Application value of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of fresh rib fractures by physicians
-
摘要:
目的 探讨人工智能(AI)软件对放射科住院医师、主治医师在新鲜肋骨骨折病灶检出率的差异及其应用AI前后的一致性评价,评估应用AI后各级医师诊断新鲜肋骨骨折效能的提高情况。 方法 收集因急性胸部外伤行胸部CT扫描病例300例,其中确诊为肋骨骨折的152例病例。将6位医师分为住院医师组和主治医师组两组,3人/组,对随机分配的300例CT图像独立阅片。在间隔为4周的洗脱期后,医师结合AI第2次阅片。采用卡方检验比较两组医师对新鲜肋骨骨折病灶及不同类型病灶检出率的差异,并评价各组应用AI前后的一致性、敏感度、特异度差异。 结果 应用AI后住院医师、主治医师对所有新鲜肋骨骨折、完全性骨折、不完全性骨折的检出率均高于医师单独阅片,差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。住院医师+AI、主治医师+AI对全部肋骨骨折、不完全性骨折的Kappa值与Phi系数均明显提高,不完全性骨折提高幅度最显著。住院医师+AI、主治医师+AI检出新鲜肋骨骨折敏感度与住院医师、主治医师单独阅片的差异有统计学意义(P<0.001),特异度的差异无统计学意义。 结论 AI可有效提高不同级别医师对新鲜肋骨骨折的检出效能,并提高不同级别医师之间的一致性、敏感度。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the difference of detection rate of fresh rib fracture lesions between radiology residents and attending physicians by artificial intelligence (AI) software and the consistency evaluation before and after application of AI, and to evaluate the improvement of efficiency of doctors at all levels in diagnosing fresh rib fractures after applying AI. Methods A total of 300 patients with acute chest trauma underwent chest CT scan, 152 of which were confirmed to be rib fracture. 6 physicians were divided into resident physician group and attending physician group, with three physicians in each. 300 randomly assigned CT images were reviewed independently. After the washout interval of 4 weeks, the physicians combined with AI read the film for second time. Chi-square test was used to compare the difference in the detection rate of fresh rib fracture lesions and different types of lesions between the two groups, and to evaluate the difference in consistency, sensitivity and specificity before and after the application of AI in each group. Results After applying AI, the detection rate of all fresh rib fractures, complete fractures and incomplete fractures by residents and attending physicians was higher than that by physicians alone, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.001). The Kappa values and Phi coefficients of all rib fractures and incomplete fractures were significantly improved by residents + AI and attending physicians + AI, and the improvement of incomplete fractures was the most significant. The sensitivity of fresh rib fractures detected by residents+AI, attending physicians+AI were significantly different from that by residents and attending physicians alone (P<0.001), there was no significant difference in specificity. Conclusion AI can effectively improve the detection efficiency of fresh rib fractures among physicians of different levels, and improve the consistency and sensitivity among physicians of different levels. -
Key words:
- artificial intelligence /
- fresh rib fracture /
- computer tomography
-
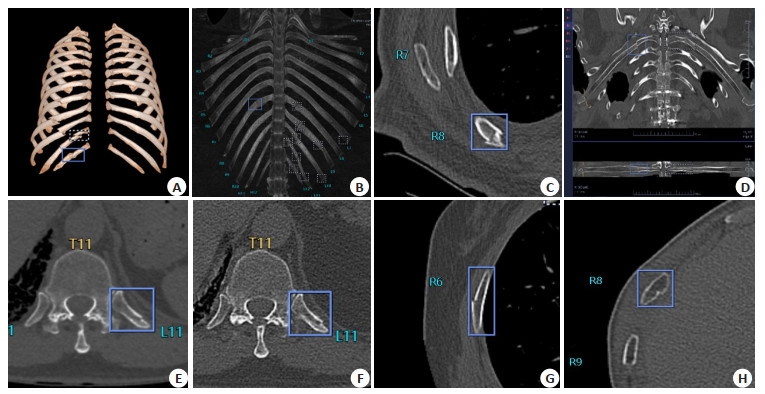
图 1 AI自动生成的患者VR图像(A)、全肋肋骨骨折标记(B)及单肋肋骨骨折标记(C~H)
Figure 1. AI automatically generated patient VR images (A), whole rib fracture markers (B) and single rib fracture markers (C-H). A: The quality of VR image automatically generated by AI is better than manual 3D reconstruction. The blue box marks the complete fracture of the left 12th rib; B: AI-labeled complete rib fracture analysis, the blue frame for the right 8th posterior rib complete fracture; C: The AI-labeled rib fracture results interface shows the AI blue box marking the complete fracture of the right 8th posterior rib, with the fracture line penetrating through all the bone cortex; D: The single-rib analysis of AI is a multi-angle rotation and straightening analysis of the single rib of the right post-eighth rib fracture; E: A case of incomplete fracture of the left 11th posterior rib with linear low-density fracture on the medial margin of the cortical bone; F: One month later, the bone density of the fracture site increased and callus formed; G-H shows incomplete fractures missed by all physicians, with AI marked in blue boxes; G: A typical incomplete fracture; H: The medial margin of the cortical bone is slightly concave.
表 1 不同组对不同类型骨折的检出情况
Table 1. Detection of different types of fractures in different groups
Method Complete rib fractures Incomplete rib fractures All fractures True- positive False-positive False-negative True- positive False-positive False-negative True- positive False-positive False-negative AI 152 2 0 363 77 5 515 79 5 GS 161 0 0 370 1 0 531 1 0 RP 141 0 20 204 1 166 345 1 186 RP+AI 159 0 2 328 0 42 487 0 44 AP 135 0 26 206 0 164 341 0 190 AP+AI 160 0 1 332 0 38 492 0 39 GS: Gold standard; RP: Resident physician; AI: Artificial intelligence; AP: Attending physician. 表 2 不同类型肋骨骨折的检出率
Table 2. The detection rate of different types of rib fractures
Types of fractures Resident physician Resident physician+AI P Attending physician Attending physician +AI P Total 64.97 91.71 <0.001 64.21 92.66 <0.001 Completeness 87.58 98.76 <0.001 83.85 99.38 <0.001 Incompleteness 55.14 88.65 <0.001 55.68 89.73 <0.001 表 3 住院医师与主治医师的诊断结果之间的关联性
Table 3. The correlation between the diagnostic results of resident physicians and attending physicians
RP vs AP Kappa Degree of consistency Phi coefficient Degree of correlation Total 0.401 Moderate 0.401 Moderate completeness 0.611 Good 0.622 Good Incompleteness 0.287 Poor 0.287 Poor 表 4 住院医师+AI与主治医师+AI诊断结果之间的关联性
Table 4. The correlation between resident physicians, AIVS attending physicians, and AI diagnostic results
RP+AI vs AP+AI Kappa Degree of consistency Phi coefficient Degree of correlation Total 0.554 Moderate 0.554 Moderate completeness 0.66 Good 0.66 Good Incompleteness 0.54 Moderate 0.54 Moderate 表 5 住院医师、主治医师应用AI后检出新鲜肋骨骨折病灶敏感度、特异度
Table 5. Sensitivity and specificity of detecting fresh rib fracture lesions using AI by resident physicians and attending physicians (n)
Method Result GS Total Positive Negative RP Positive 124 11 135 Negative 24 141 165 Total 148 152 300 RP+AI Positive 148 2 150 Negative 1 149 150 Total 149 151 300 AP Positive 122 8 130 Negative 26 144 170 Total 148 152 300 AP+AI Positive 147 2 149 Negative 1 150 151 Total 148 152 300 -
[1] 刘基, 尹婷婷, 王康, 等. DR与CT三维重建在胸部外伤骨折中的诊断意义[J]. 中华肺部疾病杂志: 电子版, 2022, 15(1): 105-7. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-6902.2022.01.031 [2] Sharma OP, Oswanski MF, Jolly S, et al. Perils of rib fractures[J]. Am Surg, 2008, 74(4): 310-4. doi: 10.1177/000313480807400406 [3] 张光霞, 何英, 杨绍光, 等. 司法鉴定中肋骨骨折影像诊断符合率影响因素的研究[J]. 中国医药科学, 2022, 12(20): 24-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYKX202220006.htm [4] 赵润润, 苏宜江, 于一龙, 等. 胸部外伤手术107例临床分析[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2015, 22(7): 707-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXYX201507023.htm [5] Bemelman M, de Kruijf MW, van Baal M, et al. Rib fractures: to fix or not to fix? an evidence-based algorithm[J]. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2017, 50(4): 229-34. doi: 10.5090/kjtcs.2017.50.4.229 [6] Chapman BC, Overbey DM, Tesfalidet F, et al. Clinical utility of chest computed tomography in patients with rib fractures CT chest and rib fractures[J]. Arch Trauma Res, 2016, 5(4): e37070. [7] England JR, Cheng PM. Artificial intelligence for medical image analysis: a guide for authors and reviewers[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2019, 212(3): 513-9. doi: 10.2214/AJR.18.20490 [8] 孟祥虹, 吴迪嘉, 马信龙, 等. 深度卷积神经网络技术自动诊断肋骨骨折的CT应用初探[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2022, 28(2): 205-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYK202202019.htm [9] Zhou QQ, Wang JS, Tang W, et al. Automatic detection and classification of rib fractures on thoracic CT using convolutional neural network: accuracy and feasibility[J]. Korean J Radiol, 2020, 21(7): 869-79. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0651 [10] 刘想, 谢辉辉, 许玉峰, 等. 人工智能对提高放射科住院医生诊断胸部肋骨骨折一致性的价值[J]. 北京大学学报: 医学版, 2023, 55(4): 670-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BYDB202304017.htm [11] 杨力, 蒲红, 朱缨. MSCT扫描及三维重建技术在降低隐匿性骨折漏诊率中的临床应用[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2017, 15(7): 137-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR201707043.htm [12] 余开冠, 孙芳仁. MSCT与DR检查外伤性肋骨骨折的临床应用对比分析[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2022, 32(7): 1260-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ202207043.htm [13] Guermazi A, Tannoury C, Kompel AJ, et al. Improving radiographic fracture recognition performance and efficiency using artificial intelligence[J]. Radiology, 2022, 302(3): 627-36. doi: 10.1148/radiol.210937 [14] 谭辉, 田占雨, 潘宁, 等. 基于深度学习的计算机辅助诊断系统在提高急性肋骨骨折诊断效能上的价值[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2020, 39(12): 2493-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS202012031.htm [15] Meng XH, Wu DJ, Wang Z, et al. A fully automated rib fracture detection system on chest CT images and its impact on radiologist performance[J]. Skeletal Radiol, 2021, 50(9): 1821-8. [16] Zhou ZY, Fu ZH, Jia JC, et al. Rib fracture detection with dual-attention enhanced U-net[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2022, 2022: 8945423. [17] Niiya A, Murakami K, Kobayashi R, et al. Development of an artificial intelligence-assisted computed tomography diagnosis technology for rib fracture and evaluation of its clinical usefulness[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 8363. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12453-5 [18] 萧毅, 刘士远. 人工智能将改变影像医学的未来[J]. 科技与金融, 2018(10): 11-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJJR201810009.htm [19] 程齐, 欧阳雪晖. 人工智能在影像医学中的实际应用[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2023, 46(3): 571-4. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2023.03.34 [20] Cohen M, Puntonet J, Sanchez J, 等. 人工智能与放射科医生: X线片上手腕骨折的诊断效能[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志, 2023, 46(4): 493. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWLC202304072.htm -







 下载:
下载: