Comparation of diagnostic value of CESM and conventional mammography in breast benign and malignant diseases
-
摘要:
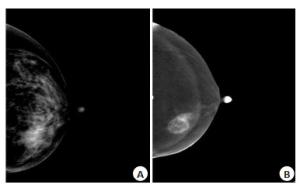
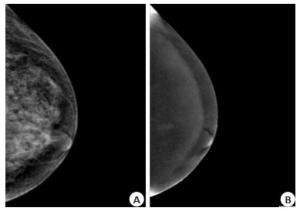
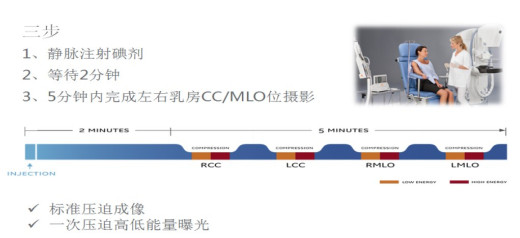
目的探讨比较常规乳腺X线摄影(MG)与对比增强乳腺能谱摄影(CESM)对乳腺良恶性疾病的诊断价值。 方法对2018年5月~2020年4月同时完成CESM和MG检查并最终获得病理诊断的74例患者纳入研究,均为女性,年龄22~56岁(41.02±8.24岁)。采用Stenographe Essential全数字化乳腺机,经由上肢静脉注射碘对比剂后采用头尾位(CC位)和内外斜位(MLO位),一次压迫高低能曝光,得到低能图像和经过特定算法处理的高能减去低能的减影图像,由3名放射科乳腺专业医师对所得图像进行质量分析并做出影像学诊断,以病理为标准,比较CESM与MG对乳腺良恶性疾病诊断差异,并进一步对比两种方法诊断为同一肿瘤分级的诊断符合率差异,分析比较两种方法的诊断效。 结果共40例乳腺恶性肿瘤、42例良性病变。MG在诊断良恶性病变的灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值、阴性预测值及准确率分别为77.50%、80.95%、79.48%、70.27%及79.07%,而CESM的灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值、阴性预测值及准确率分别为100%、90.47%、90.90%、100%及95.12%(P < 0.05)。MG在诊断乳腺肿瘤分级3~5级中的诊断符合率分别为79.00%、66.70%、86.70%、85.70%及100%,CESM为100%、92.30%、87.50%、90%及100%(P < 0.05)。 结论CESM诊断乳腺良恶性疾病优于MG,尤其是在诊断3级及4A级的肿瘤中。 -
关键词:
- 对比增强乳腺能谱摄影 /
- 乳腺摄影 /
- 乳腺良恶性疾病
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the diagnostic value of comparing conventional mammography (MG) and contrastenhanced spectralmammography (CESM) for benign and malignantbreast diseases, using pathological results as the gold standard. MethodsSeventy-four patients who completed CESM and MG tests and obtained pathological diagnosis from May 2018 to April 2020 were included in the study. All patients were female, aged 22-56 years, with an average age of 41.02±8.24 years old. Using the American GE Stenographe Essential fully digital mammary gland machine, through the upper limb after intravenous injection of iodine contrast agent USES the end (CC) and internal and external oblique (MLO), by a pressure high and low to exposure, we obtain low energy image and subtraction angiography image of high energy subtracting low energy by special algorithm. Three radiology breast specialist performed quality analysis of the images and made imaging diagnosis. Taking pathology as the standard, the difference in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases between cesm and Mg was compared, and the diagnostic coincidence rate of the two methods for the same tumor grade was further compared, and the diagnostic efficacy of the two methods was analyzed and compared. ResultsThe sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy of MG in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions were 77.50%, 80.95%, 79.48%, 70.27% and 79.07%, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy of CESM were 100%, 90.47%, 90.90%, 100% and 95.12% respectively (P < 0.05). In the study, the diagnostic coincidence rate of MG in grade 3-5 breast tumor grade was 79.00%, 66.70%, 86.70%, 85.70% and 100% respectively, while CESM was 100%, 92.30%, 87.50%, 90% and 100% (P < 0.05). ConclusionCESM is superior to conventional mammography in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases, especially in the diagnosis of grade 3and 4A tumors. -
表 1 对照病理CESM与MG对乳腺良恶性疾病的诊断结果(n)
Table 1. Comparison of pathological CESM and MG in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases
项目 病理诊断为恶性 病理诊断为良性 MG 合计 MG 合计 恶性(+) 良性(-) 恶性(+) 良性(-) CESM 恶性(+) 31 9 40 4 0 4 良性(-) 0 0 0 4 34 38 合计 31 9 40 8 34 42 MG: Mammography; CESM: Contrast-enhanced spectralmammography. 表 2 CESM与MG对乳腺良恶性疾病的诊断效能对比(%)
Table 2. Comparison of CESM and MG in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases
检查方法 敏感度 特异度 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 诊断符合率 CESM 100.00 90.47 90.90 100.00 95.12 MG 77.50 80.95 79.48 70.27 79.07 表 3 对照病理CESM与MG对乳腺肿瘤的分级对比(n)
Table 3. Comparison of breast tumor grade between pathological CESM and MG
MG-BI-RADS CESM-BI-RADS 病理结果 良性(n=42) 恶性(n=40) 3(n=43) 3(n=34) 34 9 4A(n=5) 4B(n=4) 4A(n=15) 3(n=3) 5 10 4A(n=5) 4B(n=6) 4C(n=1) 4B(n=15) 3(n=1) 2 13 4A(n=3) 4B(n=8) 4C(n=1) 5(n=1) 4C(n=7) 3(n=0) 1 6 4A(n=1) 4B(n=3) 4C(n=1) 5(n=2) 5(n=2) 5(n=2) 0 2 表 4 CESM与MG对乳腺肿瘤的分级效能对比
Table 4. Comparison of CESM and MG for grading efficacy of breast tumors
乳腺分级 MG CESM n 病理结果 符合率(%) n 病理结果 符合率(%) - + - + 3 43 34 9 79.07 38 38 0 100.00 4A 15 5 10 66.67 13 1 12 92.31 4B 15 2 13 86.67 16 2 14 87.50 4C 7 1 6 85.71 10 1 9 90.00 5 2 0 2 100.00 5 0 5 100.00 -
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590 [2] DeSantis CE, Fedewa SA, Goding Sauer A, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2015: Convergence of incidence rates between black and white women[J]. CACancer J Clin, 2016, 66(1): 31-42. doi: 10.3322/caac.21320 [3] 曲玉虹, 陈倩倩, 曹崑.对比增强能谱乳腺X线摄影的临床应用及进展[J].中国医学影像技术, 2019, 35(4): 511-4. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZYXX201904011.htm [4] Lobbes MB, Smidt ML, Houwers J, et al. Contrast enhanced mammography: techniques, current results, and potential indications [J]. Clin Radiol, 2013, 68(9): 935-44. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2013.04.009 [5] Daniaux M, De Zordo T, Santner W, et al. Dual-energy contrastenhanced spectral mammography (CESM)[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2015, 292(4): 739-47. doi: 10.1007/s00404-015-3693-2 [6] 宋丽君, 张家君, 卢川.乳腺影像报告与数据系统临床应用进展[J].中国医学影像技术, 2017, 33(11): 1728-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZYXX201711044.htm [7] 张承中, 王庆国, 王建丰, 等.对比增强能谱乳腺X线摄影在诊断乳腺癌中的可行性研究[J].放射学实践, 2014, 29(12): 1420-3. [8] Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, et al. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis: correlation in invasive breast carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 1991, 324(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101 [9] Fallenberg EM, Dromain C, Diekmann F, et al. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography versus MRI: Initial results in the detection of breast cancer and assessment of tumour size[J]. Eur Radiol, 2014, 24(1): 256-64. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-3007-7 [10] Ursin G, Ma HY, Wu AH, et al. Mammographic density and breast cancer in three ethnic groups[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2003, 12(4): 332-8. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12692108/ [11] 杨柳, 李白艳, 郑欢露, 等.增强能谱乳腺摄影与MRI诊断乳腺癌效能比较: Meta分析[J].中国医学影像技术, 2019, 35(7): 1038-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZYXX201907026.htm [12] Lee-Felker SA, Tekchandani L, Thomas M, et al. Newly diagnosed breast cancer: comparison of contrast-enhanced spectral mammography and breast MR imaging in the evaluation of extent of disease[J]. Radiology, 2017, 285(2): 389-400. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017161592 [13] Hobbs MM, Taylor DB, Buzynski S, et al. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM) and contrast enhanced MRI (CEMRI): Patient preferences and tolerance[J]. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol, 2015, 59(3): 300-5. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.12296 [14] Lalji UC, Houben IPL, Prevos R, et al. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography in recalls from the Dutch breast cancer screening program: validation of results in a large multireader, multicase study [J]. Eur Radiol, 2016, 26(12): 4371-9. doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4336-0 [15] Richter V, Hatterman V, Preibsch H, et al. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography in patients with MRI contraindications[J]. Acta Radiol, 2018, 59(7): 798-805. doi: 10.1177/0284185117735561 [16] Patel BK, Lobbes MBI, Lewin J. Contrast enhanced spectral mammography: a review[J]. Semin Ultrasound CT MR, 2018, 39 (1): 70-9. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2017.08.005 [17] Savaridas SL, Taylor DB, Gunawardana D, et al. Could parenchymal enhancement on contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM) represent a new breast cancer risk factor? Correlation with known radiology risk factors[J]. Clin Radiol, 2017, 72(12): 1085. e1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2017.07.017 [18] Dromain C, Thibault F, Diekmann F, et al. Dual-energy contrastenhanced digital mammography: initial clinical results of a multireader, multicase study[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2012, 14(3): R94. doi: 10.1186/bcr3210 [19] Yaffe MJ, Mainprize JG. Risk of radiation-induced breast cancer from mammographic screening[J]. Radiology, 2011, 258(1): 98-105. doi: 10.1148/radiol.10100655 [20] Jong RA, Yaffe MJ, Skarpathiotakis M, et al. Contrast-enhanced digital mammography: initial clinical experience[J]. Radiology, 2003, 228(3): 842-50. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2283020961 -







 下载:
下载: