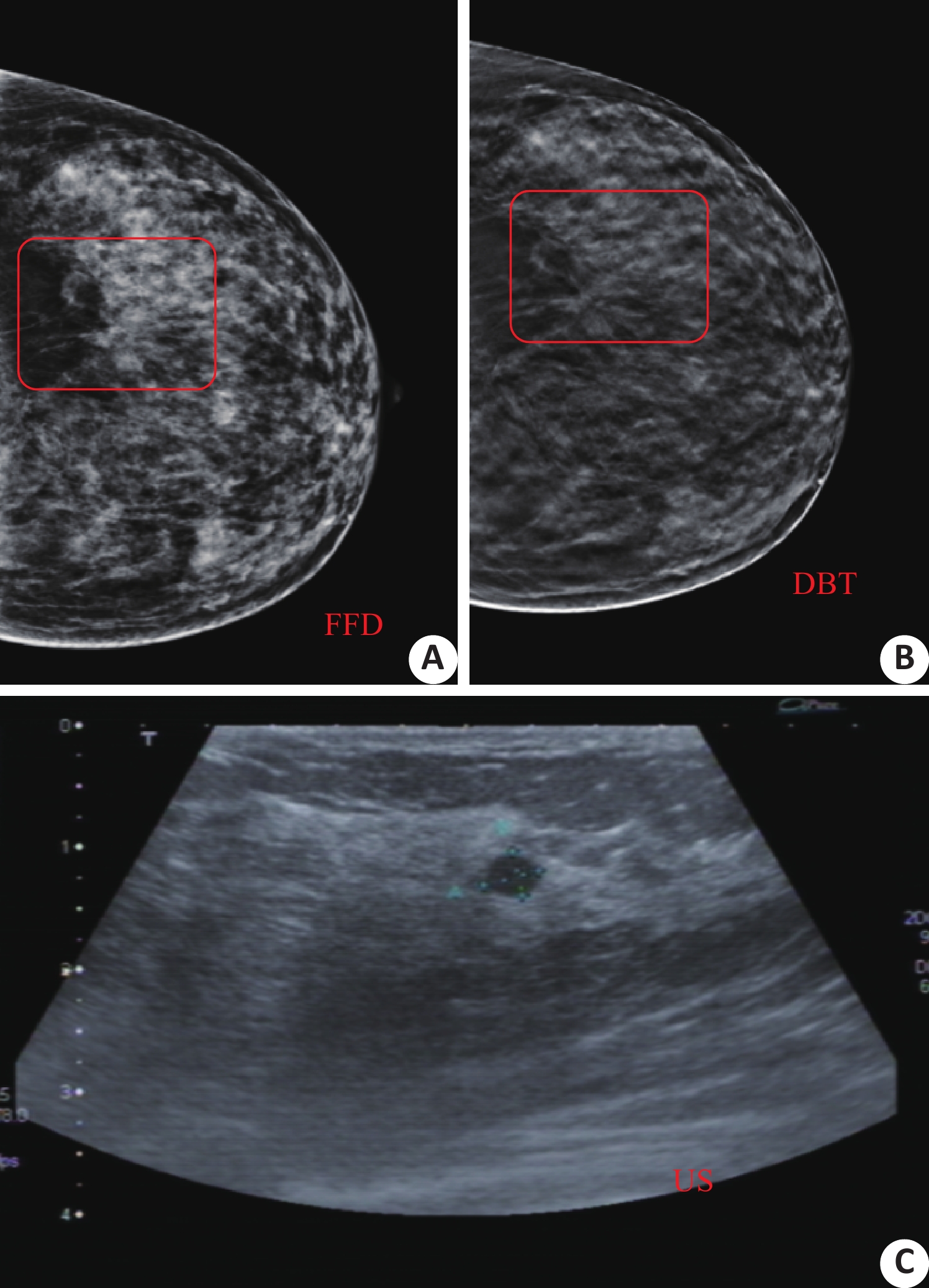
Comparison of mammography and ultrasonography in benign and malignant structural distortion
-
摘要:
目的研究乳腺X线摄影(全数字化乳腺摄影与数字乳腺断层摄影)及彩超对于结构扭曲良恶性病变诊断效能对比研究及结构扭曲在X线征象的分析方法。 方法收集本院2013年6月~2018年12月就诊的51例乳腺疾病患者,年龄20~70岁(44.84±8.738岁),均接受全数字化乳腺摄影、数字乳腺断层摄影及彩超检查且发现单纯结构扭曲征象,同时具有病理结果,根据乳腺影像报告和数据系统进行阅片诊断,比较3种影像学方法的诊断效能及结构扭曲的征象分析。 结果Fisher精确算法分析显示,结构扭曲X线征象(中心密度、病灶边缘情况、病变区周围腺体结构)均在良恶性鉴别存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。ROC曲线分析发现,3种检查方式曲线下面积均大于0.5,均具有乳腺疾病诊断价值。3种检查方法,数字乳腺断层摄影敏感度 ( 67.5%)大于全数字化乳腺摄影( 62.2%)及彩超(61.9%),特异性数字乳腺断层摄影均高于其他两者。 结论数字乳腺断层摄影相对于全数字化乳腺摄影、彩超能更好地观察结构扭曲病变,提高诊断效能。 Abstract:ObjectiveTo study the comparative study of mammography (full digital mammography FFDM, digital mammography DBT) and ultrasonography on benign and malignant structural distortion and its X-ray sign analysis. MethodsCollecting 51 patients, with the age from 20 to 70 years old (average 44.84±8.738) , who underwent FFDM, DBT and color Doppler ultrasound examinations from June 2013 to December 2018 and found signs of structural distortion and pathological findings. According to the mammography report and data system, the diagnostic diagnosis and the analysis of the signs of structural distortion of the three imaging methods were compared. ResultsFisher's precise algorithm was used to analyze the X-ray signs of structural distortion, which had significant difference between benign and malignant (P<0.05). The diagnostic efficiency of three methods in breast diseases was analyzed by ROC curve. The study found that the area under the curve were greater than 0.5, is a valuable diagnostic sensitivity. ConclusionCompared with FFDM,and US, DBT can better observe the structural distortion and improve the diagnostic efficacy. -
表 1 乳腺X线各征象分析
Table 1. Analysis of signs of breast X line
Sign Benign(n) malignant(n) P Center density <0.01 LOW 19 2 Equal 9 8 High 13 Marginal situation <0.01 Infiltration 12 14 Stellate 1 6 Vague 15 3 Lesion area structure <0.01 Disappear 11 22 Visible 17 1 -
[1] Kamra A, Jain VK, Singh S, et al. Characterization of Architectural Distortion in Mammograms Based on texture analysis using support vector machine classifier with clinical evaluation[J]. J Digit Imaging, 2016, 29(1): 104-14. doi: 10.1007/s10278-015-9807-3 [2] Durand MA, Wang S, Hooley RJ, et al. Tomosynthesis-detected architectural distortion: management algorithm with radiologic-pathologic correlation[J]. Radiographics, 2016, 42(2): 311-21. [3] 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会. 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌诊治指南与规范(2017年版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2017, 27(9): 695-759. [4] Zeeshan M, Salam B, Khalid QB, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of digital mammography in the detection of breast cancer[J]. Cureus, 2018, 10(4): e2448-59. [5] Phantana-Angkool A, Forster MR, Warren YE, et al. Rate of radial scars by core biopsy and upgrading to malignancy or high-risk lesions before and after introduction of digital breast tomosynthesis[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2018, 36(9): 1012-23. [6] Lewin JM, Dorsi CJ, Hendrick RE, et al. Clinical comparison of full-field digital mammography and screen-film mammography for detection of breast cancer[J]. AJR, 2002, 179(3): 671-7. doi: 10.2214/ajr.179.3.1790671 [7] Burton A, Byrnes G, Stone J, et al. Mammographic density assessed on paired raw and processed digital images and on paired screen-film and digital images across three mammography systems[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2016, 18(2): 130-41. [8] 朱薇萍, 张盛箭, 顾雅佳. 乳腺X线摄影、磁共振对结构扭曲良恶性病变的对比研究[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2016, 26(8): 1422-5. [9] 刘万花. 乳腺疾病影像诊断学[M]. 江苏: 江苏科学技术出版社, 2011. [10] 马 捷, 徐坚民, 孙国平, 等. 乳腺结构扭曲征象的X线分析[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2007, 23(4): 527-31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-3289.2007.04.014 [11] Lacson R, Harris K, Brawarsky P, et al. Evaluation of an automated information extraction tool for imaging data elements to populate a breast cancer screening registry[J]. J Digit Imaging, 2015, 28(5): 567-75. doi: 10.1007/s10278-014-9762-4 [12] Sarah WS, Jennifer G, Nathalie J, et al. Pathology results of architectural distortion on detected with digital breast tomosynthesis without definite sonographic correlate[J]. Am J Surg, 2019, 51(1): 29-40. [13] Zyout I, Togneri R. A computer-aided detection of the architectural distortion in digital mammograms using the fractal dimension measurements of BEMD[J]. Comput Med Imaging Graph, 2018, 57(4): 520-31. [14] Dibble EH, Lourenco AP, Baird GL, et al. Comparison of digital mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis in the detection of architectural distortion[J]. Eur Radiol, 2018, 28(1): 3-10. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-4968-8 [15] Mariscotti G, Durando M, Houssami N. Comparison of synthetic mammography, reconstructed from digital breast tomosynthesis, and digital mammography: evaluation of lesion conspicuity and BI-RADS assessment categories[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2017, 166(3): 765-73. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4458-3 [16] Patel BK, Covington M, Pizzitola VJ, et al. Initial Experience of tomosynthesis-guided vacuum-assisted biopsies of tomosynthesis-detected (2D Mammography and Ultrasound Occult) architectural distortions[J]. Am J Roentgenol, 2018, 210(6): 1395-400. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.18802 [17] Si QC, Jian XY, Qing SC, et al. Significance and application of digital breast tomosynthesis for the BI-RADS classification of breast cancer[J]. J PCP, 2015, 16(9): 4109-14. [18] Partyka L, Lourenco AP, Mainiero MB. Detection of mammographically occult architectural distortion on digital breast tomosynthesis screening: initial clinical experience[J]. Am J Roentgenol, 2014, 203(1): 216-22. doi: 10.2214/AJR.13.11047 [19] Taskin F, Durum Y, Soyder A, et al. Review and management of breast lesions detected with breast tomosynthesis but not visible on mammography and ultrasonography[J]. Acta Radiol, 2017, 58(12): 1442-7. doi: 10.1177/0284185117710681 [20] Jin YK, Hyun JK, Jong KS, et al. Biologic profiles of invasive breast cancers detected only with digital breast tomosynthesis[J]. AJR, 2017, 209(1): 1-8. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.18430 [21] Destounis S, Arieno A, Morgan R, et al. Qualitative versus quantitative mammographic breast density assessment: applications for the US and abroad[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2017, 7(2): 30-41. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics7020030 [22] 李明强, 马 昆, 陶 熙, 等. 数字乳腺层析成像系统影像链的设计与优化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(2): 192-200. -







 下载:
下载: