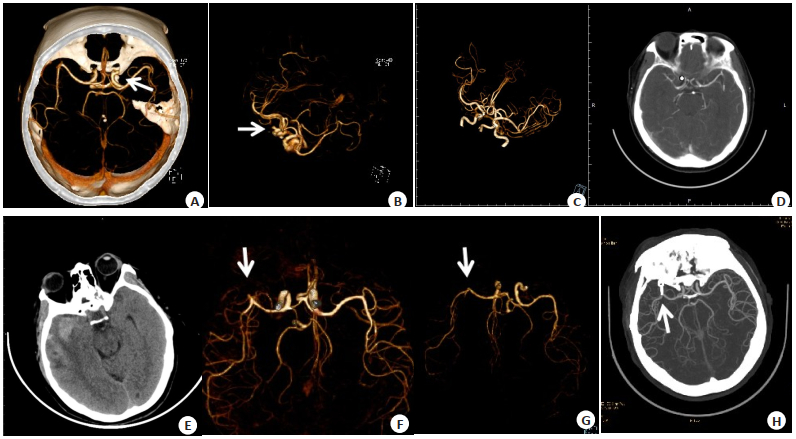
Head and neck CT angiography has higher diagnostic and value for intracranial aneurysms
-
摘要:
目的 探究头颈部CT血管成像(CTA)在颅内动脉瘤中的诊断效果及在手术指导中的应用价值。 方法 选择2018年6月~ 2021年9月本院收治的129例颅内动脉瘤疑似患者纳入研究对象,均行头颈部CTA诊断和磁共振血管成像(MRA)诊断,以数字减影血管造影(DSA)作为金标准,比较头颈部CTA诊断和MRA诊断对颅内动脉瘤的诊断及手术应用价值。 结果 以DSA诊断为“金标准”,129例颅内动脉瘤疑似患者经DSA诊断证实有80例确诊为颅内动脉瘤,头颈部CTA诊断准确度为92.24%,敏感度为95.06%,特异性为87.50%,阳性预测值为92.77%,阴性预测值为91.30%;MRA诊断准确度为88.37%,敏感度为91.46%,特异性为82.97%,阳性预测值为90.36%,阴性预测值为84.78%。头颈部CTA诊断和MRA诊断的病灶检出部位差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。头颈部CTA诊断检出 < 3 mm直径的瘤体数量多于MRA诊断(P < 0.05)。头颈部CTA诊断Kappa值为0.850,MRA诊断的Kappa值为0.747,头颈部CTA诊断与DSA诊断一致性更高。 结论 头颈部CT血管成像对颅内动脉瘤的诊断价值更高,对手术治疗具有更好的指导作用。 -
关键词:
- 电子计算机断层扫描血管成像 /
- 颅内动脉瘤 /
- 诊断价值 /
- 手术指导
Abstract:Objective To explore the diagnostic efficiency of head and neck computerized tomography angiography (CTA) for intracranial aneurysms and its application value in surgical guidance. Methods A total of 129 patients with suspected intracranial aneurysms admitted to the hospital were enrolled as the research objects from June 2018 to September 2021. All patients underwent head and neck CTA and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). Taking digital subtraction angiography (DSA) as the golden standard, application value of head and neck CTA and MRA in the diagnosis and surgical guidance of intracranial aneurysms was compared. Results Taking DSA diagnosis as the golden standard, there were 80 cases confirmed with intracranial aneurysms in the 129 patients. The diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of head and neck CTA and MRA were 92.24%, 95.06%, 87.50%, 92.77%, 91.30% and 88.37%, 91.46%, 82.97%, 90.36%, 84.78%, respectively. There was no significant difference in detection sites of lesions between head and neck CTA and MRA (P > 0.05). The number of tumors with diameter < 3 mm by head and neck CTA was more than that by MRA (P < 0.05). The Kappa values of head and neck CTA and MRA were 0.850 and 0.747, respectively. The diagnosis consistency between head and neck CTA and DSA was higher. Conclusion The diagnostic value of head and neck CTA is higher for intracranial aneurysms, which is of better guidance roles in surgical treatment. -
表 1 头颈部CTA诊断诊断结果
Table 1. Diagnostic results of head and neck CTA (n)
DSA诊断 头颈部CTA诊断 MRA诊断 合计 阳性 阴性 阳性 阴性 阳性 77 6 75 8 83 阴性 4 42 7 39 46 合计 81 48 82 47 129 DSA: 数字减影血管造影; CTA: CT血管成像; MRA: 磁共振血管成像. 表 2 病灶检出部位比较
Table 2. Detection of lesion location [n(%)]
病灶检出部位 头颈部CTA诊断 MRA诊断 χ2/Fisher P 颈内动脉 12(15.00) 11(13.75) 0.025 0.875 大脑前动脉 9(11.25) 8(10.00) 0.040 0.842 前交通动脉 22(27.50) 22(27.50) 0.011 0.918 后交通动脉 18(22.50) 17(21.25) 0.013 0.927 大脑中动脉 4(5.00) 5(6.25) - 0.744 大脑后动脉 7(8.75) 7(8.75) 0.003 0.959 椎基底动脉 5(6.25) 5(6.25) 0.002 0.966 合计 77(96.25) 75(93.75) 0.526 0.468 表 3 不同直径瘤体检出情况比较
Table 3. Detection of tumors of different diameters [n(%)]
瘤体直径(mm) 头颈部CTA诊断 MRA诊断 χ2/ Fisher P < 3(n=20) 18(90.00) 12(60.00) 4.801 0.028 3~5(n=27) 26(96.29) 24(92.30) 1.081 0.299 6~9(n=21) 20(95.23) 18(85.71) 1.105 0.293 > 9(n=12) 12(100.00) 12(100.00) - 1.000 表 4 诊断价值比较
Table 4. Comparison of diagnostic value
诊断方法 准确度(%) 敏感度(%) 特异性(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) Kappa值 头颈部CTA诊断 93.02 96.25 87.75 92.77 93.47 0.850 MRA诊断 88.37 91.46 82.97 90.36 84.78 0.747 χ2 0.051 0.031 0.056 0.012 0.059 - P 0.821 0.861 0.812 0.912 0.808 - -
[1] Etminan N, Dörfler A, Steinmetz H. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms-pathogenesis and individualized management[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2020, 117(14): 235-42. [2] Molenberg R, Aalbers MW, Appelman APA, et al. Intracranial aneurysm wall enhancement as an indicator of instability: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Neurol, 2021, 28(11): 3837-48. doi: 10.1111/ene.15046 [3] Furukawa H, Wada K, Tada Y, et al. Mast cell promotes the development of intracranial aneurysm rupture[J]. Stroke, 2020, 51(11): 3332-9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.030834 [4] Shikata F, Shimada K, Sato H, et al. Potential influences of gut microbiota on the formation of intracranial aneurysm[J]. Hypertension, 2019, 73(2): 491-6. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11804 [5] Kwon OK. Headache and aneurysm[J]. Neuroimaging Clin N Am, 2019, 29(2): 255-60. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2019.01.004 [6] Petridis AK, Kamp MA, Cornelius JF, et al. Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Deutsches Ärzteblatt Int, 2017, 114(13): 226-36. [7] Hainc N, Mannil M, Anagnostakou V, et al. Deep learning based detection of intracranial aneurysms on digital subtraction angiography: a feasibility study[J]. Neuroradiol J, 2020, 33(4): 311-7. doi: 10.1177/1971400920937647 [8] Al Kasab S, Nakagawa D, Zanaty M, et al. In vitro accuracy and inter-observer reliability of CT angiography in detecting intracranial aneurysm enlargement[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2019, 11(10): 1015-8. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-014737 [9] Ryu KH, Baek HJ, Moon JI, et al. Usefulness of noncontrast-enhanced silent magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) for treated intracranial aneurysm follow-up in comparison with time-of-flight MRA[J]. Neurosurgery, 2020, 87(2): 220-8. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyz421 [10] 武丽卿. 256层螺旋CT脑血管成像在颅内动脉瘤诊断中的应用价值[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2018, 18(2): 204-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWLC201802020.htm [11] 徐鹏, 陈英, 施小燕, 等. 3D-CTA对颅内后循环出血性动脉瘤早期诊断的价值[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2020, 29(1): 126-31. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2020.01.020 [12] 赵伟国, 粘琦玉, 夏文骞. CTA联合彩色多普勒超声诊断颅内动脉瘤的准确性及影像特点研究[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2021, 19(1): 41-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2021.01.014 [13] 邓喜青, 王炜, 李一辉, 等. 双源双能量CTA与DSA测量颅内动脉瘤几何参数Bland-Altman一致性分析[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2020, 36(12): 2024-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2020.12.034 [14] 郭书丽, 张翠兰, 逯书娟, 等. 对比剂增强MRA与MR血管壁成像技术在颅内动脉瘤诊断中的联合应用价值研究[J]. 中国医学装备, 2020, 17(6): 50-3. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2020.06.014 [15] 朱君孺, 马燕. 多层螺旋CT扫描成像诊断颅内动脉瘤患者的影像学特征及其应用优越性分析[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2020, 18(9): 37-9, 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2020.09.012 [16] 张翠兰, 郭书丽, 王延岗, 等. CTA与MRA在颅内不同部位动脉瘤诊断及破裂出血风险预测的价值研究[J]. 中国医学装备, 2019, 16(7): 84-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXZB201907021.htm [17] 邹明洋, 曾玉蓉, 唐润辉, 等. 1.5T MRA与64排螺旋CTA在颅内动脉瘤患者诊断中的比较分析[J]. 广州医科大学学报, 2019, 47(1): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXI201901007.htm [18] 肖寄余, 喻红. CTA和MRA对颅内动脉瘤的诊断价值比较[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2020, 22(11): 1727-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn431274-20190530-00643 [19] 李锐, 郭文才, 吴过, 等. 计算机体层血管成像联合IL-6、TNF-α水平检测对颅内动脉瘤的诊断价值[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2022, 45(5): 733-6. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2022.05.20 [20] 安红俭, 李勇毅. 脑动脉CTA与MRA对颅内动脉瘤的诊断价值分析[J]. 贵州医药, 2019, 43(12): 1966-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2019.12.058 -







 下载:
下载: