Explorations of cell-free DNA on trace touch DNA samples
-
摘要:
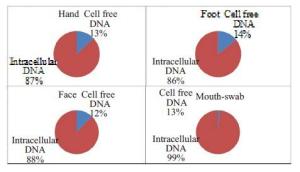
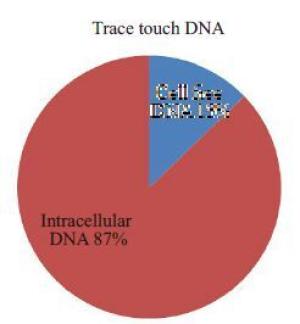
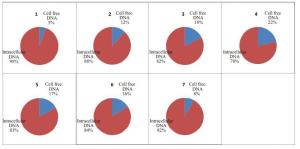
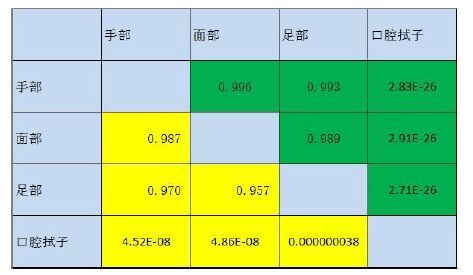
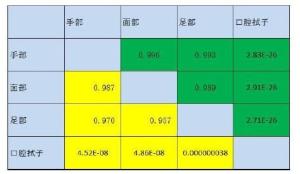
目的探究接触类生物检材的游离DNA问题,游离DNA和细胞内DNA含量的比例问题,以及游离DNA在法医检验中的影响。 方法对手部、面部和足部的皮肤及口腔粘膜进行模拟微量接触类检材的制备,对模拟检材进行浸泡,对游离DNA进行定量和STR扩增,对剩余检材使用常规程序进行DNA提取、定量和STR扩增,并对结果进行分析和讨论。 结果实验观察到,78.55%的样品检测到了游离DNA,其中,手部模拟检材的游离DNA检测率为82.1%,脸部模拟检材的游离DNA检测率为82.1%,口腔模拟检材的游离DNA检测率为96.4%,足部模拟检材的游离DNA检测率为53.6%,微量接触类检材中游离DNA量占DNA总量的12.9%。 结论接触类生物检材中提取到的DNA,除了包括细胞内DNA,还存在一定比例的细胞外游离DNA,这为微量接触类检材的DNA有效提取和检验提供了新的理论依据。 Abstract:Objective To investigate cell-free DNA on trace touch DNA samples and the amount and proportion of the cell free DNA and the intracellular DNA and the influence of cell-free DNA in forensic analysis. Methods To manufacture mock exhibits and then the DNA extracted from the samples was quantified using standard manufacture's procedures, and the results were analyzed and discussed. Results This experiment shows that the cell free DNA has been detected in 78.55% of the samples. The detection rates in hand touch DNA samples, face touch DNA samples, foot touch DNA samples and mouth-swab respectively are 82.1%,82.1%,53.6% and 92.4%. The amount of cell free DNA is 12.9% of the amount of total DNA in trace/touch DNA samples. Conclusion The cell free DNA did exist extracellular, and the amount of the cell free DNA occupy a proportion in the exhibits of touch DNA. This study showed a new theory of the question of cell free DNAof touch DNA. -
Key words:
- Forensic biological evidence /
- Cell free DNA /
- Trace/touch DNA /
- STR
-
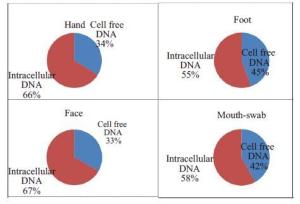
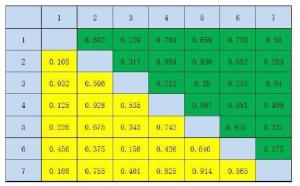
表 1 表1 手部、面部、脚部和口腔拭子的游离DNA量和细胞内DNA量(ng)
Table 1. 英文标题
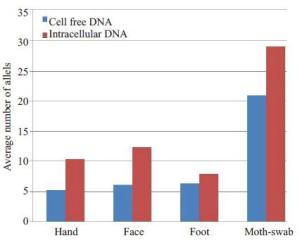
个体 游离DNA 细胞内DNA 手部 面部 足部 口腔拭子 手部 面部 足部 口腔拭子 1 0.17 0.26 0.16 0.08 3.41 4.22 0.22 1910.34 2 0 0.02 0.03 12.77 1.16 0.3 0.38 350.46 3 0.4 0.32 0.08 8.78 2.58 1.76 0.89 970.76 4 0.17 0.16 0.38 32.16 0.7 1.13 1.04 763.2 5 0.22 0.41 0.11 14.16 0.43 2.62 0.61 1097.93 6 0.04 0.14 0.02 7.41 0.57 2.15 0.43 1152.68 7 0.44 0.38 0.06 21.23 0.76 0.25 1.48 1018.82 表 2 手部、面部、脚部和口腔拭子的游离DNA和总DNA的STR等位基因数
个体 游离DNA 细胞内DNA 手部 面部 足部 口腔拭子 手部 面部 足部 口腔拭子 1 4 2 3 5 17 12 4 30 2 0 4 7 12 7 5 5 29 3 13 6 11 22 11 11 19 27 4 8 5 7 31 7 11 13 31 5 7 9 13 29 11 17 10 29 6 0 6 2 19 8 22 2 29 7 5 11 2 29 12 9 3 29 -
[1] Wiegand P, Kleiber M. DNA typing of epithelial cells after strangulation[J]. Int J Legal Med, 1997, 110(4): 181-3. doi: 10.1007/s004140050063 [2] Kita T, Yamaguchi H, Yokoyama M, et al. Morphological study of fragmented DNA on touched objects[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2008, 3(1): 32-6. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2008.09.002 [3] Clayton TM, Whitaker JP, Sparkes R, et al. Analysis and interpretation of mixed forensic stains using DNA STR profiling[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 1998, 91(1): 55-70. doi: 10.1016/S0379-0738(97)00175-8 [4] Elliott K, Hill DS, Lambert C, et al. Use of laser microdissection greatly improves the recovery of DNA from sperm on microscope slides[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2003, 137(1): 28-36. doi: 10.1016/S0379-0738(03)00267-6 [5] Adamowicz MS, Bourke MT. A systematic analysis of secondary DNA transfer[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 44(1999): 1270-2. http://www.docin.com/p-1492478951.html [6] Eken E, Mitchell RJ. Investigation of secondary DNA transfer of skin cells under controlled test conditions[J]. Legal Med, 2010, 12 (3): 117-20. doi: 10.1016/j.legalmed.2010.01.003 [7] Goray M, Mitchell RJ, van Oorschot RA. Investigation of secondary DNA transfer of skin cells under controlled test conditions[J]. Leg Med (Tokyo), 2010, 12(3): 117-20. doi: 10.1016/j.legalmed.2010.01.003 [8] Alessandrini F, Cecati M, Pesaresi M, et al. Fingerprints as evidence for a genetic profile: morphological study on fingerprints and analysisz of exogenous and individual factors affecting DNA typing[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2003, 48(3): 586-92. [9] Budowle B, Onorato AJ, Callaghan TF, et al. Mixture interpretation: defining the relevant features for guidelines for the assessment of mixed DNA profiles in forensic casework[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2009, 54(4): 810-21. [10] Kishore R, Hardy WR, Anderson VJ, et al. Optimization of DNA extraction from low-yield and degraded samples using the BioRobot (R) EZ1 and BioRobot (R) M48[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2006, 51(5): 1055-61. [11] mankiewicz R. The story of mathematics[M]. new jersey: princeton university press, 2004: 158-61. [12] fisher BJ. Guinness,gosset,fisher,and small samples[J]. Statistical Science, 1987, 2(1): 42-52. doi: 10.1214/ss/1177013435 [13] howell D. Statistical methods for psychology[M]. san francisco: wadsworth publishing press, 2006: 324-7. [14] Goray M, Eken E, Mitchell RJ, et al. Secondary DNA transfer of biological substances under varying test conditions[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2010, 4(2): 62-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2009.05.001 -






 下载:
下载: