Clinical observation of two different surgical positions in the treatment of patients with lumbar disc herniation
-
摘要:
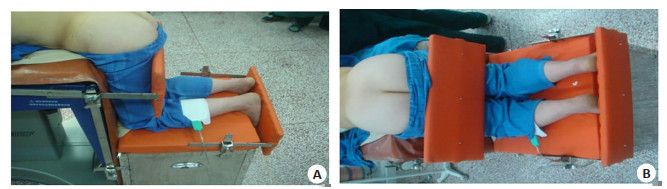
目的 比较两种不同体位下行开放性手术治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床疗效,探讨简易跪式手术床在跪式体位下行椎板开窗减压髓核摘除术的临床优势。 方法 选取2019年12月~2020年12月于河西学院附属张掖人民医院骨科收治的132例单节段单侧腰椎间盘突出症患者,行单侧椎板开窗减压髓核摘除术治疗。采用随机数字表法将患者进行分组,就采用简易跪式手术床在跪式体位下手术治疗的患者(观察组,n=67)和采用常规手术床在俯卧位下手术治疗的患者(对照组,n=65)手术效果展开对比。比较两组患者的手术时间、术中出血量、术后卧床时间、术后住院时间及并发症发生情况的差异;比较两组患者术前、术后1周及1、3、6月的Oswestry功能障碍指数、疼痛视觉模拟评分及两组患者术后6月的临床疗效(MacNab优良率)。 结果 观察组的手术时间、术中出血量、卧床时间、住院时间及并发症例数均小于对照组(P < 0.05);与术前相比,两组患者术后1周及1、3、6月的Oswestry功能障碍指数和视觉模拟评分均明显低于术前(P < 0.05);与对照组相比,术后1周及1、3、6月,观察组患者的Oswestry功能障碍指数和视觉模拟评分均低于对照组(P < 0.05);术后随访6月,观察组患者手术治疗后的临床疗效优于对照组(MacNab优良率91.04% vs 84.62%,P < 0.05)。 结论 两种术式均可行椎板单侧开窗减压髓核摘除,消除神经症状。跪式体位下行椎板单侧开窗减压髓核摘除术能够明显缓解患者术后的疼痛程度,提高手术疗效,术后患者恢复快。 Abstract:Objective To compare the clinical effect of two kinds of open operation in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation under different position, and discuss the clinical advantage of simple kneeling operation table in the lamina decompression and decompression of nucleus pulpotomy under kneeling position. Methods A total of 132 patients with single lumbar disc herniation were treated with unilateral laminectomy decompression of Lumbar core. Patients were randomly divided into two groups. We used a numerical table extraction method to compare the surgical outcomes of patients treated with a simple kneeling table in the kneeling position (observation group, n=67) and patients treated with a conventional table in the prone position (control group, n=65). The operative time, intraoperative blood loss, postoperative bed time, postoperative hospital stay and complications of two groups were compared. The Oswestry dysfunction index (ODI), visual analogue score (VAS) and clinical efficacy (MacNab excellent and good rate) of the two groups before operation, 1 week after operation and 1, 3, 6 months after operation were compared. Results The operative time, intraoperative blood loss, bed time, hospital stay and the number of complications in the observation group were significantly less than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Compared with before surgery, ODI index and VAS score of 2 groups 1 week and 1, 3, 6 months after surgery were significantly lower than before surgery (P < 0.05). Compared with control group, ODI index and VAS score of observation group were lower than control group at 1 week and 1, 3, 6 months after surgery (P < 0.05). After 6 months of follow-up, the clinical efficacy of observation group was significantly better than control group (MacNab excellent and good rate: 91.04% vs 84.62%, P < 0.05). Conclusion Both methods are feasible for unilateral lamina decompression and removal of nucleus pulposus. Postoperative MRI showed that the responsible disc and nerve compression operation was satisfactory. But kneeling position of unilateral fenestration of the lamina and decompression of the nucleus pulposus can significantly relieve the postoperative pain of patients, improve the surgical effect, and postoperative patients recover quickly. -
表 1 两组患者手术指标比较
Table 1. Comparison of the surgical index between the observation group and control group (Mean±SD)
组別 手术时间(min) 术中出血量(mL) 术后卧床时间(d) 平均住院时间(d) 并发症(n) 观察组(n=67) 85.85±12.55 110.78±29.45 2.53±0.69 8.57±1.69 3 对照组(n=65) 92.98±19.19 201.92±41.28 3.28±0.90 11.08±1.85 7 χ2/t -2.520 -14.564 -5.334 -8.152 4.285 P < 0.013 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.05 表 2 两组手术前后VAS评分比较
Table 2. Comparison of the VAS scores before and after surgery between the two groups (Mean±SD)
组別 术前 术后1周 术后1月 术后3月 术后6月 F P 观察组(n=67) 7.76±1.42 2.70±1.02 2.43±0.87 1.93±0.74 1.21±0.79 458.39 < 0.001 对照组(n=65) 7.72±1.40 3.62±1.27 3.31±1.16 2.66±0.99 2.05±2.67 256.55 < 0.001 t 0.156 -4.556 -4.887 -4.821 -6.572 P 0.877 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 表 3 两组手术前后ODI指数比较
Table 3. Comparison of the ODI indexes before and after surgery between the two groups (Mean±SD)
组別 术前 术后1周 术后1月 术后3月 术后6月 F P 观察组(n=67) 67.95±7.40 33.19±5.12 26.00±5.19 20.73±5.48 13.37±4.81 939.54 < 0.001 对照组(n=65) 68.91±7.77 42.62±7.42 35.92±4.75 25.49±5.59 18.67±5.30 623.12 < 0.001 t -0.728 -8.477 -11.462 -4.938 -6.014 P 0.468 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 表 4 两组患者术后临床疗效比较分析
Table 4. Comparison of the clinical efficacy after surgery between the two groups[n(%)]
组別 优 良 可 差 观察组(n=67) 49(73.13) 12(17.91) 5(7.46) (1.49) 对照组(n=65) 35(53.85) 20(30.77) 8(12.31) 2(3.08) -
[1] 张功林, 章鸣, 蔡国荣, 等. 下腰椎简易跪式手术床的设计与应用[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2007, 13(8): 501, 505. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5572.2007.08.025 [2] Schonauer C, Bocchetti A, Barbagallo G, et al. Positioning on surgical table[J]. Eur Spine J, 2004, 13(Suppl 1): S50-5. [3] 王永恒, 张功林, 龚铁军. 简易跪式手术床的设计与应用[J]. 中国伤残医学, 2012, 20(8): 60-1. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6567.2012.08.040 [4] 杨军, 杨群, 田霖, 等. 过屈跪位与俯卧位下L4/L5椎板间隙形态差异及其在经椎板间入路经皮内窥镜下椎间盘切除术治疗腰椎椎间盘突出症中的意义[J]. 脊柱外科杂志, 2018, 16(5): 289-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2957.2018.05.008 [5] Kwee MM, Ho YH, Rozen WM. The prone position during surgery and its complications: a systematic review and evidence-based guidelines[J]. Int Surg, 2015, 100(2): 292-303. doi: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00256.1 [6] Fukui M, Chiba K, Kawakami M, et al. Japanese orthopaedic association back pain evaluation questionnaire. part 2. verification of its reliability: the subcommittee on low back pain and cervical myelopathy evaluation of the clinical outcome committee of the Japanese orthopaedic association[J]. J Orthop Sci, 2007, 12(6): 526-32. doi: 10.1007/s00776-007-1168-4 [7] Ishitani H, Tamura T, Kanaya S, et al. Examination of the regression model to quantify the degree of low back pain and lower limb symptoms in patients with lumbar disc herniation by the Japanese Orthopaedic Association Back Pain Evaluation Questionnaire (JOABPEQ)[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(12): e0243861. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243861 [8] Gum JL, Glassman SD, Carreon LY. Clinically important deterioration in patients undergoing lumbar spine surgery: a choice of evaluation methods using the Oswestry Disability Index, 36-Item Short Form Health Survey, and pain scales: clinical article[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2013, 19(5): 564-8. doi: 10.3171/2013.8.SPINE12804 [9] Werner DAT, Grotle M, Gulati S, et al. Can a successful outcome after surgery for lumbar disc herniation be defined by the oswestry disability index raw score?[J]. Global Spine J, 2020, 10(1): 47-54. doi: 10.1177/2192568219851480 [10] Thaler M, Lechner R, Foedinger B, et al. Driving reaction time before and after surgery for disc herniation in patients with preoperative paresis[J]. Spine J, 2015, 15(5): 918-22. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.06.052 [11] Vialle LR, Vialle EN, Suárez Henao JE, et al. Lumbar disc herniation[J]. Revista Brasileira De Ortopedia Engl Ed, 2010, 45(1): 17-22. doi: 10.1590/S0102-36162010000100004 [12] Cheng ZX, Zheng YJ, Feng ZY, et al. Chinese Association for the Study of Pain: expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment for lumbar disc herniation[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2021, 9(9): 2058-67. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i9.2058 [13] Thackeray A, Fritz JM, Lurie JD, et al. Nonsurgical treatment choices by individuals with lumbar intervertebral disc herniation in the United States: associations with long-term outcomes[J]. Am J Phys Med Rehabil, 2017, 96(8): 557-64. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000685 [14] Chen CM, Sun LW, Tseng C, et al. Surgical outcomes of full endoscopic spinal surgery for lumbar disc herniation over a 10-year period: a retrospective study[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(11): e0241494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241494 [15] Lee YC, Zotti MGT, Osti OL. Operative management of lumbar degenerative disc disease[J]. Asian Spine J, 2016, 10(4): 801-19. doi: 10.4184/asj.2016.10.4.801 [16] Abdullah F, Bai A, Sahil F, et al. Lumbar disc herniation: comparing pain relief after medical and surgical intervention[J]. Cureus, 2021, 13(6): e15885. [17] Lorio M, Kim C, Araghi A, et al. International society for the advancement of spine surgery policy 2019-surgical treatment of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy[J]. Int J Spine Surg, 2020, 14(1): 1-17. doi: 10.14444/7001 [18] Hamawandi SA, Sulaiman Ⅱ, Al-Humairi AK. Open fenestration discectomy versus microscopic fenestration discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: a randomized controlled trial[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2020, 21(1): 384. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03396-x [19] Li QY, Zhou YC. Comparison of conventional fenestration discectomy with Transforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy for treating lumbar disc herniation: minimum 2-year long-term follow-up in 1100 patients[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2020, 21(1): 628. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03652-0 [20] Xu BS, Xu HW, Destandau J, et al. Anatomic investigation of lumbar transforaminal fenestration approach and its clinical application in far lateral disc herniation[J]. Medicine, 2017, 96(29): e7542. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007542 [21] Yang YL, Yan X, Li WH, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes and pain assessment after posterior lumbar interbody fusion for recurrent lumbar disc herniation[J]. Orthop Surg, 2020, 12(3): 907-16. doi: 10.1111/os.12706 [22] 韩红, 吕平. 跪式体位下行下腰椎手术患者的麻醉管理体会[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2011, 27(9): 926-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMZ201109043.htm [23] 曹鹏, 梁裕, 龚耀成, 等. 胸膝跪式体位下小切口椎板间开窗髓核摘除术治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 上海医学, 2007, 30(2): 136-7, 154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHYX200702023.htm [24] Pointillart V, Broc G, Senegas J. A novel paraspinal surgical approach for lumbar lateral extraforaminal root entrapment[J]. Eur Spine J, 1997, 6(2): 102-5. doi: 10.1007/BF01358741 [25] Pirouzi S, Emami F, Taghizadeh S, et al. Is abdominal muscle activity different from lumbar muscle activity during four-point kneeling?[J]. Iran J Med Sci, 2013, 38(4): 327-33. [26] 邢庆国. 不同体位行经皮椎间孔镜技术治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效比较[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2019, 40(1): 90-2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7234.2019.01.031 [27] Du L, Gao YZ, Gao K, et al. Lateral position versus prone position for cervical laminoplasty: a retrospective comparative study[J]. Ther Clin Risk Manag, 2020, 16: 133-40. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S227799 [28] Shriver MF, Zeer V, Alentado VJ, et al. Lumbar spine surgery positioning complications: a systematic review[J]. Neurosurg Focus, 2015, 39(4): E16. doi: 10.3171/2015.7.FOCUS15268 [29] Nicol M, Sun Y, Craig N, et al. Incidence of thromboembolic complications in lumbar spinal surgery in 1, 111 patients[J]. Eur Spine J, 2009, 18(10): 1548-52. doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-1035-4 [30] Jin SJ, Park YS, Kim SH, et al. Effect of prone positional apparatus on the occurrence of acute kidney injury after spine surgery[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 128: e597-e602. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.04.216 -







 下载:
下载: