MRI features of breast cancer and their relationship with sentinel lymph node and axillary lymph node metastasis
-
摘要:
目的 分析乳腺癌MRI影像学特征及其与前哨淋巴结和腋窝淋巴结转移的关系。 方法 选择我院2019年5月~2022年5月收治的117例乳腺癌患者作为研究对象,其中前哨淋巴结结转移41例,腋窝淋巴结转移34例,无转移42例;对患者行乳腺癌MRI扫描检查;绘制ROC曲线分析诊断腋窝淋巴结转移和前哨淋巴结转移的价值。 结果 乳腺癌前哨淋巴结转移、腋窝淋巴结转移患者MRI影像学检查的短长径比低于无转移者,相对表观扩散系数(rADC)值高于无转移,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);乳腺癌前哨淋巴结转移、腋窝淋巴结转移和无转移患者环形强化情况的差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);乳腺癌MRI影像学特征联合应用预测前哨淋巴结模型为Log(P)=-0.602×短长径比+0.675×rADC-0.754×环形强化+0.895;乳腺癌MRI影像学特征联合应用预测腋窝淋巴结转移模型为Log(P)=-0.685×短长径比+0.712×rADC-0.695×环形强化+0.794;短长径比、rADC、环形强化三指标联合应用预测乳腺癌前哨淋巴结转移的AUC高于各指标单独应用,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);短长径比、rADC、环形强化三指标联合应用预测腋窝淋巴结转移的AUC高于各指标单独应用,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 乳腺癌MRI影像学特征与前哨淋巴结和腋窝淋巴结转移高度相关,且MRI影像学特征联合应用可显著有效预测前哨淋巴结转移和腋窝淋巴结转移。 Abstract:Objective To explore the MRI imaging features of breast cancer and its relationship with sentinel lymph node and axillary lymph node metastasis. Methods A total of 117 patients with breast cancer admitted to our hospital from May 2019 to May 2022 were selected as the study objects, including 41 patients with sentinel lymph node metastasis, 34 with axillary lymph node metastasis and 42 without metastasis. The patients underwent MRI scan for breast cancer. ROC curve was drawn to analyze the diagnostic value of axillary lymph node metastasis and sentinel lymph node metastasis. Results Breast cancer patients with sentinel lymph node metastasis and axillary lymph node metastasis had significantly lower ratio of ratio of short diameter to long diameter in MRI imaging than those without metastasis. The relative apparent diffusion coefficient (rADC) value was significantly higher than that without metastasis(P < 0.05). There were significant differences in ring enhancement between patients with sentinel lymph node metastasis, axillary lymph node metastasis and those without metastasis (P < 0.05). The prediction model of sentinel lymph node by combined application of MRI features of breast cancer was Log(P)=-0.602×ratio of short diameter to long diameter+0.675×rADC-0.754×ring enhancement+0.895. The combined application of MRI features to predict axillary lymph node metastasis was Log(P)=-0.685×ratio of short diameter to long diameter+0.712×rADC-0.695×ring enhancement+0.794. The combined application of ratio of short diameter to long diameter, rADC and ring enhancement in predicting the AUC of sentinel lymph node metastasis was significantly higher than that applied alone, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Combined application of ratio of short diameter to long diameter, rADC and ring enhancement was significantly higher in predicting axillary lymph node metastasis AUC than that applied alone, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion MRI imaging features of breast cancer are highly correlated with sentinel and axillary lymph node metastasis. The combined application of MRI imaging features can significantly and effectively predict sentinel lymph node metastasis and axillary lymph node metastasis. -
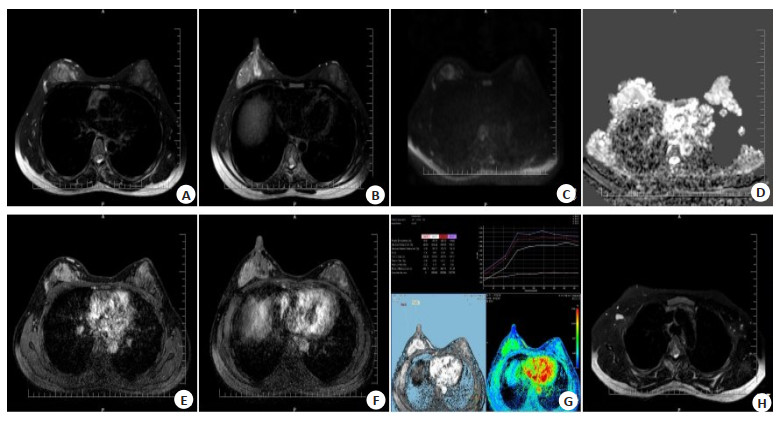
图 1 患者女,30岁,发现右乳肿块1月余
Figure 1. Female patient, 30 years old, right breast mass discovered for over a month. MRI showed irregular masses in the right upper and outer breast quadrants, with shallow lobulation and no obvious burrs at the edges. T2WI showed high signal intensity (A, B), DWI showed slightly high signal intensity (C), with an ADC value of approximately 1.09×10-3 mm2/s (D). Dyn THRIVE dynamic enhancement scan shows significant enhancement like masses (E, F), TIC time signal intensity curve showed a plateau type (G), and the right armpit shows slight enlargement of lymph nodes. Surgical pathology: infiltrating carcinoma of the right breast.
图 2 患者女,34岁,发现右乳肿物1月余
Figure 2. Female patient, 34 years old, right breast mass discovered for over a month. MRI showed multiple patchy and nodular shadows in the right lateral breast quadrant, with high/slightly high signal intensity (B) on T2WI, uneven high signal intensity (C) on DWI, and decreased ADC signal intensity (D), with a value of approximately 0.98×10-3mm2/s. Dyn THRIVE dynamic enhancement scan showed significant uneven enhancement (A), and the TIC time signal intensity curve showed a plateau (E). The right armpit showed slight lymph node enlargement (F). Surgical pathology: infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the right breast, grade 3, with cancer metastasis seen in the right axillary sentinel lymph node.
图 3 患者女,50岁,发现右乳肿物1周
Figure 3. Female patient, 50 years old, right breast mass discovered for 1 week. MRI showed an abnormal signal mass in the lateral quadrant of the right breast, which was lobulated and has burrs on the edge. T2WI showed slightly high signal (A), DWI showed high signal (C), ADC diffusion was limited (D). Dynamic enhancement scan showed significant uneven enhancement (B), and the dynamic enhancement curve showed an outflow type (E). An enlarged lymph node (F) was seen in the right axilla. Surgical pathology: non-specific infiltrating carcinoma of the right breast; Cancer metastasis could be seen in the right armpit.
表 1 各组乳腺癌MRI影像学特征调查结果
Table 1. Investigation results of MRI imaging features of breast cancer in each group (Mean±SD)
Group Maximum diameter (cm) Ratio of short diameter to long diameter ADC (10-3 mm2/s) rADC (10-1) Sentinel lymph node metastasis (n=41) 2.21±0.41 0.75±0.05 0.65±0.08 5.89±1.02 Axillary lymph node metastasis (n=34) 2.19±0.39 0.73±0.07 0.63±0.10 5.75±0.96 No transfer (n=42) 2.04±0.42 0.86±0.08 0.62±0.09 3.84±0.94 F 1.201 5.654 0.754 5.321 P 0.759 <0.001 0.839 <0.001 ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient; rADC: Relative apparent diffusion coefficient. 表 2 患者肿块位置、强化及TIC指标调查结果
Table 2. Results of tumor location, enhancement and TIC indexes (n)
Group Location of the mass Ring sign TIC Outside Inside Mammary areola Yes No Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Sentinel lymph node metastasis (n=41) 19 14 8 16 25 14 22 5 Axillary lymph node metastasis (n=34) 15 12 7 13 21 13 18 3 No transfer (n=42) 22 12 8 32 10 22 18 2 χ2 0.637 15.196 3.743 P 0.959 0.001 0.442 TIC: Time-signal intensity curve. 表 3 乳腺癌MRI影像学特征联合应用预测前哨淋巴结模型
Table 3. Breast cancer MRI imaging features combined with predictive sentinel lymph node model.
Index b SE χ2 P OR 95% CI Lower limit Upper limit Ratio of short diameter to long diameter -0.602 0.183 10.822 0.001 0.548 0.383 0.784 rADC 0.675 0.225 9.000 0.003 1.964 1.264 3.053 Ring enhancement -0.754 0.209 13.015 < 0.001 0.470 0.312 0.709 Constant term 0.895 0.232 14.882 < 0.001 2.447 1.553 3.856 表 4 乳腺癌MRI影像学特征联合应用预测腋窝淋巴结转移模型
Table 4. Breast cancer MRI imaging features combined with application to predict axillary lymph node metastasis model
Index b SE χ2 P OR 95% CI Lower limit Upper limit Ratio of short diameter to long diameter -0.685 0.201 11.614 0.001 0.504 0.340 0.747 rADC 0.712 0.198 12.931 < 0.001 2.038 1.383 3.004 Ring enhancement -0.695 0.187 13.813 < 0.001 0.499 0.346 0.720 Constant term 0.794 0.203 15.299 < 0.001 2.212 1.486 3.293 表 5 乳腺癌MRI影像学特征预测前哨淋巴结转移的价值
Table 5. Value of MRI imaging features of breast cancer in predicting sentinel lymph node metastasis
Index AUC SE P 95% CI Lower limit Upper limit Ratio of short diameter to long diameter 0.873 0.037 < 0.001 0.799 0.946 rADC 0.856 0.041 < 0.001 0.775 0.937 Ring enhancement 0.894 0.037 < 0.001 0.822 0.966 Constant term 0.975 0.018 < 0.001 0.940 1.000 表 6 乳腺癌MRI影像学特征预测腋窝淋巴结转移的诊断价值
Table 6. Value of MRI imaging features of breast cancer in predicting axillary lymph node metastasis.
Index AUC SE P 95% CI Lower limit Upper limit Ratio of short diameter to long diameter 0.860 0.044 < 0.001 0.774 0.946 rADC 0.876 0.040 < 0.001 0.798 0.954 Ring enhancement 0.867 0.041 < 0.001 0.787 0.947 Joint application 0.973 0.017 < 0.001 0.939 1.000 -
[1] Ou XC, Zhu JB, Qu YM, et al. Imaging features of sentinel lymph node mapped by multidetector-row computed tomography lymphography in predicting axillary lymph node metastasis[J]. BMC Med Imaging, 2021, 21(1): 193. doi: 10.1186/s12880-021-00722-0 [2] Song BI. A machine learning-based radiomics model for the prediction of axillary lymph-node metastasis in breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer, 2021, 28(3): 664-71. doi: 10.1007/s12282-020-01202-z [3] Ren T, Lin S, Huang P, et al. Convolutional neural network of multiparametric MRI accurately detects axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with pre neoadjuvant chemotherapy[J]. Clin Breast Cancer, 2022, 22(2): 170-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2021.07.002 [4] 侯筱飒, 杨振江. 前哨淋巴结阳性乳腺癌患者发生非前哨淋巴结转移的危险因素分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2021, 20(3): 284-9. doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2021.03.010 [5] Qiu SQ, Zhang GJ, Jansen L, et al. Evolution in sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2018, 123: 83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.09.010 [6] Cao SY, Liu X, Cui JW, et al. Feasibility and reliability of sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients with positive axillary nodes at initial diagnosis: an up-to-date meta-analysis of 3, 578 patients[J]. Breast, 2021, 59: 256-69. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2021.07.015 [7] Tinterri C, Gentile D, Gatzemeier W, et al. Preservation of axillary lymph nodes compared with complete dissection in T1-2 breast cancer patients presenting one or two metastatic sentinel lymph nodes: the SINODAR-ONE multicenter randomized clinical trial[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2022, 29(9): 5732-44. doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-11866-w [8] Zhang X, Yang ZH, Cui WJ, et al. Preoperative prediction of axillary sentinel lymph node burden with multiparametric MRI-based radiomics nomogram in early-stage breast cancer[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(8): 5924-39. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07674-z [9] 单嫣娜, 龚向阳, 丁忠祥, 等. 动态增强MRI影像组学特征预测乳腺癌腋窝淋巴结转移的价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2019, 53(9): 742-7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2019.09.006 [10] Lee JW, Kim SY, Han SW, et al. Clinical significance of peritumoral adipose tissue PET/CT imaging features for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer[J]. J Pers Med, 2021, 11(10): 1029. doi: 10.3390/jpm11101029 [11] 陈柯余. 乳腺癌前哨淋巴结转移相关因素分析及个体化行前哨淋巴结活检的探索[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2021. [12] Calabrese A, Santucci D, Landi R, et al. Radiomics MRI for lymph node status prediction in breast cancer patients: the state of art[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2021, 147(6): 1587-97. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03606-6 [13] Xiong JJ, Zuo W, Wu Y, et al. Ultrasonography and clinicopathological features of breast cancer in predicting axillary lymph node metastases[J]. BMC Cancer, 2022, 22(1): 1155. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10240-z [14] Samiei S, Granzier RWY, Ibrahim A, et al. Dedicated axillary MRI-based radiomics analysis for the prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(4): 757. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040757 [15] 朱娅娣, 郁义星, 杨玲. 动态增强MRI影像组学模型术前预测乳腺癌前哨淋巴结转移[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志, 2021, 44(6): 632-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWLC202106003.htm [16] Chen C, Qin YH, Chen HT, et al. A meta-analysis of the diagnostic performance of machine learning-based MRI in the prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients[J]. Insights Imaging, 2021, 12(1): 156. doi: 10.1186/s13244-021-01034-1 [17] Morawitz J, Bruckmann NM, Dietzel F, et al. Comparison of nodal staging between CT, MRI, and[18F]-FDG PET/MRI in patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2022, 49(3): 992-1001. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05502-0 [18] 暴珞宁, 王瑛, 陈东, 等. 超声影像组学标签预测乳腺癌前哨淋巴结转移的价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2021, 37(15): 2007-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYZ202115020.htm [19] 薛梅, 李静, 车树楠, 等. 乳腺癌多模态磁共振影像特征与腋窝淋巴结转移的相关性研究[J]. 磁共振成像, 2020, 11(7): 540-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGZC202007019.htm [20] 苏春艳, 杨智, 付兵, 等. 乳腺癌多模态MRI表现与前哨淋巴结是否转移的临床价值研究[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2020, 36(4): 579-82. [21] Turan U, Aygun M, Duman BB, et al. Efficacy of US, MRI, and F-18 FDG-PET/CT for detecting axillary lymph node metastasis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2021, 11(12): 2361. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11122361 -







 下载:
下载: