The effects of Propofol on membrane properties and postsynaptic current in hippocampal pyramidal neurons of mice
-
摘要:
目的观察异丙酚对小鼠鼠海马锥体神经元膜特性和突触后电流的影响。 方法用冰冻切片的方法将C57小鼠海马半脑切成300 μm厚度。运用全细胞膜片钳技术记录海马锥体神经元在异丙酚作用前后动作电位反应、I-V曲线及突触后电流反应后变化情况。 结果异丙酚明显减少不同刺激强度下胞体动作电位产生的个数,加入异丙酚后使锥体细胞动作电位发放个数由5±3个降至2±1个(P<0.01),而对动作电位幅度无显著影响。异丙酚可改变海马锥体神经元对兴奋性电压刺激的I-V曲线平台期反应,使最大电流幅度由1647.63±124.02 pA增加至2955.08±119.10 pA(P<0.01)。异丙酚可降低锥体神经元突触后电流,加入异丙酚前为146.5±25.89 pA,加入异丙酚后为72.8±18.71 pA(P<0.01),20 min洗脱异丙酚后电流幅度恢复至132.1±30.2 pA(P<0.01)。 结论异丙酚可降低海马锥体神经元动作电位发放数,改变I-V曲线兴奋性平台期反应和可逆地降低神经元突触后电流反应。 Abstract:Objective To observe the effects of Propofol on membrane characteristics and postsynaptic current of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Methods The method of frozen section cut hippocampus into 300um thickness in C57 mice. Using whole cell patch clamp technique records the hippocampal neuronal responses of action potential(AP), I-V curves and postsynaptic current during using propofol before and after. Results Propofol decreased significantly the number of action potential under different stimulus intensity before (5±3) and during (2±1) propofol application(P<0.01), but had no significant effect on the AP amplitude. Zeneca may change the hippocampal pyramidal neurons plateau reaction to excitatory voltage stimulus in I-V curve, the max current amplitude increased from(1647.63±124.02)pA to(2955.08±119.10)pA(P<0.01). Propofol can decrease the pyramidal neuronal postsynaptic current from(146.5±25.89)pA to(72.8±18.71)pA(P<0.01), and then return to(132.1± 30.2)pA (P<0.01)after washing 20 min. Conclusion Propofol can reduce hippocampal pyramidal neuronal AP number, change the I-V curve plateau responses and decreased reversibly postsynaptic currents. -
Key words:
- propofol /
- hippocampal pyramidal neuron /
- action potential /
- postsynaptic current
-
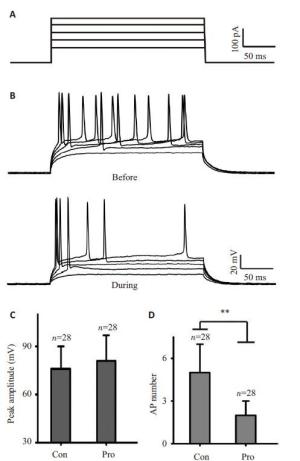
图 1 异丙酚对海马锥体神经元动作电位的影响
Figure 1. The effect of action potential of hippocampal pyramidal neurons for Propofol. A: The current injection protocol for pyramidal cells. The injection current levels were 100 pA,150 pA,200 pA,250 pA,300 pA,respectively,duration was 200 ms,with 0 pA holding current. Upper panel,reference responses; bottom panel,during application of 100 uM propofol; B: The action potential waveform produced by injecting current by propofol perfusion before or later. C: Comparison the peak amplitude of control and propofol group. Con: Control group,n= 28; Pro: Propofol group,n=28. Error bars are ±SE. D: Comparison the action potential (AP) of control and propofol group. Error bars are ±SE. **P<0.01. Independent-sample T test.
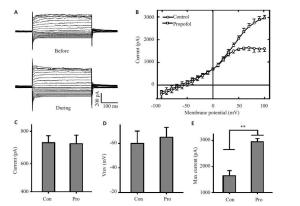
图 2 异丙酚对海马锥体神经元I-V曲线影响
Figure 2. The effect of I-V curves of hippocampal pyramidal neurons for Propofol. A: Example of membrane current waveforms recorded from a pyramidal neuron before and during propofol application. The cell was held at -70 mV,and voltage commands varied from -100 to +100 mV in 10 mV steps. Upper panel,reference responses; bottom panel,during application of 100 uM propofol. B: The current-voltage functions (I-V curves) derived from the steady-state responses in A. Open circles and open squares represent responses before and during propofol application,respectively. n=36. Error bars are ±SE. C: Comparison the current of control and propofol group when V=0 mV. D: Comparison the reversal potential (Vrev) of control and propofol group when I=0 mV. E: Comparison the max current of control and propofol group during 50 to 100 mV stimulus. Error bars are ±SE. **P<0.01. Independent-sample T test.
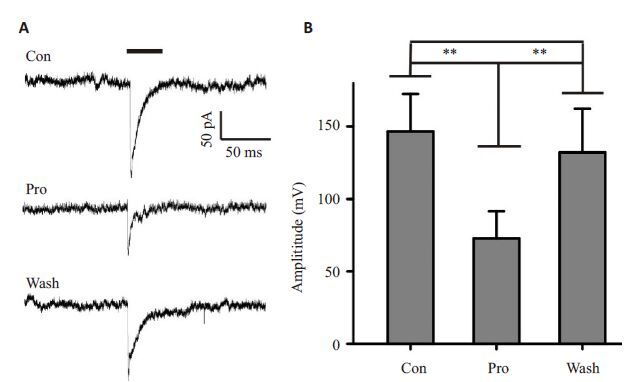
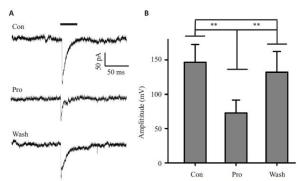
图 3 异丙酚对海马锥体神经元突触后电流影响
Figure 3. The effect of postsynaptic currents of hippocampal pyramidal neurons for Propofol. A: The magnitude of postsynaptic currents obtain the control response (top trace). 100 μm propofol (middle trace) and wash propofol (bottom trace). Bar: 0.5 V,10 ms electic stimulus. B: Average amplitudes of postsynaptic current in response to 100 μm propofol. n=22. Error bars are ±SE. **P<0.01. Independent-sample T test.
-
[1] Tanelian DL, Kosek P, Mody I, et al. The role of the GABAA receptor/chloride Channel complex in anesthesia[J]. Anesthesiology, 1993, 78(4): 757-76. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199304000-00020 [2] Martella G, De Persis C, Bonsi P, et al. Inhibition of persistent Sodium current fraction and voltage-gated L-type Calcium current by propofol in cortical neurons: Implications for its antiepileptic activity[J]. Epilepsia, 2005, 46(5): 624-35. doi: 10.1111/epi.2005.46.issue-5 [3] 罗爱林, 杉山和英, 田玉科, 等. 联合使用异丙酚和地西泮对鼠感觉神经元γ-氨基丁酸调控的氯电流的影响[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2000(1): 28-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHMZ200001013.htm [4] Xu L, Jia YJ. Expressi on and distribution of C-fos oncogene within central nervous system of the rat following halothane anesthesia[J]. J Med Coll PLA, 1997, 12(5): 273-8. [5] 姚泰. 生理学[M]. 5版. 北京: 卫生出版社, 2003: 24-31. [6] Torkkeli PH, Sekizawa S, French AS. Inactivation of voltageactivated Na(+ ) currents contributes to different adaptation properties of paired mechanosensory neurons[J]. J Neurophysiol, 2001, 85(4): 1595-602. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11287483 [7] Franks NP, Lieb WR. Anaesthetics set their sites on ion channels[J]. Nature, 1997, 389(4): 334-5. -






 下载:
下载: