Application of OSMS in radiotherapy of children's tumors
-
摘要:
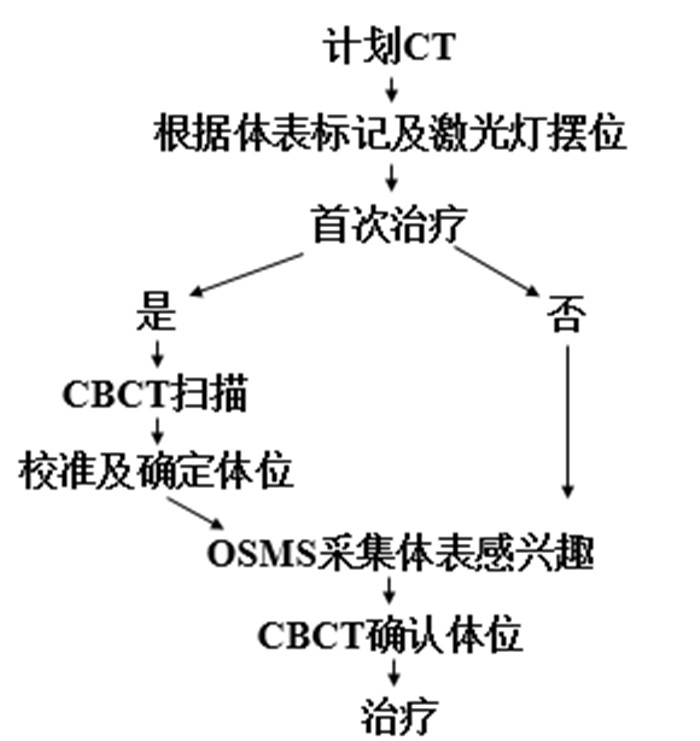
目的探讨光学体表追踪技术(OSMS)在儿童肿瘤精准放射治疗中的摆位精度及其应用价值。 方法选取6例儿童肿瘤患者,应用体表标记、激光灯配合OSMS协助摆位,每次摆位后治疗前进行锥形束CT(CBCT)扫描。分别记录OSMS及CBCT的左右、头脚、上下方向移动的误差。分析两组摆位误差关系,应用Bland-Altman法评估两种系统的一致性。治疗期间利用OSMS监测患者体位变化。 结果CBCT与OSMS的左右、头脚、上下方向的移动误差分别是:0.207±0.076 cm,0.207±0.073 cm;0.186±0.072 cm,0.183±0.069 cm;0.206±0.068 cm,0.198±0.071 cm,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。在CBCT与OSMS的左右、头脚、上下方向的移动差值分别有4.65%(6/129)、5.43%(7/129)、3.88%(5/129)在95% LoA之外,在其一致性范围内,差值的绝对值最大分别为0.06、0.09、0.11 cm。 结论OSMS是一种高精度、高效的图像引导方式,能精准地减少摆位误差,提高摆位的效率,适合于儿童肿瘤的精准放疗。 Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the positioning accuracy and application value of optical body surface tracking technology (OSMS) in precision radiotherapy for children's tumors. MethodsSix pediatric tumor patients were included. The body surface marking, laser light and optical surface tracking technology (OSMS) were applied to verified the patients pretreatment position, and perform CBCT scan before treatment after each positioning. The error of the left and right, head and foot, up and down directions of OSMS and CBCT were record. The χ2 test was used to compare the two groups to analyze the set-up error relationship between the two groups, and the Bland-Altman method was used to evaluate the consistency of the two systems. During treatment, the patient's posture changes were observed by OSMS monitors. ResultsThe movement errors of CBCT and OSMS in the left and right, head and foot, and up and down directions were: 0.207±0.076 cm, 0.207±0.073 cm; 0.186±0.072 cm, 0.183±0.069 cm; 0.206±0.068 cm, 0.198±0.071 cm, which had no significant difference (P>0.05). There were 4.65% (6/129), 5.43% (7/129), 3.88% (5/129) of movement differences between CBCT and OSMS in the left and right, head and foot, up and down directions Outside of 95% LoA. In the consistency range, the maximum absolute values of the differences were 0.06, 0.09, 0.11 cm, respectively. ConclusionOSMS is a high-precision and high-efficiency image guidance method, which can accurately reduce positioning errors and improve positioning efficiency. It is suitable for precise radiotherapy of childhood tumors. -
Key words:
- childhood tumors /
- image-guided radiotherapy /
- OSMS /
- CBCT /
- set-up error
-
表 1 患者摆位移动统计
Table 1. Statistics of patient position movement(cm)
参数 左右 头脚 上下 CBCT OSMS CBCT OSMS CBCT OSMS 均数 0.207 0.207 0.187 0.183 0.206 0.198 标准差 0.076 0.073 0.072 0.073 0.068 0.071 t 0.037 0.724 1.710 P 0.971 0.471 0.090 CBCT: 锥形束CT; OSMS: 光学体表追踪技术. -
[1] Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492 [2] Pallotta S, Vanzi E, Simontacchi G, et al. Surface imaging, portal imaging, and skin marker set-up vs. CBCT for radiotherapy of the Thorax and pelvis[J]. Et Al, 2015, 191(9): 726-33. [3] Krengli M, Gaiano S, Mones E, et al. Reproducibility of patient setup by surface image registration system in conformal radiotherapy of prostate cancer[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2009, 4: 9. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-4-9 [4] Alderliesten T, Betgen A, Elkhuizen PH, et al. Estimation of heart-position variability in 3D-surface-image-guided deep-inspiration breath-hold radiation therapy for left-sided breast cancer[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2013, 109(3): 442-7. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2013.09.017 [5] Alderliesten T, Sonke JJ, Betgen A, et al. 3D surface imaging for monitoring intrafraction motion in frameless stereotactic body radiotherapy of lung cancer[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2012, 105(2): 155-60. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2012.08.016 [6] Li G, Ballangrud A, Chan M, et al. Clinical experience with two frameless stereotactic radiosurgery (fSRS) systems using optical surface imaging for motion monitoring[J]. J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2015, 16(4): 149-62. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i4.5416 [7] Alaei P, Spezi E. Imaging dose from cone beam computed tomography in radiation therapy[J]. Phys Med, 2015, 31(7): 647-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2015.06.003 [8] Krasin MJ, Xiong XP, Wu SJ, et al. The effects of external beam irradiation on the growth of flat bones in children: modeling a dose-volume effect[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2005, 62(5): 1458-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.01.024 [9] Lin C, Donaldson SS, Meza JL, et al. Effect of radiotherapy techniques (IMRT vs. 3D-CRT) on outcome in patients with intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma enrolled in COG D9803: a report from the Children's Oncology Group[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2012, 82(5): 1764-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.01.036 [10] Miralbell R, Lomax A, Cella L, et al. Potential reduction of the incidence of radiation-induced second cancers by using proton beams in the treatment of pediatric tumors[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2002, 54(3): 824-9. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3016(02)02982-6 [11] Bölling T, Weege J, Eich HT, et al. Acute and late side effects to salivary glands and oral mucosa after head and neck radiotherapy in children and adolescents. Results of the "Registry for the evaluation of side effects after radiotherapy in childhood and adolescence"[J]. Head Neck, 2015, 37(8): 1137-41. doi: 10.1002/hed.23715 [12] Stanley DN, McConnell KA, Kirby N, et al. Comparison of initial patient setup accuracy between surface imaging and three point localization: a retrospective analysis[J]. J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2017, 18(6): 58-61. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12183 [13] Hattel SH, Andersen PA, Wahlstedt IH, et al. Evaluation of setup and intrafraction motion for surface guided whole-breast cancer radiotherapy[J]. J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2019, 20(6): 39-44. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12599 [14] Peguret N, Dahele M, Slotman BJ, et al. RPM tracing for the detection of changes in lung tumor position: in response to Alderliesten et al. Radiother Oncol 2012; 105(2): 155-60[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2013, 107(2): 261-2. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2013.03.020 [15] Prasert A, Kanjana B. Accuracy evaluation of image-guided radiation therapy guided by optical surface monitoring system for treatment of intracranial tumors[J]. J Thai Assoc Radiat Oncol, 2019, 25(2): 28-36. [16] Betgen A, Alderliesten T, Sonke JJ, et al. Assessment of set-up variability during deep inspiration breath hold radiotherapy for breast cancer patients by 3D-surface imaging[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2013, 106(2): 225-30. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2012.12.016 [17] Bartoncini S, Fiandra C, Ruo Redda MG, et al. Target registration errors with surface imaging system in conformal radiotherapy for prostate cancer: study on 19 patients[J]. La Radiol Med, 2012, 117 (8): 1419-28. doi: 10.1007/s11547-012-0823-9 [18] Alderliesten T, Betgen A, Elkhuizen PH, et al. Estimation of heart-position variability in 3D-surface-image-guided deep-inspiration breath-hold radiation therapy for left-sided breast cancer[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2013, 109(3): 442-7. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2013.09.017 -







 下载:
下载: