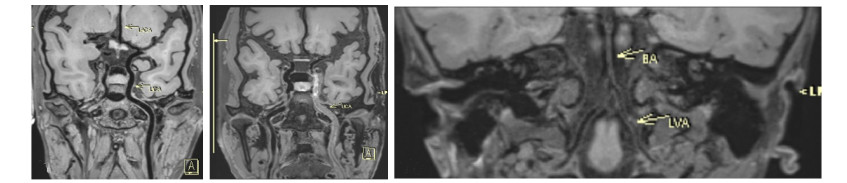
Relationship between carotid atherosclerotic plaque and plasma Lp-PLA2 level in patients with cerebral infarction based on high-resolution magnetic resonance scanning
-
摘要:
目的 采用高分辨率MRI扫描法,探讨颈动脉粥样硬化(CAS)斑块影像学特征与脑梗死患者血浆脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2(Lp-PLA2)水平的关系。 方法 选取2019年6月~2020年6月于我院收治的196例脑梗死患者为脑梗死组,另选取同期我院收治的无脑梗死患者40例为对照组,对比两组一般资料及斑块分布; 分析脑梗死组患者斑块性质; 根据斑块是否稳定将脑梗死患者分为稳定斑块组(n=61)、不稳定斑块组(n=123)和无斑块组(n=12),对比3组生化指标(总胆固醇、三酰甘油、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇、低密度蛋白胆固醇)及Lp-PLA2水平; 对比不同斑块分级(0级、1级、2级、3级)患者Crouse积分与Lp-PLA2水平; 采用Pearson分析法分析脑梗死患者Crouse积分与Lp-PLA2相关性。 结果 196例脑梗死患者中,184例(93.88%)有CAS斑块; 对照组40例中,9例(22.50%)有CAS斑块; 脑梗死组CAS斑块发生率高于对照组(P < 0.05); 稳定斑块组、不稳定斑块组和无斑块组生化指标中总胆固醇、三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇及Lp-PLA2表达水平均为无斑块组 < 稳定斑块组 < 不稳定斑块组(P < 0.05),3组高密度脂蛋白胆固醇表达水平均为不稳定斑块组 < 稳定斑块组 < 无斑块组(P < 0.05); 脑梗死患者不同斑块分级Crouse积分和Lp-PLA2水平差异比较均有统计学意义(P < 0.05),且Crouse积分和Lp-PLA2水平比较1级 < 2级 < 3级(P < 0.05); 经Pearson相关性分析结果显示:脑梗死患者斑块分级Crouse积分和Lp-PLA2水平呈正相关关系(P < 0.05)。 结论 脑梗死患者经高分辨率MRI扫描可显示CAS斑块大小和性质可见明显异常,且CAS斑块分级与血清Lp-PLA2水平有一定的相关性,血清Lp-PLA2水平可反映患者CAS斑块情况。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the relationship between the imaging characteristics of carotid atherosclerotic plaque (CAS) and plasma lipoprotein- associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) in patients with cerebral infarction by high resolution MRI scanning. Methods A total of 196 patients with cerebral infarction admitted to our hospital from June 2019 to June 2020 were selected as the cerebral infarction group. Forty patients without cerebral infarction admitted to our hospital wards during the same period were selected as the control group. The general information and plaque distribution of the two groups were compared. The plaque properties of all patients with cerebral infarction were compared. Patients with cerebral infarction were divided into stable plaque group (n=61), unstable plaque group (n=123) and no plaque group (n=12) according to whether the plaque was stable. Biochemical indexes (total cholesterol, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, low density protein cholesterol) and Lp-PLA2 levels in the three groups were compared. Crouse score and Lp-PLA2 level in patients with different plaque grades (grade 0, 1, 2 and 3) were compared. The correlation between Crouse score and Lp-PLA2 in patients with cerebral infarction was analyzed by Pearson analysis. Results Among 196 patients with cerebral infarction, 184 (93.88%) had CAS plaque. Of the 40 in control group, 9 (22.50%) had CAS plaques; The incidence of CAS plaque in cerebral infarction group was higher than that in control group (P < 0.05). The expression levels of total cholesterol, triglyceride, low density protein cholesterol and Lp- PLA2 in the stable plaque group, the unstable plaque group and the non-plaque group were lower than that in the stable plaque group and the unstable plaque group (P < 0.05), and the high density lipoprotein cholesterol expression levels in the three groups were lower than that in the stable plaque group and the non-plaque group (P < 0.05). There were statistically significant differences in Crouse score and Lp-PLA2 level in different plaque grades of cerebral infarction patients (P < 0.05). The Crouse score and Lp-PLA2 level were compared in grade 1 < grade 2 < grade 3 (P < 0.05). The Pearson correlation analysis showed that there was a positive correlation between plaque grade Crouse score and Lp-PLA2 level in patients with cerebral infarction (P < 0.05). Conclusion High resolution MRI scan of cerebral infarction patients can show significant abnormalities in the size and nature of CAS plaques. There is a certain correlation between CAS plaque grade and serum Lp-PLA2 level, and serum Lp-PLA2 level can reflect the status of CAS plaques in patients. -
表 1 两组一般资料对比
Table 1. Comparison of two groups of general data (n)
组别 性别 年龄(岁, Mean±SD) 糖尿病 高血压 吸烟 饮酒 男 女 脑梗死组(n=196) 101 95 60.49±6.31 93 84 57 43 对照组(n=40) 25 15 60.77±6.24 18 16 17 11 χ2/t 1.612 0.256 0.083 0.112 3.239 3.529 P 0.205 0.798 0.777 0.739 0.072 0.06 表 2 颈动脉斑块性质与CAS斑块分布情况
Table 2. Characteristics of Carotid artery plaque and distribution of CAS plaque (n)
组别 斑块分型 部位 颈总动脉 颈动脉分叉处 颈内动脉 脑梗死组(n=196) Ⅰ~Ⅱ型 12 12 18 Ⅲ型 24 6 18 Ⅳ~Ⅴ型 31 49 37 Ⅵ型 37 18 73 Ⅶ型 0 0 12 Ⅷ型 0 7 13 对照组(n=40) Ⅰ~Ⅱ型 3 8 9 Ⅲ型 0 0 2 Ⅳ~Ⅴ型 0 0 0 Ⅵ型 0 0 0 Ⅶ型 0 0 0 Ⅷ型 0 0 0 CAS: 颈动脉粥样硬化. 表 3 3组生化指标及Lp-PLA2水平对比
Table 3. Comparison of biochemical indices and Lp-PLA2 levels among three groups (Mean±SD)
组别 TC(mmol/L) TG(mmol/L) HDL(mmol/L) LDL(mmol/L) Lp-PLA2(ng/mL) Fib(g/L) 无斑块组(n=12) 3.94±0.45 1.42±0.18 1.34±0.19 2.47±0.30 127.05±14.77 3.38±0.42 稳定斑块组(n=61) 4.54±0.56 1.59±0.20 1.35±0.20 2.49±0.31 176.93±19.28 3.43±0.44 不稳定斑块组(n=123) 5.08±0.61 2.01±0.22 1.19±0.15 3.15±0.37 216.98±24.59 3.46±0.46 F 32.906 107.693 20.664 84.433 130.433 0.229 P < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.796 TC: 总胆固醇; TG: 三酰甘油; HDL: 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇; LDL: 低密度蛋白胆固醇; Lp-PLA2: 脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2. 表 4 脑梗死患者斑块分级Crouse积分和Lp-PLA2水平比较
Table 4. Comparison of plaque grading Crouse score and Lp-PLA2 level in patients with cerebral infarction (Mean±SD)
组别 Crouse(分) Lp-PLA2(ng/mL) 1级(n=76) 3.26±0.37 166.42±18.18 2级(n=58) 3.94±0.43 212.59±24.20 3级(n=50) 4.58±0.51 243.59±27.62 F 144.354 179.201 P < 0.001 < 0.001 -
[1] 李楠, 郑关毅. 高血压颈动脉粥样硬化痰瘀证与脑梗死的关系[J]. 福建医科大学学报, 2020, 54(5): 308-12, 347. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4194.2020.05.006 [2] Xu M, He XY, Huang P. The relationship between the mean platelet volume and carotid atherosclerosis and prognosis in patients with acute cerebral infarction[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020(6): 6685740. [3] 杨秀芹. 老年脑梗死病人再发缺血性卒中与脑出血微血管病变和预后的关系分析[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2017, 15(5): 619-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1349.2017.05.033 [4] Alhusaini S, Karama S, Nguyen TV, et al. Association between carotid atheroma and cerebral cortex structure at age 73 years[J]. Ann Neurol, 2018, 84(4): 576-87. doi: 10.1002/ana.25324 [5] Sui BB, Gao PY. High-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging of carotid and intracranial vessels[J]. Acta Radiol, 2019, 60 (10): 1329-40. doi: 10.1177/0284185119826538 [6] Danihel L, Madarász Š, Blazícek P, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and the risk of ischemic stroke[J]. Česká a Slovenská Neurol a Neurochir, 2018, 2018(3): 308-13. [7] 黄玉静, 吴正刚, 黄晶, 等. 血浆脂蛋白磷脂酶A2、同型半胱氨酸与急性脑梗死患者病情严重程度及血脂水平的相关性分析[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2017, 17(35): 6909-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWCX201735026.htm [8] Kao TH, Pan HC, Sun MH, et al. Upper thoracic sympathectomy for axillary osmidrosis or bromidrosis[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2004, 11(7): 719-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2003.11.001 [9] Okazaki S, Moriwaki H, Minematsu K, et al. Extremely early computed tomography signs in hyperacute ischemic stroke as a predictor of parenchymal hematoma[J]. Cerebrovasc Dis, 2008, 25 (3): 241-6. doi: 10.1159/000113862 [10] 李自超, 王欣, 马冬梅, 等. 脑梗死患者颈动脉粥样硬化斑块数量的影响因素[J]. 西安交通大学学报: 医学版, 2018, 39(2): 292-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAYX201802032.htm [11] 李春玲, 蔺田芳. 高分辨率磁共振成像技术对大脑中动脉粥样硬化斑块的评价分析[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2018, 28(2): 203-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ201802010.htm [12] Zhao DL, Li C, Chen XH, et al. Reproducibility of 3.0T high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging for the identification and quantification of middle cerebral arterial atherosclerotic plaques[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2019, 28(7): 1824-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.04.020 [13] Tibuakuu M, Kianoush S, DeFilippis AP, et al. Usefulness of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity and C-reactive protein in identifying high-risk smokers for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (from the atherosclerosis risk in communities study)[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2018, 121(9): 1056-64. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.01.020 [14] 陆怡德, 吴佳宁, 彭奕冰. 血清Lp-PLA2水平在急性缺血性脑卒中患者中的临床应用[J]. 检验医学, 2020, 35(2): 129-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHYY202002009.htm [15] 黄耀忠, 王永健, 李明海, 等. 血浆脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2水平与急性颈动脉硬化性脑梗死防治效果及硬化斑块稳定性的相关性研究[J]. 卒中与神经疾病, 2018, 25(3): 272-5, 280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0478.2018.03.008 [16] Yan Z, Fu BS, He D, et al. The relationship between oxidized low-density lipoprotein and related ratio and acute cerebral infarction[J]. Medicine, 2018, 97(39): e12642. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012642 [17] 梅花, 曹建. 颈动脉粥样硬化患者血浆脂蛋白磷脂酶A2水平与脑血管意外发生的关系[J]. 内科急危重症杂志, 2018, 24(6): 483-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKJW201806017.htm [18] Yur'eva EA, Sukhorukov VS, Murashov AN, et al. Biochemical indicators of atherogenic and protective activity of xydiphone in experimental animals[J]. Bull Exp Biol Med, 2012, 153(4): 459-62. doi: 10.1007/s10517-012-1740-6 [19] 陈娟, 万曦, 陈玲, 等. 急性脑梗死患者颈动脉斑块内新生血管超声造影评价及其与血清YKL-40蛋白及Lp-PLA2水平的相关性分析[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2020, 20(15): 2877-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWCX202015015.htm [20] Huang L, Yao SG. Carotid artery color Doppler ultrasonography and plasma levels of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and cystatin C in arteriosclerotic cerebral infarction[J]. J Int Med Res, 2019, 47(9): 4389-96. doi: 10.1177/0300060519859141 -







 下载:
下载: