Value of amide proton chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI in predicting the prognosis of neurological function in cerebral infarction
-
摘要:
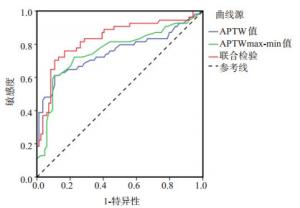
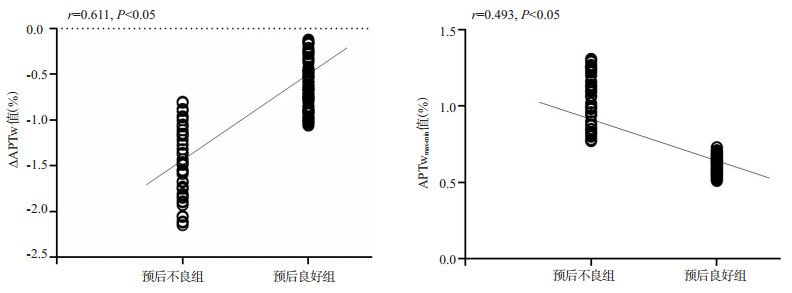
目的分析氨基质子化学交换饱和磁共振成像预测脑梗死神经功能预后的价值。 方法选择2017年7月~2019年7月我院收治的138例脑梗死患者,根据其入院3月后的改良Rankin量表评分(mRS)分为预后良好组(mRS < 2分,n=84)与预后不良组(mRS≥2分,n=54),两组均行氨基质子化学交换饱和磁共振成像检查,对两组氨基质子加权信号值(APTw)进行定量分析比较,分析ΔAPTw值、APTwmax-min值与脑梗死神经功能预后的关系,分析∆APTw值、APTwmax-min值对脑梗死神经功能预后的预测价值。 结果预后不良组∆APTw值低于预后良好组(P < 0.05);预后不良组APTwmax-min值高于预后良好组(P < 0.05);∆APTw值与脑梗死神经功能预后呈正相关(P < 0.05);APTwmax-min值与脑梗死神经功能预后呈负相关(P < 0.05);∆APTw值减小、APTwmax-min值增加是脑梗死神经功能预后不良的危险因素(P < 0.05);∆APTw值联合APTwmax-min值预测脑梗死神经功能预后的AUC为0.832,敏感度为75.91%,特异性为83.32%,准确度为88.32%,∆APTw值的临界值为-0.92,APTwmax-min值的临界值为0.75。 结论氨基质子化学交换饱和磁共振成像中APTw的定量分析能够较好的预测脑梗死神经功能预后,在脑梗死患者氨基质子化学交换饱和磁共振成像检查过程中若发现∆APTw值减小、APTwmax-min值增加,临床应及时采取干预措施,改善其预后。 -
关键词:
- 氨基质子化学交换饱和磁共振成像 /
- 脑梗死 /
- 预后 /
- 相关性 /
- 预测价值
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate value of amide proton chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI in predicting the prognosis of neurological function in cerebral infarction. MethodsA total of 138 patients with cerebral infarction in our hospital from July 2017 to July 2019 were enrolled. Based on modified Rankin scale score (mRS) at post-admission 3 months, they were divided into two groups: good prognosis group (n=84, mRS < 2) and poor prognosis group (n=54, mRS≥2). All patients received amide proton chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI examinations. The amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) signal intensity was quantitatively analyzed in both groups. The correlation of ∆APTw value and APTwmax-min value with neurological function prognosis of cerebral infarction was analyzed, and the predictive value of two indicators on neurological function prognosis was also verified. ResultsThe ∆APTw value of poor prognosis group was lower than that of good prognosis group (P < 0.05). APTwmax-min value of poor prognosis group was higher than that of good prognosis group (P < 0.05). ∆APTw value was positively correlated with prognosis of cerebral infarction neurological function (P < 0.05). APTwmax-min value was negatively correlated with neurological function prognosis of cerebral infarction (P < 0.05). Decrease in ∆APTw value and increase in APTwmax-min value were risk factors for poor neurological prognosis of cerebral infarction (P < 0.05). The AUC, sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of ∆APTw value combined with APTwmax-min in predicting the neurological prognosis of cerebral infarction were 0.832, 75.91%, 83.32%, and 88.32%, respectively. The critical values of ∆APTw and APTwmax-min were-0.92 and 0.75, respectively. ConclusionQuantitative analysis of APTW in amide proton chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI has high value in predicting the neurological function prognosis of cerebral infarction, moreover, clinical intervention measures are of vital importance when there is a decrease in ∆APTw value and increase in APTwmax-min value. -
表 1 两组∆APTW值、APTwmax-min值比较
Table 1. Comparison of ∆APTw and APTwmax-min between the two groups (%, Mean±SD)
组别 ∆APTW值 APTwmax-min值 预后良好组(n=84) -0.59±0.47 0.62±0.11 预后不良组(n=54) -1.48±0.69 1.05±0.29 t 8.319 -10.425 P < 0.001 < 0.001 表 2 脑梗死神经功能预后的影响因素分析
Table 2. Analysis of influencing factors of neurological function prognosis in cerebral infarction
变量 P 相对危险度 95%CI 年龄 0.592 1.251 0.551~2.841 性别 0.230 0.671 0.349~1.288 BMI 0.167 1.590 0.823~3.071 合并糖尿病 0.550 1.234 0.620~2.453 合并高血压 0.330 1.439 0.692~2.995 合并高血脂 0.248 0.987 0.965~1.009 合并心脏病 0.368 1.616 0.569~4.588 吸烟史 0.350 1.072 0.927~1.240 饮酒史 0.755 1.017 0.914~1.132 ∆APTw值减小 < 0.001 2.927 1.347~5.288 APTwmax-min值 0.008 2.319 1.319~4.629 -
[1] 王琳, 沈广澍. ESSEN卒中风险评分低危和高危脑梗死患者应用3D-TOF-MRA的颅内血管特点分析[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2018, 29(7): 461-3, 467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYX201807004.htm [2] 郝璐, 贾琳, 王红, 等. MRI-PWI对脑梗死前期患者微循环状态评价的研究[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2019, 17(8): 1-3, 14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2019.08.001 [3] Huang P, He XY, Xu M. Effect of argatroban injection on clinical efficacy in patients with acute cerebral infarction: preliminary findings[J]. Eur Neurol, 2021: 1-5. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/348670294_Effect_of_Argatroban_Injection_on_Clinical_Efficacy_in_Patients_with_Acute_Cerebral_Infarction_Preliminary_Findings [4] Inoue K, Shimokawa S, Yoshioka F, et al. A case of pediatric moyamoya disease with severe cerebral vasospasm and delayed cerebral infarction following an intraventricular hemorrhage[J]. Childs Nerv Syst, 2021, 37(2): 695-8. doi: 10.1007/s00381-020-04769-2 [5] Chan RW, Chen H, Myrehaug S, et al. Quantitative CEST and MT at 1.5T for monitoring treatment response in glioblastoma: early and late tumor progression during chemoradiation[J]. J Neurooncol, 2021, 151(2): 267-78. doi: 10.1007/s11060-020-03661-y [6] Villano D, Romdhane F, Irrera P, et al. A fast multislice sequence for 3D MRI-CEST pH imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 85(3): 1335-49. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28516 [7] Poblador Rodriguez E, Moser P, Auno S, et al. Real-time motion and retrospective coil sensitivity correction for CEST using volumetric navigators (vNavs) at 7T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 85(4): 1909-23. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28555 [8] 戴真煜, 陈飞, 姚立正, 等. 磁共振扩散张量成像和三维伪连续动脉自旋标记在鉴别超急性与急性缺血性脑梗死中的联合应用[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(17): 1327-32. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.17.009 [9] 张思雨, 孙洪赞. 酰胺质子转移加权成像在肿瘤中的应用进展[J]. 磁共振成像, 2019, 10(8): 629-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGZC201908017.htm [10] 黄振宇, 李武铭, 江桂华. 氨基质子饱和转移效应MRI技术研究进展[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2018, 34(9): 1422-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201809052.htm [11] 陈龙, 余成新. 磁共振氨基质子转移成像对颅脑疾病的诊断价值[J]. 实用医技杂志, 2017, 24(9): 999-1000. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYJ201709032.htm [12] 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2018, 51(9): 666-82. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2018.09.004 [13] 沈丽萍, 杨江胜, 刘东柏, 等. 高迁移率族蛋白B1水平与急性脑梗死病情严重程度及预后的关联研究[J]. 中华神经医学杂志, 2019, 18(11): 1131-5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-8925.2019.11.009 [14] Jin T, Wang P, Hitchens TK, et al. Enhancing sensitivity of pH-weighted MRI with combination of amide and guanidyl CEST [J]. Neuroimage, 2017, 157: 341-50. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.06.007 [15] Breitling J, Meissner JE, Zaiss M, et al. Optimized dualCEST-MRI for imaging of endogenous bulk mobile proteins in the human brain [J]. NMR Biomed, 2020, 33(5): e4262. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4262 [16] Crescenzi R, Donahue PMC, Mahany H, et al. CEST MRI quantification procedures for breast cancer treatment-related lymphedema therapy evaluation[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2020, 83(5): 1760-73. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28031 [17] Goerke S, Breitling J, Korzowski A, et al. Clinical routine acquisition protocol for 3D relaxation-compensated APT and rNOE CEST-MRI of the human brain at 3T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 86(1): 393-404. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28699 [18] Zhou J, Heo HY, Knutsson L, et al. APT-weighted MRI: Techniques, current neuro applications, and challenging issues[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 50(2): 347-64. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26645 [19] Khlebnikov V, Siero JCW, Bhogal AA, et al. Establishing upper limits on neuronal activity-evoked pH changes with APT-CEST MRI at 7 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 80(1): 126-36. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27013 [20] Zhou J, Heo HY, Knutsson L, et al. APT-weighted MRI: Techniques, current neuro applications, and challenging issues[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 50(2): 347-64. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26645 [21] Lee SY, Kim DY, Sohn MK, et al. Determining the cut-off score for the Modified Barthel Index and the Modified Rankin Scale for assessment of functional independence and residual disability after stroke[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(1): e0226324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226324 [22] Borggrefe J, Goertz L, Abdullayev N, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy with the novel NeVa M1 stent retriever: do the drop zones represent a risk or a benefit?[J]. World Neurosurg, 2021, 148: e121-9. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.12.075 [23] 陈南耀, 余丹. 联合检测血清miR-124与miR-182的表达水平对急性脑梗死诊断与预后评估的价值[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2019, 27(6): 502-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3949.2019.06.008 [24] Ye F, Bao GS, Xu HS, et al. Effect of platelet count on long-term prognosis of cerebral infarction[J]. Restor Neurol Neurosci, 2020, 38(3): 265-70. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/344074899_Effect_of_platelet_count_on_long-term_prognosis_of_cerebral_infarction [25] 赵建华, 李月娟, 梁可可, 等. 肢体缺血后处理改善脑梗死预后和认知障碍[J]. 国际神经病学神经外科学杂志, 2019, 46(3): 268-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWSK201903009.htm -







 下载:
下载: