Value of B-flow and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in the imaging of synovial blood flow of small joints of wrist and hand in rheumatoid arthritis
-
摘要:
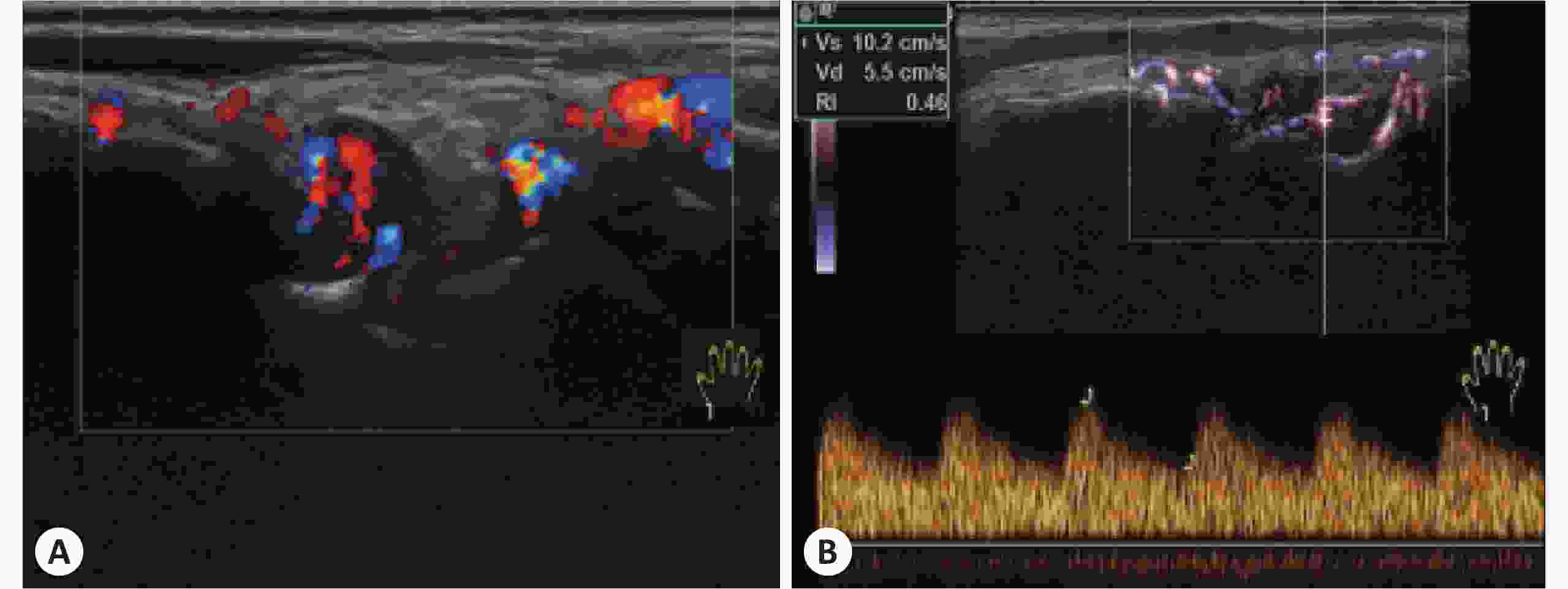
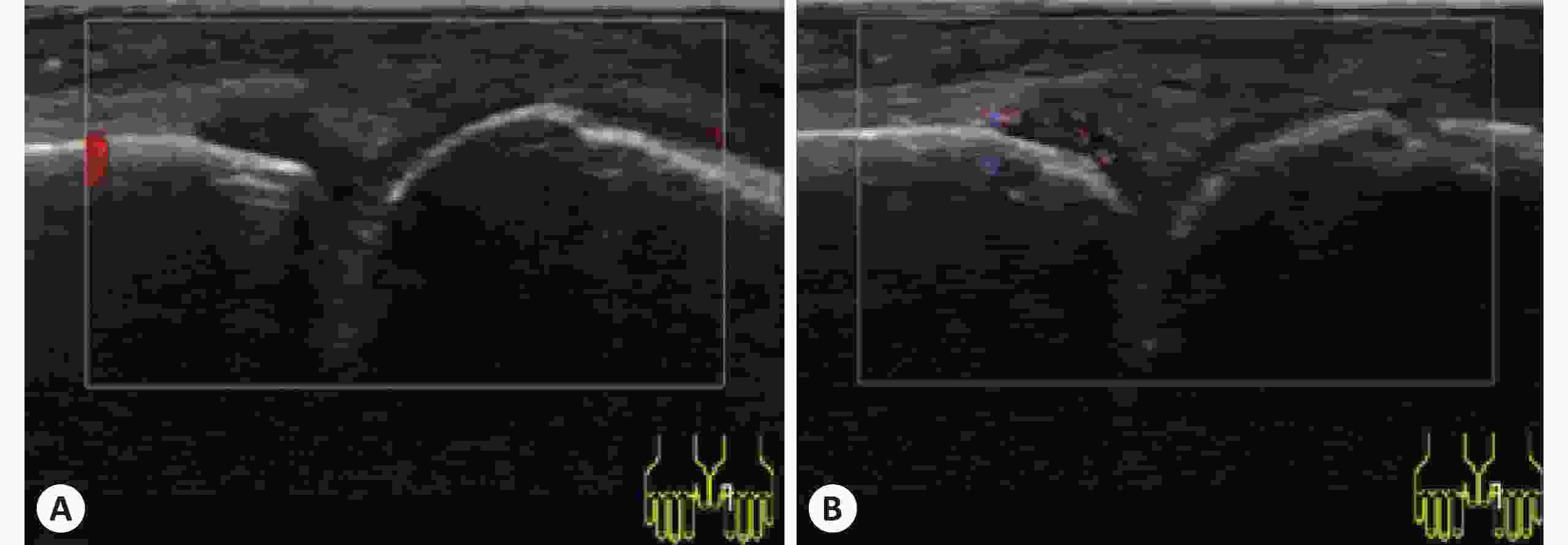
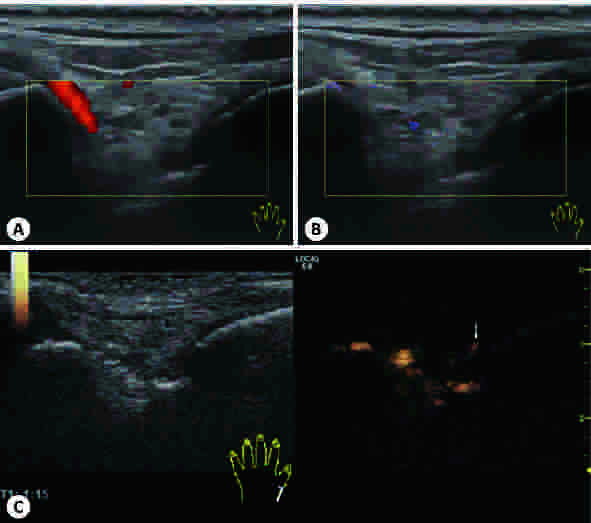
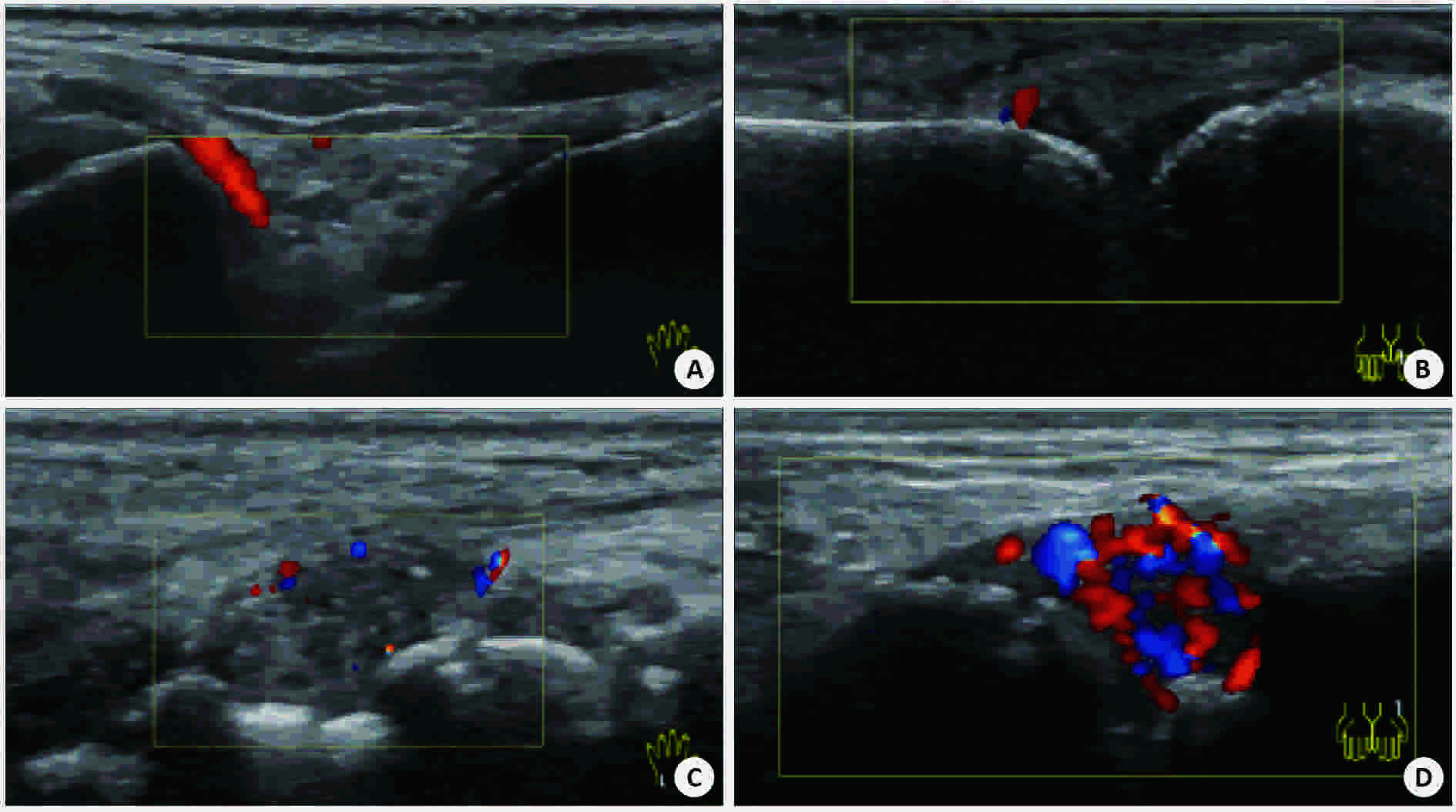
目的 探讨彩色多普勒、B-flow及超声造影在类风湿性关节炎手腕小关节滑膜血流显像的价值。 方法 采用GE Logiq S8 18 M马球棍形线阵探头检查240例类风湿性关节炎患者腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节,应用彩色多普勒检查滑膜血流信号并按Szkudlarek半定量法分为0~3级。对250个滑膜血流信号1级及以上的关节,应用频谱多普勒测量滑膜血管翳阻力指数(RI)并与半定量法作相关性分析。应用B-flow检查滑膜血流信号并与彩色多普勒比较两种技术对滑膜血流显示率的差异。对90个彩色多普勒显示滑膜无血流的类风湿性关节炎关节行超声造影,并与B-flow比较两种技术对滑膜血流检出率的差异。 结果 240例类风湿性关节炎滑膜均为不均匀低回声。其中200例类风湿性关节炎关节滑膜可探及血流信号(1级82例、2级72例、3级46例)。随着血流分级的增加,RI逐渐减低,血流分级与RI呈负相关。彩色多普勒与B-flow对类风湿性关节炎关节滑膜血流信号的显示率分别为154/250及206/250,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。90个彩色多普勒显示滑膜无血流的类风湿性关节炎关节,B-flow与超声造影的血流显示率为56/90与74/90,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 B-flow与超声造影较彩色多普勒对类风湿性关节炎关节滑膜血流显示率高,尤以超声造影明显,滑膜血管翳RI可有效评估类风湿性关节炎活动性,对类风湿性关节炎早期诊断及治疗用药,甚至治疗终点的决定有重要指导意义。 Abstract:Objective To explore the value of Color Doppler Flow Imaging technology (CDFI), B-flow and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in the blood flow imaging of synovial lesion in small joints of wrist and hand with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Methods A GE Logiq S8 18M polo stick-form linear array probe was used to examine the wrist joints, metacarpophalangeal joints and proximal interphalangeal joints of 240 RA patients. CDFI was applied to detect the synovial blood flow, and the result was classified into 0 ~ 3 according to Szkudlarek semi-quantitative method. For 250 cases whose synovial blood flow were over level 1, spectral doppler technology was applied to measure the resistance index (RI) of synovial pannus which was then used for the correlation analysis with the semi-quantitative method, and B-flow Ultrasound Imaging technology was used to examine the blood flow of synovium. The results of B-flow and CDFI were compared to study the difference of display rate between two devices. For 90 cases whose synovium of lesion joints had no blood signals as CDFI showed, CEUS was used and the result of which was compared with that of B-flow to study the difference of detection rate of synovial pannus. Results The synovium of 240 RA samples all appeared low heterogeneous echo, among which blood flow of synovium was detected in 200 RA cases (82 of level 1, 72 of level 2, 46 of level 3). As the blood flow classification increased, RI decreased gradually; therefore, blood flow classification correlated negatively with RI. 2. The detection rates of blood flow in synovial lesion joints of RA patients displayed by CDFI and B-flows were (154/250) and (206/250), and the difference was significant (P<0.05).As for the 90 cases whose synovium of lesion joints had no blood signals as CDFI showed, the blood flow detection rates by B-flow and CEUS were (56/90) and (74/90), and the difference was significant (P<0.05). Conclusions Compared with CDFI, B-flow and CEUS have higher detection rates of blood flow of RA synovium, especially CEUS, and they play an important role in the early diagnosis of RA and even the determination of therapeutic endpoints. RI of synovial pannus can effectively evaluate the activity of RA, and has guiding significance to clinical diagnosis, therapy and medication. -
表 1 RA患者腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜血流参数分析
血流分级 腕关节阻力指数 掌指关节阻力指数 近端指间关节阻力指数 0级(n=40) - - - 1级(n=82) 0.62±0.04 0.60±0.03 0.69±0.02 2级(n=72) 0.50±0.02 0.58±0.03 0.58±0.04 3级(n=46) 0.41±0.01 0.40±0.02 0.40±0.01 表 2 RA患者86个CDFI显示无血流的RA关节滑膜B-flow与超声造影血流结果
类别 B-flow + B-flow- 合计 超声造影 + 56 18 74 超声造影 - 0 16 16 合计 56 34 90 χ2=14.5, P<0.05. -
[1] Knevel R, Lukas C, van Heijde D, et al. Defining erosive disease typical of RA in the light of the ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria for rheumatoid arthritis;results of the data driven phase[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013, 72(4): 590-5. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202778 [2] Nam JL, Hensor EM, Hunt L, et al. Ultrasound findings predict progression to inflammatory arthritis in anti-CCP antibody-positive patients without clinical synovitis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2016, 75(12): 2060-7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208235 [3] 朱梅, 于慧敏, 王菲. 超声造影对类风湿关节炎腕部关节滑膜病变诊断价值的探讨[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2015, 31(05): 439-42. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgcsyxzz201505020 [4] 许华宁, 纪伟, 宋旭光. 超声造影在类风湿关节炎膝关节滑膜病变疗效评估中的初步研究[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2017, 8(26): 708-12. http://news.medlive.cn/xctmr/info-progress/show-131107_241.html [5] Humphreys JH, Verstappen SM, Hyrich KL, et al. The incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in the UK: comparisons using the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria and the 1987 ACR classification criteria[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013, 72(8): 1315-20. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201960 [6] Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American college of rheumatology/european league against rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010, 69(9): 1580-8. [7] Szkudlarek M, Court-Payen M, Strandberg C, et al. Contrast-enhanced power Doppler ultrasonography of the metacarpophalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Eur Radiol, 2003, 13(1): 163-8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-002-1459-2 [8] Weidekamm C, Koller M, Weber A, et al. Diagnostic value of high-resolution B-mode and Doppler sonography for imaging of hand and finger joints in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2003, 48(2): 325-33. doi: 10.1002/art.10784 [9] Arend CF. Ultrasonography in rheumatoid arthritis: what rheumatologists should know[J]. Rev Bras Reumatol, 2013, 53(1): 88-100. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2255502113700099 [10] 林增坤, 刘红梅. 超高频术中探头评价健康中青年人群的手腕关节滑膜厚度[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(08): 1144-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2016.08.21 [11] 蔡晓菡, 杨舒萍, 陈宏浦, 等. 超声在类风湿关节炎中的应用[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2016, 24(06): 471-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2016.06.019 [12] 张凌燕, 向茜, 唐远姣, 等. 类风湿性关节炎滑膜超声造影定量分析与临床及实验室检查指标的相关性研究[J]. 四川大学学报: 医学版, 2014, 45(6): 1001-4. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_hxykdxxb201406026 [13] Klauser A, Demharter J, De Marchi A, et al. Contrast enhanced gray-scale sonography in assessment of joint vascularity in rheumatoid arthritis: results from the IACUS study group[J]. Eur Radiol, 2005, 15(12): 2404-10. doi: 10.1007/s00330-005-2884-9 [14] Rheumatic IM, Byori R. Roles of Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography in the Management of Rheumatic Diseases[J]. Rinsho Byori, 2015, 63(5): 580-9. [15] Vlad V, Micu M, Porta F, et al. Ultrasound of the hand and wrist in rheumatology[J]. Med Ultrason, 2012, 14(1): 42-8. http://www.medultrason.ro/assets/Magazines/Medultrason-2012-vol14-no2/08Vlad-corectat.pdf [16] Carotti M, Salaffi F, Morbiducci J, et al. Colour doppler ultrasonography evaluation of vascularization in the wrist and finger joints in rheumatoid arthritis patients and healthy subjects[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2012, 81(8): 1834-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2010.01.005 [17] Terslev L, Torp-Pedersen S, Savnik A, et al. Doppler ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of synovial inflammation of the hand in rheumatoid arthritis-A comparative study[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2003, 48(9): 2434-41. doi: 10.1002/art.v48:9 [18] 常帅, 赵亮, 陈丹, 等. 超声造影判断类风湿性关节炎膝滑膜炎活动性的价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2014, 30(5): 444-8. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_zgcsyxzz201405020 [19] Cai XH, Yang SP, Shen HL, et al. Application of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography and ultrasonography scores in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2015, 8(11): 20056-64. [20] Ultrasound BM, structural changes in inflammatory arthritis: synovitis, tenosynovitis[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2009, 1154(6): 139-51. [21] Paleolog EM. The vasculature in rheumatoid arthritis: cause or consequence[J]. Int J Exp Pathol, 2009, 90(3): 249-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2009.00640.x [22] Damjanov N, Radunovic G, Prodanovic SA, et al. Construct validity and reliability of ultrasound disease activity score in assessing joint inflammation in RA: comparison with DAS-28[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2012, 51(1): 120-8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker255 [23] 向茜, 邱逦. 超声造影在滑膜炎评估中的研究进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志: 电子版, 2015, 9(1): 142-5. http://journal.9med.net/upload/201501051128198775.pdf -






 下载:
下载: