Antitumor activity of Verteporfin in renal cell carcinoma 769-P cells and its mechanism
-
摘要:
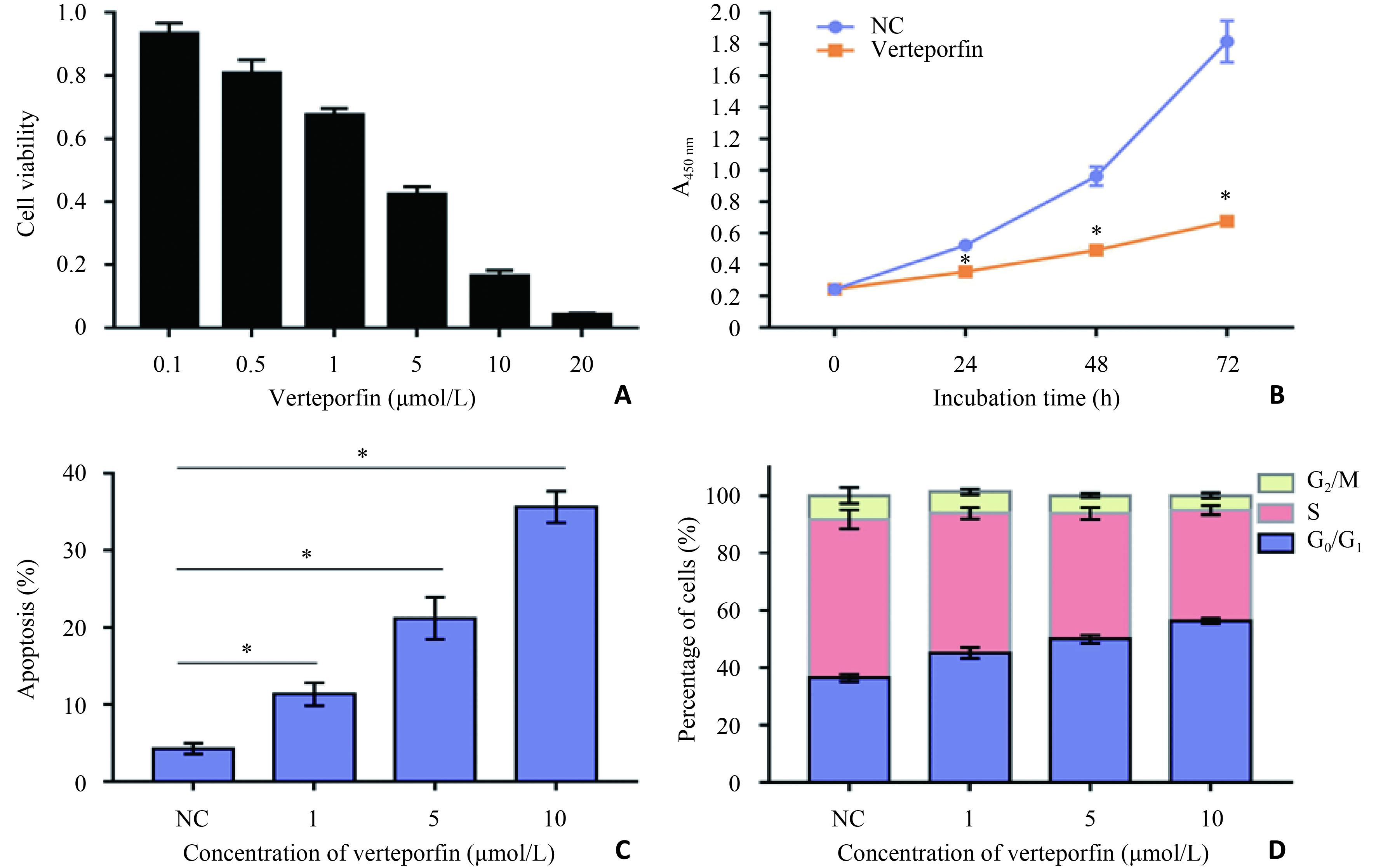
目的 研究维替泊芬影响肾癌769-P细胞的作用及潜在机制。 方法 采用不同浓度(0、1、5、10 μmol/L)维替泊芬处理肾癌细胞株769-P,分别采用CCK8检测维替泊芬对769-P细胞活性的抑制作用;流式细胞术分析维替泊芬促进769-P细胞凋亡及抑制细胞周期;划痕实验观察维替泊芬影响769-P细胞迁移能力;克隆形成实验观察维替泊芬抑制769-P细胞集落形成能力;荧光定量PCR法及免疫印迹法分别分析维替泊芬作用于769-P细胞后,CDK4、Bax、CyclinD1、Bcl-2、YAP、TEAD及caspase-3的表达量变化情况。 结果 维替泊芬对769-P细胞的半数抑制浓度为4.917 μmol/L(P<0.05)。维替泊芬可诱导769-P细胞凋亡并阻滞细胞生长周期,抑制细胞增殖作用呈浓度及时间依赖性(P<0.05)。维替泊芬处理后769-P细胞迁移能力及克隆形成能力亦呈浓度依赖性降低(P<0.05)。维替泊芬处理后769-P细胞的转录和翻译水平均受影响,caspase-3被激活,Bax及CDK4表达量增加,YAP、Bcl-2、cyclinD1和TEAD表达量减少(P<0.05)。 结论 维替泊芬具有杀伤肾癌细胞的能力,为探寻肾癌新药开拓了新方向。 Abstract:Objective To explore the ability of Verteporfin killing renal cell carcinoma 769-P cells and its potential mechanism. Methods 769-P was treated with different concentrations (0, 1, 5 and 10 μmol/L) of Verteporfin. The effect of Verteporfin on 769-P cell proliferation was assessed by CCK8. Flow cytometry was applied to examine the effect of Verteporfin on 769-P cell cycle and apoptosis. Wound healing assay and colony forming assay were applied to evaluate the capacity of cell migration and colony formation, respectively. Quantitative Real-time PCR and Western blotting were applied to determine the mRNA and protein levels of CDK4, Bax, CyclinD1, Bcl-2, YAP, TEAD and caspase-3. Results Verteporfin significantly inhibited the growth of 769-P cells with an IC50 of 4.917 μM. Verteporfin induced both apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of 769-P cells in a dose-dependent manner. The migration and colony forming ability were also inhibited by Verteporfin in a dose-dependent manner. Verteporfin regulated both transcriptional and translational level in 769-P cells. CDK4 and Bax were up-regulated while CyclinD1, Bcl-2, YAP and TEAD were down-regulated. Moreover, caspase-3 was activated. Conclusion Verteporfin has significant antitumor effect against renal tumor cells, suggesting it’s a novel therapeutic agent for renal cell carcinoma. -
Key words:
- renal cell carcinoma /
- verteporfin /
- cell cycle /
- cell apoptosis
-
表 1 实时荧光定量PCR引物序列
Gene Primer sequence(5′-3′) YAP Forward primer GCCCAGTTATACCTCAGTGTTGTAG Reverse primer GGTCTCCTTCAGGTCAGTACAG TEAD Forward primer GCCCATGTGCGAGTACCT Reverse primer TCCAGGACGCTGTTCATCA Bcl-2 Forward primer GAGCACAGAAGATGGGAACACT Reverse primer AGGTGCATGGATTTACTCAGTATC CyclinD1 Forward primer CTGGGTCTGTGCATTTCTGGTT Reverse primer CTGCTGGAAACATGCCGGTTA Bax Forward primer GATGCGTCCACCAAGAAGC Reverse primer CACGGCGGCAATCATCCT Caspase-3 Forward primer GGCTGAGCTGCCTGTAACTTG Reverse primer TGGCTCTGCCTTCATGGAAC CDK4 Forward primer GCTGCCATGGAAGGAAGAAA Reverse primer GCCTCAGAGATAAAGGCAAAGATTG GAPDH Forward primer CCTGCACCACCAACTGCTTAG Reverse primer TGAGTCCTTCCACGATACCAA -
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65(1): 5-29 doi: 10.3322/caac.21254 [2] Han ZW, Zhang Y, Sun Y, et al. ER beta-Mediated Alteration of circATP2B1 and miR-204-3p Signaling Promotes Invasion of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2018, 78(10): 2550-63 doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1575 [3] Cheng J, Zhang J, Han YT, et al. Integrative analysis of histopathological images and genomic data predicts clear cell renal cell carcinoma prognosis[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(21): e91-100 doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0313 [4] Tan X, Liu Y, Hou J, et al. Targeted therapies for renal cell carcinoma in Chinese patients: focus on everolimus[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2015, 8(4): 313-21 [5] Sun X, Lou LH, Zhong KZ, et al. MicroRNA-451 regulates chemoresistance in renal cell carcinoma by targeting ATF-2 gene[J]. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 2017, 242(12): 1299-305 doi: 10.1177/1535370217701625 [6] Rowe SP, Gorin MA, Solnes LB, et al. Correlation of Tc-99m-sestamibi uptake in renal masses with mitochondrial content and multi-drug resistance pump expression[J]. EJNMMI Res, 2017, 7(1): 80-5 doi: 10.1186/s13550-017-0329-5 [7] Giuliano S, Cormerais Y, Dufies M, et al. Resistance to sunitinib in renal clear cell carcinoma results from sequestration in lysosomes and inhibition of the autophagic flux[J]. Autophagy, 2015, 11(10): 1891-904 doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1085742 [8] Xiao W, Lou N, Ruan HL, et al. Mir-144-3p promotes cell proliferation, metastasis, sunitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by downregulating ARID1A[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2017, 43(6): 2420-33 doi: 10.1159/000484395 [9] Zhao ZY, Chen CJ, Lin JZ, et al. Synergy between von Hippel-Lindau and P53 contributes to chemosensitivity of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 14(3): 2785-90 doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5561 [10] Chen R, Zhu S, Fan XG, et al. High mobility group protein B1 controls liver Cancer initiation through yes-associated protein-dependent aerobic glycolysis[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(5): 1823-41 doi: 10.1002/hep.v67.5 [11] Ciamporcero E, Shen H, Ramakrishnan S, et al. YAP activation protects urothelial cell carcinoma from treatment-induced DNA damage[J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35(12): 1541-53 doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.219 [12] Dong L, Lin F, Wu WJ, et al. Verteporfin inhibits YAP-induced bladder Cancer cell growth and invasion via Hippo signaling pathway[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2018, 15(6): 645-52 doi: 10.7150/ijms.23460 [13] Wang L, Kim D, Wise JT, et al. p62 as a therapeutic target for inhibition of autophagy in prostate Cancer[J]. Prostate, 2018, 78(5): 390-400 doi: 10.1002/pros.v78.5 [14] Hua G, Lv X, He C, et al. YAP induces high-grade serous carcinoma in fallopian tube secretory epithelial cells[J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35(17): 2247-65 doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.288 [15] Feng JT, Gou JH, Jia J, et al. Verteporfin, a suppressor of YAP-TEAD complex, presents promising antitumor properties on ovarian Cancer[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2016, 9(3): 5371-81 [16] Garcia-Rendueles ME, Ricarte-Filho JC, Untch BR, et al. NF2 loss promotes oncogenic RAS-Induced thyroid cancers via YAP-Dependent transactivation of RAS proteins and sensitizes them to MEK inhibition[J]. Cancer Discov, 2015, 5(11): 1178-93 doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0330 [17] Chen M, Zhong L, Yao SF, et al. Verteporfin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human leukemia NB4 cells without light activation[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2017, 14(10): 1031-9 doi: 10.7150/ijms.19682 [18] Chen C, Liu TS, Zhao SC, et al. XIAP impairs mitochondrial function during apoptosis by regulating the Bcl-2 family in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 15(5): 4587-93 [19] Li G, Wang ZM, Chong T, et al. Curcumin enhances the radiosensitivity of renal cancer cells by suppressing NF-kappa B signaling pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 94(9): 974-81 [20] Huang Q, Li F, Liu X, et al. Caspase 3-mediated stimulation of tumor cell repopulation during Cancer radiotherapy[J]. Nat Med, 2011, 17(7): 860-6 doi: 10.1038/nm.2385 [21] Wei HL, Wang FH, Wang Y, et al. Verteporfin suppresses cell survival, angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via disrupting the YAP-TEAD complex[J]. Cancer Sci, 2017, 108(3): 478-87 doi: 10.1111/cas.13138 [22] Li H, Huang ZL, Gao M, et al. Inhibition of YAP suppresses CML cell proliferation and enhances efficacy of imatinib in vitro and in vivo[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2016, 35(1): 134-7 doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0414-z [23] Patnaik A, Rosen LS, Tolaney SM, et al. Efficacy and safety of abemaciclib, an inhibitor of CDK4 and CDK6, for patients with breast cancer, Non-Small cell lung cancer, and other solid tumors[J]. Cancer Discov, 2016, 6(7): 740-53 doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0095 -







 下载:
下载: