Correlation of CT imaging of severe pancreatitis with disease progression, serum amylase, red blood cell distribution width and lipocain-2
-
摘要:
目的 探究重症胰腺炎CT影像与病情进展及血清淀粉酶(AMS)、红细胞分布宽度(RDW)、脂质运载蛋白2(LCN2)的关系。 方法 回顾性收集2019年3月~2022年12月的105例重症胰腺炎患者临床资料,根据患者临床预后结果分为预后良好组(n=77)和预后不良组(n=28),比较两组患者CT影像结果[胰周外炎症CT评分(EPIC)、改良CT严重指数(MCTSI)]及血清AMS、RDW、LCN2水平,利用ROC曲线分析各指标对重症胰腺炎预后的评估价值。 结果 预后不良组器官功能衰竭数多于预后良好组(P=0.039),APACHE Ⅱ评分水平高于预后良好组(P=0.001);预后不良组EPIC、MCTSI评分高于预后良好组(P < 0.001),血清AMS、RDW、LCN2水平均高于预后良好组(P < 0.001);相关性分析显示,EPIC、MCTSI评分与血清AMS、RDW、LCN2水平呈正相关关系(r=0.591、0.668、0.684,0.573、0.637、0.652,P < 0.001);EPIC、MCTSI评分评估重症胰腺炎预后的曲线下面积为0.791、0.762,敏感度为82.14%、67.86%,特异性为64.94%、72.73%;血清AMS、RDW、LCN2评估重症胰腺炎预后的曲线下面积为0.758、0.754、0.851,敏感度为64.29%、78.57%、78.57%,特异性为76.62%、66.23%、80.52%;血清AMS、RDW、LCN2联合评估重症胰腺炎预后的曲线下面积为0.925,敏感度为92.86%,特异性为79.22%。 结论 重症胰腺炎患者较高的EPIC、MCTSI评分以及血清AMS、RDW、LCN2水平与预后不良有关,上述CT评分与血清学指标水平呈正相关关系,且均可用于评估患者病情进展后的不良结局,血清学指标联合评估效能最高。 Abstract:Objective To explore the relationship between CT imaging of severe pancreatitis and disease progression, serum amylase (AMS), red blood cell distribution width (RDW) and lipocain-2 (LCN2). Methods Clinical data of 105 patients with severe pancreatitis from March 2019 to December 2022 were retrospectively collected. The patients were divided into good prognosis group (n=77) and poor prognosis group (n=28) according to the clinical prognosis results of patients. CT imaging results [extra-pancreatic inflammation on CT (EPIC), modified CT severity index (MCTSI)] and serum AMS, RDW and LCN2 levels were compared between the two groups of patients. ROC curve was used to analyze the evaluated value of each indicator on prognosis of severe pancreatitis. Results The number of cases with organ failure in poor prognosis group was more than that in good prognosis group (P=0.039), and the APACHE Ⅱ score was higher than that in good prognosis group (P=0.001). EPIC score and MCTSI score were higher in poor prognosis group than those in good prognosis group (P < 0.001), and serum AMS, RDW and LCN2 levels were higher compared with those in good prognosis group (P < 0.001). Correlation analysis showed that EPIC score and MCTSI score were positively correlated with serum AMS, RDW and LCN2 levels (r=0.591, 0.668, 0.684 and 0.573, 0.637, 0.652, P < 0.001). The areas under the curves of EPIC score and MCTSI score on evaluating the prognosis of severe pancreatitis were 0.791 and 0.762, and the sensitivities were 82.14% and 67.86% and the specificities were 64.94% and 72.73%. The areas under the curves of AMS, RDW and LCN2 were 0.758, 0.754, 0.851, and the sensitivities were 64.29%, 78.57%, 78.57, the specificities were 76.62%, 66.23%, 80.52% respectively. The area under the curve, sensitivity and specificity of the combination of AMS, RDW and LCN2 on assessing the prognosis of severe pancreatitis were 0.925, 92.86% and 79.22%. Conclusion High EPIC score, MCTSI score and serum AMS, RDW and LCN2 levels in patients with severe pancreatitis are associated with poor prognosis. The above CT scores are positively correlated with serological indicators. All the indicators can be used to evaluate the poor outcomes after disease progression. The combination of serological indicators has the highest efficiency. -
Key words:
- severe pancreatitis /
- CT /
- disease condition /
- serum amylase /
- red blood cell distribution width /
- lipocain-2
-
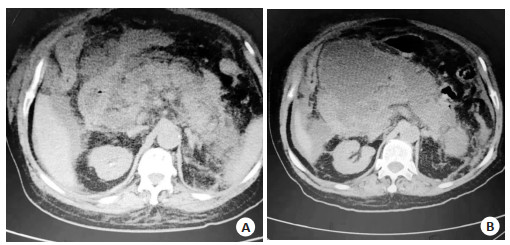
图 1 男性患者,59岁,预后良好
Figure 1. A 59-year-old male patient with good prognosis. A: Before treatment, diffuse pancreatic enlargement, decreased pancreatic tail enhancement, exudation and effusion were observed in peripheral space and bilateral prerenal space, with uniform density and unclear edge. Acute peripancreatic fluid accumulation was considered, with EPIC score of 7 points and MCTSI score of 6 points. B: After treatment, the disease condition was improved and the prognosis was good.
表 1 两组人口学特征与疾病特征
Table 1. Demographic characteristics and disease characteristics of the two groups (n)
Index Good prognosis group(n=77) Poor prognosis group(n=28) χ2/t P Age(years, Mean±SD) 57.26±10.27 61.22±8.79 1.812 0.073 Gender 0.274 0.600 Male 51 17 Female 26 11 Past medical history Hypertension 21 8 0.017 0.895 Diabetes mellitus 14 6 0.140 0.708 Coronary heart disease 18 7 0.030 0.863 Etiological classification 0.218 0.974 Biliary 29 10 Alcoholic 20 7 Hyperlipidemic 16 7 Other 12 4 Number of cases with organ failure 4.252 0.039 1 45 10 ≥2 32 18 APACHE Ⅱ score (point, Mean±SD) 22.96±6.48 27.54±5.86 3.282 0.001 Conversion to surgery 22 10 0.494 0.482 APACHE Ⅱ: Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ. 表 2 两组EPIC、MCTSI评分结果
Table 2. EPIC score and MCTSI score of the two groups (point, Mean±SD)
Group EPIC score MCTSI score Good prognosis group(n=77) 5.06±1.07 5.75±1.51 Poor prognosis group(n=28) 6.21±0.74 7.54±1.73 t 5.242 5.164 P < 0.001 < 0.001 EPIC: Extrapancreatic inflammation on abdominal computed tomography; MCTSI: Modified CT severity index. 表 3 两组血清血清AMS、RDW、LCN2水平
Table 3. Serum AMS, RDW and LCN2 levels in the two groups (Mean±SD)
Group AMS(U/L) RDW(%) LCN2(μg/L) Good prognosis group(n=77) 527.57±201.11 13.91±1.89 275.03±64.47 Poor prognosis group(n=28) 711.35±170.50 15.86±2.22 379.87±77.01 t 4.303 4.459 6.988 P < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 AMS: Serum amylase; RDW: Red blood cell distribution width; LCN2: Lipocain-2. 表 4 EPIC、MCTSI评分与血清AMS、RDW、LCN2水平的相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation between EPIC score and MCTSI score and serum AMS, RDW and LCN2 levels
CT system score AMS RDW LCN2 r P r P r P EPIC score 0.591 < 0.001 0.668 < 0.001 0.684 < 0.001 MCTSI score 0.573 < 0.001 0.637 < 0.001 0.652 < 0.001 表 5 EPIC、MCTSI评分与血清AMS、RDW、LCN2评估重症胰腺炎预后的价值
Table 5. Value of EPIC score and MCTSI score and serum AMS, RDW and LCN2 on evaluating the prognosis of severe pancreatitis
Variables AUC SE 95% CI Cut-off value Sensitivity(%) Specificity(%) EPIC 0.791 0.0418 0.701-0.864 5 82.14 64.94 MCTSI 0.762 0.0549 0.669-0.840 6 67.86 72.73 AMS 0.758 0.0503 0.665-0.836 648.38 64.29 76.62 RDW 0.754 0.0574 0.661-0.833 14 78.57 66.23 LCN2 0.851 0.0479 0.768-0.913 0.851 78.57 80.52 AMS+RDW+LCN2 0.925 0.0273 0.857-0.968 92.86 79.22 -
[1] 唐山宝, 安春霞, 则学英. 重症胰腺炎患者螺旋CT灌注参数与炎症指标及临床症状的关系[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2022, 45(3): 353-7. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2022.03.09 [2] Luo YL, Fan L, Huang LX, et al. Expression of serum autophagy-related protein P62 in patients with severe pancreatitis and its correlation with prognosis[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2022, 14(2): 1376-83. [3] 盛雅琪, 朱华栋. 急性胰腺炎相关血清学指标及评分系统综述[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2022, 31(5): 706-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDXH202011031.htm [4] Inatomi O, Bamba S, Nakai Y, et al. Diagnostic value of serum amylase levels indicating computed tomography-defined post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis[J]. Pancreas, 2020, 49(7): 955-9. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001606 [5] Karabuga B, Gemcioglu E, Konca Karabuga E, et al. Comparison of the predictive values of CRP, CRP/albumin, RDW, neutrophil/lymphocyte, and platelet/lymphocyte levels indetermining the severity of acute pancreatitis in patients with acute pancreatitis according to the BISAP score[J]. Bratislava Med J, 2022, 123(2): 129-35. doi: 10.4149/BLL_2022_020 [6] Gumpper K, Dangel AW, Pita-Grisanti V, et al. Lipocalin-2 expression and function in pancreatic diseases[J]. Pancreatology, 2020, 20(3): 419-24. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.01.002 [7] 中华医学会消化病学分会胰腺疾病学组, 中华胰腺病杂志编辑委员会, 中华消化杂志编辑委员会. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2019年, 沈阳)[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2019, 39(11): 721-30. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2019.11.001 [8] Tang MY, Zhou T, Ma L, et al. A new logistic regression model for early prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis using magnetic resonance imaging and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation Ⅱ scoring systems[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2022, 12(9): 4424-34. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-158 [9] Chen CY, Huang ZX, Li H, et al. Evaluation of extrapancreatic inflammation on abdominal computed tomography as an early predictor of organ failure in acute pancreatitis as defined by the revised Atlanta classification[J]. Medicine, 2017, 96(15): e6517. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006517 [10] Du JJ, Zhang J, Zhang XY, et al. Computed tomography characteristics of acute pancreatitis based on different etiologies at different onset times: a retrospective cross-sectional study[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2022, 12(9): 4448-61. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-1231 [11] 李成, 王丽, 李建红, 等. 血清甘油三酯与IL-6及APACHEⅡ评分对重症急性胰腺炎患者感染及预后的预测价值[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2020, 30(20): 3125-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202020021.htm [12] 罗秀平, 王洁, 吴青, 等. 急性胰腺炎评分系统的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38(9): 2188-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD202209046.htm [13] 解云川, 薛亮, 韩福刚, 等. 动态增强CT早期评价急性胰腺炎多器官功能衰竭[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2017, 33(11): 1699-702. [14] 宁晓详, 彭婕. 改良CT严重程度指数联合BISAP评分对早期急性胰腺炎预测价值[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2022, 41(4): 659-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS202204013.htm [15] Liu N, He J, Hu X, et al. Acute necrotising pancreatitis: measurements of necrosis volume and mean CT attenuation help early prediction of organ failure and need for intervention[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(10): 7705-14. [16] 金秋, 杨婧, 马红琳, 等. 不同评分系统预测高脂血症性急性胰腺炎严重程度及预后的价值分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38(11): 2551-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD202211022.htm [17] 许晨, 季杰, 周卫忠, 等. 经皮肝穿刺胆道支架植入术后高淀粉酶血症及急性胰腺炎临床预测模型的建立与验证[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2021, 30(10): 1015-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JRFS202110011.htm [18] 涂贤, 戢奇, 黄燨, 等. 红细胞分布宽度评估急性胰腺炎严重程度的研究进展[J]. 胃肠病学, 2021, 26(1): 53-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WIEC202101010.htm [19] Wang X, Zhu L, Tao K, et al. Red cell distribution width to serum albumin ratio as an early prognostic marker for severe acute pancreatitis: a retrospective study[J]. Arab J Gastroenterol, 2022, 23(3): 206-9. [20] 吴松, 周依林, 李治君. 血清LCN2、Cys C水平对急性胰腺炎并发急性肾损伤的预测价值[J]. 山东医药, 2021, 61(25): 6-9, 22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYY202125002.htm [21] 陈晨阳, 王齐艳, 吴明蓬, 等. 新亚特兰大分类下不同CT评分标准早期预测急性胰腺炎器官衰竭的价值比较[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2015, 22(1): 117-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZPWL201501042.htm -







 下载:
下载: