PI model of ultrasonic diagnosis predicting the 5- year recurrence of postoperative hepatocellular carcinoma
-
摘要:
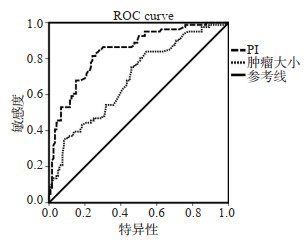
目的探讨影响肝细胞肝癌(HCC)术后5年复发情况的超声诊断因素并建立预测指数(PI)模型,评价该模型的预测价值。 方法对所有相关超声诊断因素进行Kaplan-Meier和Log-rank单因素分析和多因素Cox回归分析,得出预测因子以及回归系数,根据预测因子以及回归系数建立超声诊断预测HCC术后5年复发情况的PI模型,对PI模型进行有效性检验和多因素校正,绘制PI模型预测HCC术后5年复发情况的ROC曲线,评价该模型对于判断HCC术后5年复发情况的预测价值。 结果多因素Cox回归分析结果示:肿瘤边界(β=0.14,OR=1.23)、肿瘤部位(β=0.36,OR=1.58)、肿瘤大小(β=0.59,OR=2.42)、肿瘤数目(β= 0.41,OR=1.79)为影响HCC术后5年复发情况的独立预测因子,根据预测因子以及回归系数建立PI预测模型:PI=0.14×X1(边界清=0,边界不清=1)+0.36×X2(周围型=0,中央型=1)+0.59×X3(cm)+0.41×X4(单发=0,多发=1),PI的临界值为1.66,模型有效性(χ2=12.43,P < 0.05),PI模型经多因素校正成为独立预测因子(β=1.08,OR=2.91),PI模型的ROC曲线下的面积为0.812(0.765~ 0.957),准确度为78.7%。 结论本研究提出了超声诊断预测HCC术后5年复发情况的PI模型以及预测临界值,该模型的预测价值较高,为临床对HCC术后复发情况的精准评估提供的依据。 Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the ultrasonic diagnosis factors influencing the 5-year recurrence of postoperative hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and establish Predict Index (PI) model. MethodsKaplan-Meier and Log- rank univariate analysis and multivariate Cox regression analysis were used to analyze all related ultrasonic diagnosis factors, and the predictive factors and regression coefficients were obtained. According to the predictive factors and regression coefficients, a PI model was established to predict the 5-year recurrence of postoperative HCC by ultrasonic diagnosis. The validity of the PI model was tested and multivariate adjusted to draw ROC curve of PI model to predict the 5-year recurrence of postoperative HCC and evaluate the predictive value of this model for the 5-year recurrence of postoperative HCC. ResultsMultivariate Cox regression analysis showed that tumor boundary (β=0.14, OR=1.23), tumor site (β=0.36, OR=1.58), tumor size (β=0.59, OR=2.42), tumor number (β=0.41, OR=1.79) were independent predictors of the 5-year recurrence of postoperative HCC. According to the predictors and regression coefficient, PI prediction model was established as: PI=0.14×X1 (clear boundary=0, unclear boundary= 1)+0.36×X2 (surrounding type=0, central type=1)+0.59×X3 (cm) +0.41×X4 (single engine=0, multiple engine=1), the cut off of PI was 1.66, the validity of PI was 12.43 by χ2 test (P < 0.05). PI model was an independent predictor after multivariate factor correction (β =1.08, OR=2.91), the area under ROC curve of PI model was 0.812 (0.765-0.957), and the accuracy was 78.7%. ConclusionWe put forward PI model of ultrasonic diagnosis predicting the 5-year recurrence of postoperative HCC and the critical value at the first time. This model had a high predictive value, which provided a strong basis with clinical accurate assessment of the recurrence of postoperative HCC. -
Key words:
- hepatocellular carcinoma /
- ultrasonic diagnosis /
- recurrence /
- PI model
-
表 1 超声诊断预测HCC术后5年复发情况的Kaplan-Meier单因素分析
Table 1. Kaplan-Meier univariate analysis of ultrasound diagnosis to predict the recurrence of HCC after 5 years
项目 n 累计复发率(%) χ2 P 1年 2年 3年 5年 性別 2.83 0.063 男 123 37.0 45.1 58.4 64.4 女 55 34.5 43.7 53.7 60.8 年龄(岁) 1.76 0.223 < 55 80 35.5 41.8 54.7 60.7 ≥55 98 38.8 44.9 57.3 64.2 肝硬化 2.12 0.096 有 62 37.2 45.6 56.8 64.9 无 116 34.1 41.8 51.4 62.3 肿块回声 1.45 0.262 弱或低回声 74 34.3 42.1 54.4 62.5 中或高回声 104 37.6 44.6 59.2 65.4 肿瘤部位 8.91 0.002 中央型 76 45.2 59.6 63.2 68.7 周围型 102 30.2 42.8 50.9 57.5 肿瘤边界 7.32 0.010 边界清 87 30.5 40.2 53.5 55.2 边界不清 91 37.4 47.6 59.4 64.8 肿瘤血供 1.64 0.243 丰富 92 37.1 45.6 55.9 65.5 不丰富 86 34.2 42.2 53.7 61.3 肿瘤数目 9.12 0.000 单发 112 27.6 32.6 50.8 61.4 多发 66 39.2 45.9 57.5 66.2 肿瘤大小(cm) 8.98 0.000 < 5 131 28.2 40.9 52.7 58.5 5~10 47 40.5 56.1 64.9 67.3 HCC: 肝细胞肝癌. 表 2 超声诊断预测HCC术后5年复发情况的Cox多因素分析
Table 2. Cox multivariate analysis of ultrasound diagnosis to predict the recurrence of HCC after 5 years
选人变量 β SE Wald 自由度 P OR 95%CI 肿瘤边界 0.14 0.18 5.68 1 0.041 1.23 1.03~2.87 肿瘤部位 0.36 0.32 9.12 1 0.005 1.58 1.22~2.94 肿瘤大小 0.59 0.30 12.23 1 0.000 2.42 1.63~3.87 肿瘤数目 0.41 0.13 7.98 1 0.013 1.79 1.31~2.94 表 3 PI模型预测HCC术后5年复发情况的Cox回归分析
Table 3. Cox regression analysis of PI model to predict the recurrence of HCC after 5 years
PI值 β SE Wald值 自由度 P OR 95%CI 未校正 1.08 0.14 11.62 1 0.000 2.91 2.13~4.24 校正后 1.06 0.14 11.62 1 0.000 2.91 2.13~4.24 表 4 PI模型预测价值的验证
Table 4. Verification of PI model predictive value
界值 总数(n) 复发(n) 未复发(n) 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) 准确度(%) AUROC ≥ 1.66 105 90 15 - - - - - 0.765~0.957 < 1.66 73 23 50 - - - - - 总计 178 113 65 79.6 76.9 85.7 68.5 78.7 0.812 AUROC: 接受者操作特征曲线下面积. -
[1] Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics[J]. CA: A Cancer J Clin, 2011, 61(2): 69-90. doi: 10.3322/caac.20107 [2] Zhang XF, Qi X, Meng B, et al. Prognosis evaluation in alphafetoprotein negative hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: comparison of five staging systems[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2010, 36 (8): 718-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2010.05.022 [3] 丁雪明, 李智贤, 韦康来, 等. 肝细胞癌的超声造影定量灌注参数与MVD、VEGF表达的关系[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2009, 25(11): 1054-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCY200911022.htm [4] 阎涛, 赵建军, 毕新宇, 等. 肝细胞肝癌术后预后因素分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2013, 35(1): 54-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZL200808008.htm [5] 林满霞, 张晓儿, 陈泽斌, 等. 超声造影定量灌注分析在术前评估肝细胞癌组织分化程度中的应用[J]. 中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志, 2019, 8(4): 353-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHZW201904017.htm [6] 吴晓贝, 罗鸿昌, 李开艳, 等. 超声造影LI-RADS分类在肝细胞癌诊断中的应用价值[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2018, 27(11): 936-41. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10459-1019115498.htm [7] 刘明, 徐明, 李晓菊, 等. 超声造影定量分析评价HCC行TACE术后局部疗效的影响因素[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2019, 21(8): 1129-32, 1135. [8] 伍艳玲, 冯勤付. 原发性肝细胞肝癌手术联合放疗的进展[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2019, 39(7): 554-7. [9] Gadiparthi C, Ali B, Cholankeril R, et al. Futility of ultrasonography as a screening tool for HCC in patients waitlisted for liver transplant. is it time to revisit screening guidelines for hepatocellular carcinoma?[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 152(5): S1183-4. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039974790310_f744.html [10] N'Gbesso RD, Attia A, Mahassadi A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) observed in Abidjan: aspects and role of ultrasonography[J]. J Radiol, 1998, 79(5): 409-14. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/9757269 [11] Kim HA, Kim KA, Choi JI, et al. Comparison of biannual ultrasonography and annual non-contrast liver magnetic resonance imaging as surveillance tools for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with liver cirrhosis (MAGNUS-HCC): a study protocol[J]. BMC Cancer, 2017, 17(1): 877. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3819-y [12] Sasaki K, Shindoh J, Margonis GA, et al. Effect of background liver cirrhosis on outcomes of hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. JAMASurg, 2017, 152(3): e165059. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2016.5059 [13] Tang YF, Wang RY, Zhang YB, et al. Co-upregulation of 14-3-3ζ and P-Akt is associated with oncogenesis and recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 45(3): 1097-107. doi: 10.1159/000487351 [14] Pan YX, Chen JC, Fang AP, et al. A nomogram predicting the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients after laparoscopic hepatectomy[J]. Cancer Commun: Lond, 2019, 39(1): 55. doi: 10.1186/s40880-019-0404-6 [15] Rui SZ, Yan J, Zhang H, et al. Intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients with a high HBV-DNA load may benefit from postoperative anti-hepatitis B virus therapy[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2017, 96(30): e7608. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007608 [16] Ryu T, Takami Y, Wada Y, et al. Actual 10-year survival after surgical microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-center experience in Japan[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2019, 26(12): 4126-33. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07646-8 [17] Blüthner E, Bednarsch J, Malinowski M, et al. Dynamic liver function is an independent predictor of recurrence-free survival after curative liver resection for HCC-A retrospective cohort study[J]. Int J Surg, 2019, 71: 56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.08.033 [18] Jiang J, Hu H, Liu R, et al. Nomogram for individualized prediction of recurrence after postoperative adjuvant TACE for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2017, 96(32): e7390. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007390 [19] Ng KK, Cheung TT, Pang HH, et al. A simplified prediction model for early intrahepatic recurrence after hepatectomy for patients with unilobar hepatocellular carcinoma without macroscopic vascular invasion: an implication for adjuvant therapy and postoperative surveillance[J]. Surg Oncol, 2019, 30: 6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2019.05.017 [20] 刘畅, 张一帆. 脂肪酸代谢在恶性肿瘤发生机制及分子影像中的应用[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2020, 43(1): 16-9 doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2020.01.04 -







 下载:
下载: