A case report: death due to severe immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis
-
摘要: 免疫检查点抑制剂相关结肠炎为最常见免疫治疗相关不良反应之一,主要临床表现为腹泻。免疫检查点抑制剂相关结肠炎内镜表现为红斑(93.5%)、脆性(58.6%)、充血(48.2%)和溃疡(37.9%),超98%免疫检查点抑制剂相关结肠炎可累及远端结肠。本文报道1例重度免疫检查点抑制剂相关结肠炎死亡病例,主要临床表现为腹痛、腹泻,内镜可见黏膜粗糙、水肿,血管纹理消失,既往免疫检查点抑制剂应用病史。经一线激素及二线英夫利昔单抗治疗,患者虽内镜表现好转,但相继出现血小板减低、消化道大出血、心肌损伤等免疫治疗相关不良反应。重度免疫检查点抑制剂相关结肠炎死亡病例临床罕见,本例患者肠道免疫治疗相关不良反应应用激素及英夫利西单抗肠道疗效可,但依然未能逆转患者病程进展,相继发生其余器官免疫治疗相关不良反应最终导致临床死亡。免疫治疗相关不良反应诊治仍需更多临床探索。Abstract: Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis is one of the most common immune-related adverse events, which clinical feature is diarrhea. The endoscopic feature of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis are erythema (93.5%), brittleness (58.6%), congestion (48.2%) and ulcer (37.9%). More than 98% of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis could affect the rectum. Here we report a case of death due to severe immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis.The main clinical manifestations of the patient were abdominal pain and diarrhea. The endoscopy showed that the mucosa was rough and edematous, and the vascular texture disappeared. The patient had previously received immune checkpoint inhibitor. After treatment with glucocorticoid and infliximab, although the endoscopic performance of the patient improved, thrombocytopenia, massive gastrointestinal bleeding and myocardial damage occurred. Death due to severe immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis are rare in clinical practice. In this case, glucocorticoid and infliximab were effective, but they still failed to reverse the progress of the patient, resulting in clinical death. The diagnosis and treatment of immune-related adverse events needs more clinical exploration.
-
Key words:
- immune checkpoint inhibitor /
- colitis /
- infliximab
-
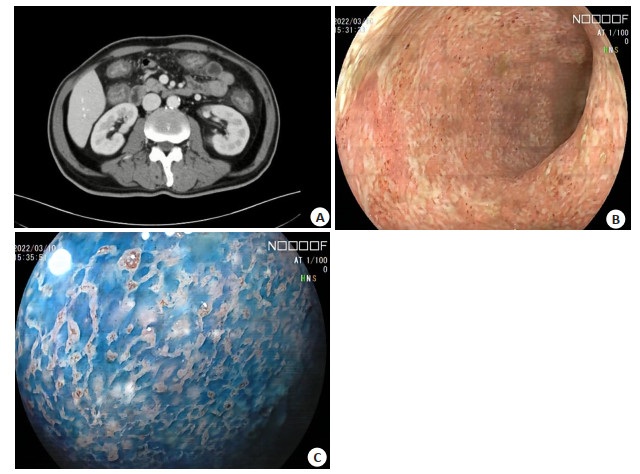
图 1 结肠弥漫性溃疡病变
Figure 1. Diffuse ulceration of colon. A: CT showed that the wall of the whole colon was thickened and edematous, and the colonic pouch disappeared. B: Colonoscopy showed that the mucosa from the sigmoid colon to the rectum was rough, edematous, and the vascular texture disappeared. Mucosa hemorrhage could be seen, and white mucus could be attached. C: Indigo carmine staining: cashmere like changes could be seen.
-
[1] Li B, Chan HL, Chen PP. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: basics and challenges[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2019, 26(17): 3009-25. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170804143706 [2] Thompson JA, Schneider BJ, Brahmer J, et al. NCCN guidelines insights: management of immunotherapy-related toxicities, version 1.2020[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2020, 18(3): 230-41. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0012 [3] Postow MA, Hellmann MD. Adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 378(12): 1165. [4] Abu-Sbeih H, Ali FS, Naqash AR, et al. Resumption of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy after immune-mediated colitis[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37(30): 2738-45. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00320 [5] Khoja L, Day D, Chen TW, et al. Tumour-and class-specific patterns of immune-related adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review[J]. Ann Oncol, 2017, 28(10): 2377-85. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx286 [6] Martins F, Sofiya L, Sykiotis GP, et al. Adverse effects of immune-checkpoint inhibitors: epidemiology, management and surveillance[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2019, 16(9): 563-80. doi: 10.1038/s41571-019-0218-0 [7] Soularue E, Lepage P, Colombel JF, et al. Enterocolitis due to immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(11): 2056-67. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-316948 [8] Wright AP, Piper MS, Bishu S, et al. Systematic review and case series: flexible sigmoidoscopy identifies most cases of checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 49(12): 1474-83. doi: 10.1111/apt.15263 [9] Hu JR, Florido R, Lipson EJ, et al. Cardiovascular toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2019, 115(5): 854-68. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz026 [10] Moslehi J, Lichtman AH, Sharpe AH, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis: manifestations and mechanisms[J]. J Clin Invest, 2021, 131(5): e145186. doi: 10.1172/JCI145186 [11] Power JR, Alexandre J, Choudhary A, et al. Electrocardiographic manifestations of immune checkpoint inhibitor myocarditis[J]. Circulation, 2021, 144(23): 1521-3. [12] Haddad TC, Zhao SZ, Li MJ, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related thrombocytopenia: incidence, risk factors and effect on survival[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2022, 71(5): 1157-65. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03068-2 [13] Akpinar H, Cetiner M, Keshav S, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency anemia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and gastrointestinal bleeding: iron deficiency anemia working group consensus report[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2017, 28(2): 81-7. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2017.17593 [14] Yarur AJ, Deshpande AR, Pechman DM, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with an increased incidence of cardiovascular events[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2011, 106(4): 741-7. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2011.63 [15] Thompson JA, Schneider BJ, Brahmer J, et al. Management of immunotherapy-related toxicities, version 1.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2022, 20(4): 387-405. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2022.0020 [16] Dougan M, Wang Y, Rubio-Tapia A, et al. AGA clinical practice update on diagnosis and management of immune checkpoint inhibitor colitis and hepatitis: expert review[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160(4): 1384-93. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.08.063 [17] Wang YH, Abu-Sbeih H, Mao E, et al. Immune-checkpoint inhibitor-induced diarrhea and colitis in patients with advanced malignancies: retrospective review at MD Anderson[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2018, 6(1): 37. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0346-6 [18] Johnson DH, Zobniw CM, Trinh VA, et al. Infliximab associated with faster symptom resolution compared with corticosteroids alone for the management of immune-related enterocolitis[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2018, 6(1): 103. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0412-0 [19] Abu-Sbeih H, Ali FS, Alsaadi D, et al. Outcomes of vedolizumab therapy in patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis: a multi-center study[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2018, 6(1): 142. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0461-4 [20] Bergqvist V, Hertervig E, Gedeon P, et al. Vedolizumab treatment for immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced enterocolitis[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2017, 66(5): 581-92. doi: 10.1007/s00262-017-1962-6 [21] Zou FW, Shah AY, Glitza IC, et al. S0137 Comparative study of vedolizumab and infliximab treatment in patients with immune-mediated diarrhea and colitis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2020, 115(1): S68. [22] Mir R, Shaw HM, Nathan PD. Mycophenolate mofetil alongside high-dose corticosteroids: optimizing the management of combination immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis[J]. Melanoma Res, 2019, 29(1): 102-6. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0000000000000543 [23] Bishu S, Melia J, Sharfman W, et al. Efficacy and outcome of tofacitinib in immune checkpoint inhibitor colitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160(3): 932-4. e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.029 [24] Thomas AS, Ma WJ, Wang YH. Ustekinumab for refractory colitis associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(6): 581-3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2031717 [25] Wang YH, Wiesnoski DH, Helmink BA, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation for refractory immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated colitis[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24(12): 1804-8. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0238-9 -







 下载:
下载: