Association between miR-146a (rs2910164) gene polymorphism and susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Chinese population: a meta-analysis
-
摘要:
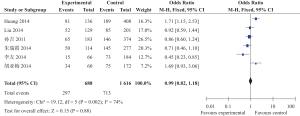
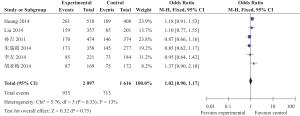
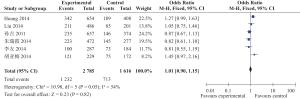
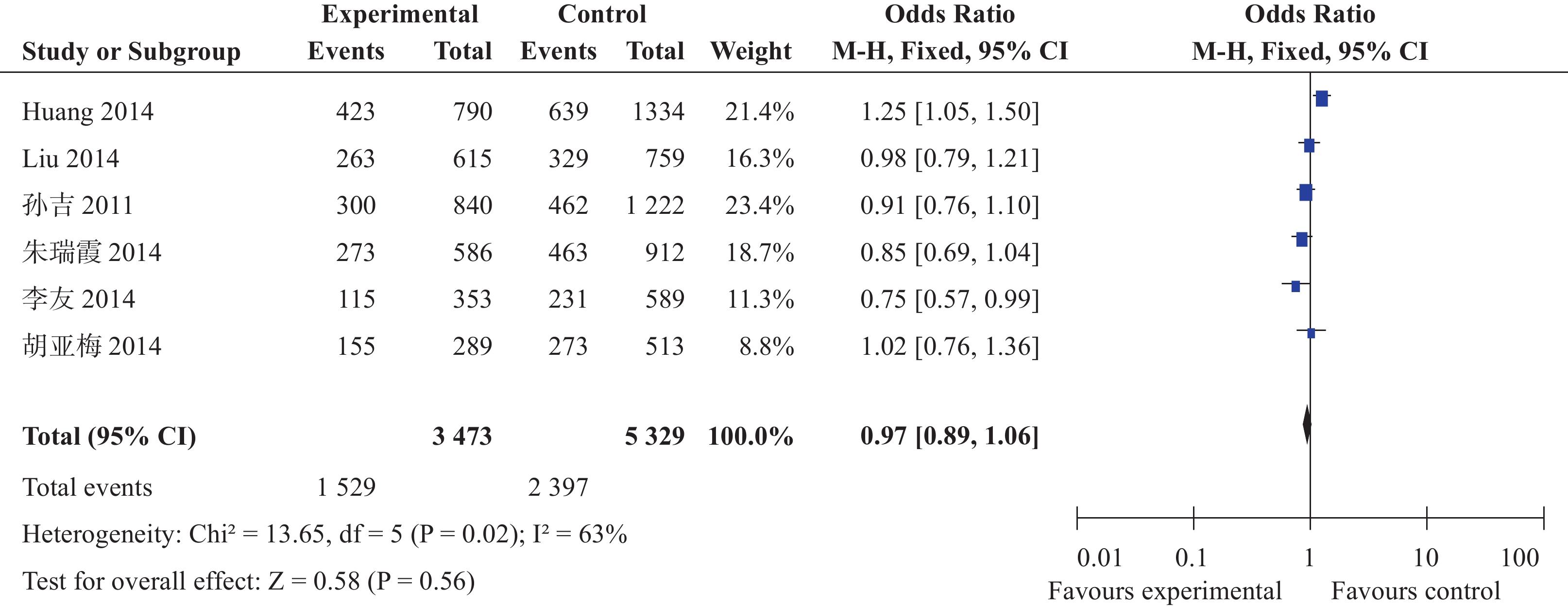
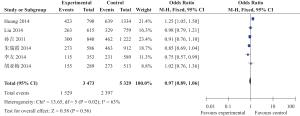
目的 探讨中国人群miR-146aC>G(rs2910164)位点单核苷酸多态性与缺血性脑卒中遗传易感性。 方法 检索2015年12月前中国生物医学文献数据库(CBM)、中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI)、维普中文科技期刊数据库(VIP)、万方数据库及PubMed、Ovid、Cochrane Library、EMBASE等数据库,搜集有关中国人群miR-146aC>G(rs2910164)位点多态性与缺血性脑卒中(IS)研究,采用NOS工具评价纳入相关性研究的质量,提取科学合理有效数据,采用Review Manager 5.0软件进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入6篇文献,共有IS患者1945例,健康对照者2456例,Meta分析尚未发现miR146a rs2910164 G/C基因多态性与缺血性脑卒中易感性具有相关性:基因型G vs C:OR=0.97,95%CI(0.89~1.06),P=0.06;基因型GG vs CC:OR=0.99,95%CI(0.82~1.18),P=0.88;基因型GC vs CC:OR=1.02,95%CI(0.90~1.17),P=0.75;基因型GG+GC vs CC:OR=1.01,95%CI(0.90~1.15),P=0.82。 结论 本研究尚未发现中国人群miR-146aC>G(rs2910164)位点多态性与缺血性脑卒中易感性之间具有相关性。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the association between miR-146a gene polymorphism and Ischemic stroke (IS) in Chinese population. Methods Publications in PubMed, Ovid, Cochrane Library EMBASE, CNKI, VIP and Wangfang Datebase were retrieved up to December 2015. Studies of investigating association between miR-146aC>G (rs2910164) and IS in Chinese population were included. Quality of inclubed studies were evaluated by a Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) tool.The valied data were extracted and analyzed by Review Manager5.0 software. Results Six studies involving 1945 patients of IS and 2456 controls were included. No association between miR-146a rs2910164 polymorphism and the risk of IS was observed [G vs C: OR=0.97, 95%CI: (0.89-1.06), P=0.06]; [GG vs CC: OR=0.99, 95%CI: (0.82-1.18), P=0.88]; [ GC vs CC: OR=1.02, 95%CI (0.90-1.17), P=0.75]; [GG+GC vs CC: OR=1.01, 95%CI (0.90-1.15), P=0.82]. Conclusion The Meta-analysis suggested that the rs2910164 polymorphism in miR-146a is not associated with IS in Chinese population. -
Key words:
- ischemic stroke /
- miR-146a /
- gene polymorphism /
- Meta-analysis /
- Chinese
-
表 1 入选文献基本情况及miR-146aC>G(rs2910164)基因型分布及等位基因频率
纳入文献 地区 组别 N (rs2910164)基因型及等位基因频率 HWE CC GC GG C G 孙吉等[5]2011 长沙 对照组 650 228 304 118 0.58 0.42 0.345 病例组 381 146 170 65 0.61 0.39 0.202 李友等[6]2014 广东 对照组 298 111 136 51 0.60 0.40 0.401 病例组 173 73 85 15 0.67 0.33 0.159 朱瑞霞等[7]2014 中国北方 对照组 381 132 185 64 0.59 0.41 0.952 病例组 368 145 173 50 0.63 0.37 0.888 胡亚梅等[8]2014 河南郑州 对照组 205 97 82 26 0.67 0.33 0.193 病例组 196 75 87 34 0.60 0.40 0.316 Huang等[9]2015 中国深圳 对照组 531 219 257 55 0.65 0.35 0.106 病例组 531 189 261 81 0.60 0.40 0.557 Liu等[10]2014 中国四川 对照组 391 116 198 77 0.55 0.45 0.650 病例组 296 85 159 52 0.56 0.44 0.131 表 2 入选资料研究方法学质量评价(分)
纳入研究 入选人群选择 组间可比性 暴露因素测量 合计 (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) 孙吉等[5]2011 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 8 李友等[6]2014 1 0 1 1 2 1 1 1 8 朱瑞霞等[7]2014 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 7 胡亚梅等[8]2014 1 0 1 1 2 1 1 1 8 Huang等[9]2015 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 9 Liu等[10]2014 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 9 (1): 病例确定是否恰当(1分); (2): 病例的代表性(1分); (3): 对照组的选择(1分); (4): 对照组的确定(1分); (5): 实验设计和数据统计分析时考虑病例组和对照组的可比性(2分); (6): 暴露因素的确定(1分); (7): 病例组和对照组暴露因素的确定方法相同(1分); (8): 无应答率(1分). -
[1] Liu L, Wang D, Wong K.S, et al. Stroke and stroke care in China: Huge burden, significant workload and a national priority[J]. Stroke, 2011, 42(5), 3651-4. [2] Goldstein LB, Adams R, Becker K, et al. Primary prevention of ischemic stroke: A statement for healthcare professionals from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2001, 103(1): 163-82. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.103.1.163 [3] Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism and function[J]. Cell, 2004, 116(2): 281-97. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5 [4] Pushparaj PN, Aarthi JJ, Kumar SD, et al. RNAi and RNAa--the yin and yang of RNAome[J]. Bioinformatics, 2008, 2(6): 235-7. [5] 孙 吉. miRNA-146a和EPHX2基因多态性与长沙地区汉族人群缺血性脑卒中遗传易感性的关联研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2011. [6] 李 友, 朱 菁, 马国达, 等. miR-146a基因多态性与腔隙性脑梗死的关系[J]. 山东医药, 2014, 54(16): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2014.16.001 [7] Zhu R, Liu X, He Z, et al. miR-146a and miR-196a2 polymorphisms in patients with ischemic stroke in the northern Chinese Han population[J]. Neurochem Res, 2014, 39(9): 1709-16. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1364-5 [8] 胡亚梅, 李书剑, 姜晓峰, 等. miR-146aC>G, miR-149T>C基因多态性与缺血性脑卒中易感性的研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2014, 14(29): 5643-8. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0232698159/ [9] Huang S, Zhou S, Zhang Y, et al. Association of the genetic polymorphisms in pre-microRNAs with risk of ischemic stroke in a Chinese population[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(2): e0117007-12. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117007 [10] Liu Y, Ma Y, Zhang B, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in pre-microRNAs and risk of ischemic stroke in a Chinese population[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2014, 52(4): 473-80. doi: 10.1007/s12031-013-0152-z [11] Falcone GJ, Malik R, Dichgans M, et al. Current concepts and clinical applications of stroke genetics[J]. Lancet Neurology, 2014, 13 (4) :405-8. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70029-8 [12] Meschia JF, Arnett DK, Ay H, et al. Stroke genetics network (SiGN) study: design and rationale for a genome-wide association study of ischemic stroke subtypes[J]. Stroke, 2013, 44(10): 2694-702. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.001857 [13] Sharma P, Yadav S, Meschia JF. Genetics of ischaemic stroke[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2013, 84(12): 1302-8. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-304834 [14] Anderson V, Gomes A, Greenham M, et al. Social competence following pediatric stroke: contributions of brain insult and family environment[J]. Soc Neurosci, 2014, 9(5): 471-83. doi: 10.1080/17470919.2014.932308 [15] Hamano T, Kawakami N, Li X, et al. Neighbourhood environment and stroke: a follow-up study in Sweden[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e56680-4. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056680 [16] Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets[J]. Cell, 2005, 120(1): 15-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035 [17] Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs[J]. Nature, 2004, 431(76): 350-5. [18] 吕国天, 王 爽, 王庆坤. 微小RNA-146a rs2910164及微小RNA-499 rs3746444与缺血性脑卒中的关系[J]. 新医学,2016,47(04):257-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2016.04.012 [19] Zhu H, Zhang H, Bao L, et al. Analysis of association of genetic polymorphisms of microRNAs with ischemic stroke[J].Chin J Med Genet, 2017, 34(2): 261-5. [20] Du J, Cui C, Zhang S, et al. Association of MicroRNA-146a and MicroRNA-149 polymorphisms with strokes in Asian populations: an updated Meta-analysis[J]. Angiology,2017, 68(10): 863-70. doi: 10.1177/0003319717704323 [21] Su ZF, Sun ZW, Zhang Y, et al. Regulatory effects of miR-146a/b on the function of endothelial progenitor cells in acute ischemic stroke in mice[J]. J Med Sci, 2017, 33(8):369-78. -






 下载:
下载: