with BI-RADS 3-5 microcalcifications[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(11): e111217. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111217. [7] del Carmen MG, Hughes KS, Halpern E, et al. Racial differences in mammographic breast density[J]. Cancer, 2003, 98(3): 590-6. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11517 [8] 钟树兴, 郭红梅, 洪晓纯, 等. 乳腺超声成像与钼靶在检出乳腺肿块微钙化中的临床价值分析[J]. 中国医学创新, 2019, 16(12): 143-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2019.12.037 [9] Baltzer PAT, Bennani-Baiti B, Stöttinger A, et al. Is breast MRI a helpful additional diagnostic test in suspicious mammographic microcalcifications?[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2018, 46: 70-4. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.10.012 [10] Brnic D, Brnic D, Simundic I, et al. MRI and comparison mammography: a worthy diagnostic alliance for breast microcalcifications?[J]. Acta Radiol, 2016, 57(4): 413-21. doi: 10.1177/0284185115585036 [11] 刘丽珍, 刘建新, 赖伟, 等. 钼靶X线、MRI动态增强联合高频彩超对含钙化灶乳腺良恶性病变的诊断价值分析[J]. 包头医学院学报, 2019, 35(4): 19-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BTYX201904008.htm [12] Shimauchi A, Machida Y, Maeda I, et al. Breast MRI as a problemsolving study in the evaluation of BI-RADS categories 3 and 4 microcalcifications: is it worth performing?[J]. Acad Radiol, 2018, 25(3): 288-96. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2017.10.003 [13] Eun NL, Son EJ, Gweon HM, et al. The value of breast MRI for BIRADS category 4B mammographic microcalcification: based on the 5th edition of BI-RADS[J]. Clin Radiol, 2018, 73(8): 750-5. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2018.04.014 [14] Linda, Zuiani C, Londero V, et al. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in probably benign (BI-RADS category 3) microcalcifications of the breast[J]. Radiol Med, 2014, 119(6): 393-9. doi: 10.1007/s11547-013-0361-0 [15] 宋丽君, 张家君, 卢川. 乳腺影像报告与数据系统临床应用进展[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2017, 33(11): 1728-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201711044.htm [16] Xu P, Yang M, Liu Y, et al. Breast non-mass-like lesions on contrastenhanced ultrasonography: Feature analysis, breast image reporting and data system classification assessment[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2020, 8(4): 700-12. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i4.700 [17] 隋旭蕾, 唐小锋. 数字化乳腺摄影评价无肿块型乳腺癌微钙化的研究进展[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2018, 28(1): 148-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ201801046.htm [18] Kolb TM, Lichy J, Newhouse JH. Comparison of the performance of screening mammography, physical examination, and breast US and evaluation of factors that influence them: an analysis of 27, 825 patient evaluations[J]. Radiology, 2002, 225(1): 165-75. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2251011667 [19] Bok SK, Jeon Y, Hwang PS. Ultrasonographic evaluation of the effects of progressive resistive exercise in breast cancer-related lymphedema[J]. Lymphat Res Biol, 2016, 14(1): 18-24. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2015.0021 [20] Henrot P, Leroux A, Barlier C, et al. Breast microcalcifications: the lesions in anatomical pathology[J]. Diagn Interv Imaging, 2014, 95 (2): 141-52. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2013.12.011 [21] 张家庭, 李泉水, 李征毅, 等. 乳腺良恶性钙化的声像学特征分析[J]. 中华医学超声杂志: 电子版, 2007, 4(4): 234-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6448.2007.04.014 [22] Kettenbach J, Helbich TH, Huber S, et al. Computer-assisted quantitative assessment of power Doppler US: effects of microbubble contrast agent in the differentiation of breast tumors[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2005, 53(2): 238-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.04.017 [23] 左稳, 韩文彬, 陈竹碧, 等. MRI动态增强成像联合扩散加权成像在乳腺癌术前诊断应用价值[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2018, 16(7): 36-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2018.07.012 [24] 周阳阳, 石太峰, 侯卓, 等. 磁共振动态对比增强联合弥散加权成像对乳腺癌的诊断价值[J]. 江苏医药, 2017, 43(15): 1090-2. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YIYA201715010.htm [25] Agrawal G, Su MY, Nalcioglu O, et al. Significance of breast lesion descriptors in the ACR BI-RADS MRI lexicon[J]. Cancer, 2009, 115 (7): 1363-80. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24156 [26] 余涛, 王聪, 凌洪. MRI动态增强扫描对乳腺钼靶摄影中含簇状钙化灶良恶性病变的诊断鉴别价值[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2020, 18 (5): 122-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2020.05.038 [27] Pinker K, Helbich TH, Morris EA. The potential of multiparametric MRI of the breast[J]. Br J Radiol, 2017, 90(1069): 20160715. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160715 [28] Hovanessian Larsen LJ, Peyvandi B, Klipfel N, et al. Granulomatous lobular mastitis: imaging, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2009, 193(2): 574-81. doi: 10.2214/AJR.08.1528 [29] AlSharif S, Tremblay F, Omeroglu A, et al. Infiltrating syringomatous adenoma of the nipple: Sonographic and mammographic features with pathologic correlation[J]. J Clin Ultrasound, 2014, 42(7): 427-9. doi: 10.1002/jcu.22150 [30] Xiao XY, Jiang QC, Wu H, et al. Diagnosis of sub-centimetre breast lesions: combining BI-RADS-US with strain elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound- a preliminary study in China[J]. Eur Radiol, 2017, 27(6): 2443-50. doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4628-4 -






 下载:
下载: