Evaluation of characteristic of breast cancer bone metastasis with 99mTc-MDP bone imaging
-
摘要:
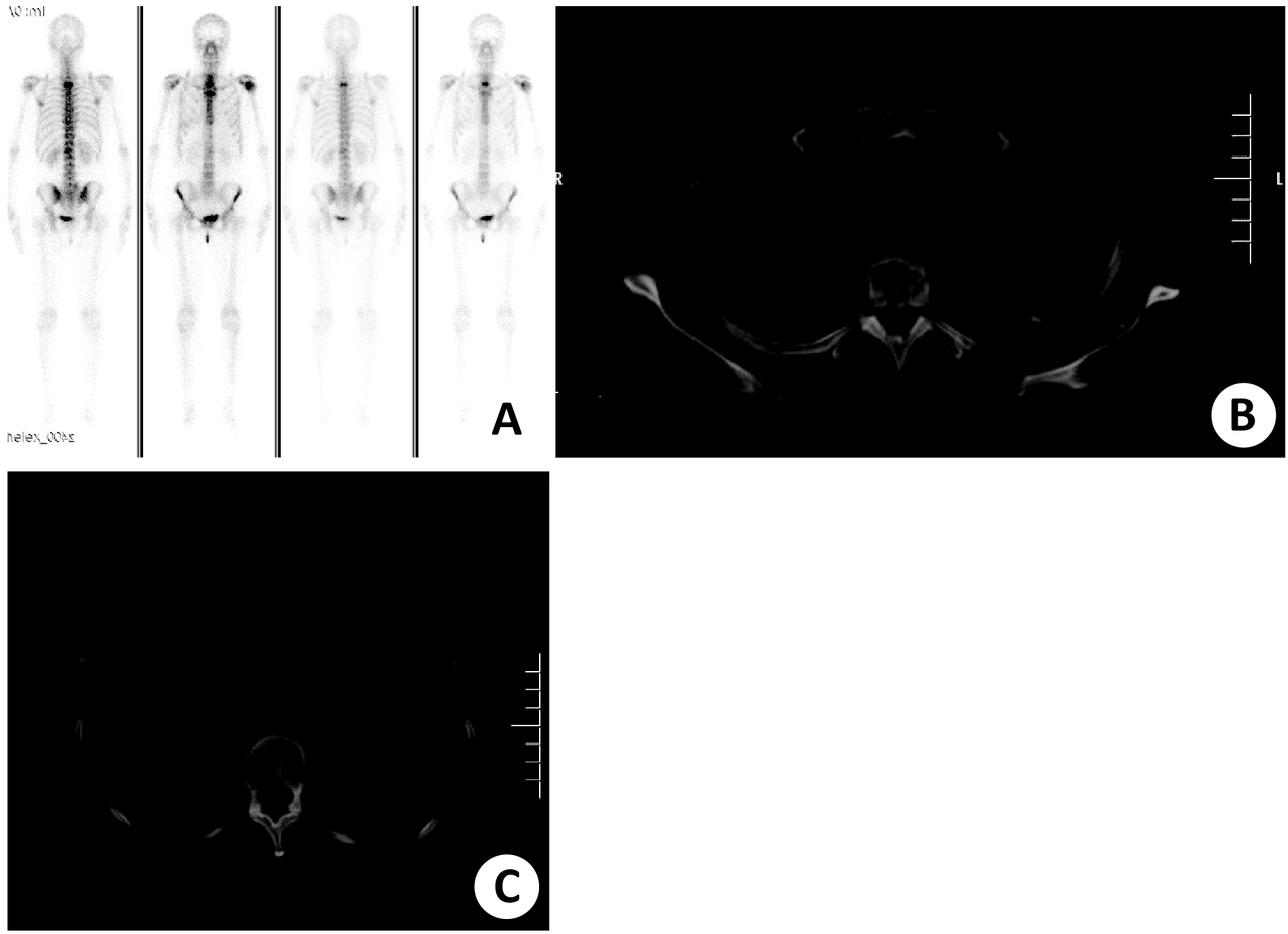
目的 探讨乳腺癌骨转移99mTc-亚甲基二膦酸盐(MDP)全身骨显像及SPECT/CT融合显像的特征。 方法 收集我院2016年1月~2017年5月经病理组织学及免疫组化确诊的乳腺癌资料。初诊时即发现骨转移的患者46例,所有患者均在治疗前行99mTc-MDP全身骨显像,疑骨转移或不明原因骨痛部位行SPECT/CT融合显像。分析三阴乳腺癌(TNB)与非TNBC骨转移病灶分布情况,总结乳腺癌骨转移99mTc-MDP全身骨显像及SPECT/CT融合显像的特点。 结果 共检出46例患者204处病变,脊柱62处(30.39%),是转移最常见部位,其次肋骨57处(27.94%)、胸部骨31处(15.20%)、骨盆骨28处(13.73%)、颅面骨15处(7.35%)、四肢骨11处(5.39%)。三阴乳腺癌与非三阴乳腺癌、TNBC与非TNBC骨转移在脊柱、肋骨、胸部骨、骨盆骨、颅面骨及四肢骨的病灶分布比例差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.591,P=0.988)。三阴乳腺癌骨转移占整个乳腺癌骨转移的28.26%(13/46)。13例TNBC骨转移共51处病灶,放射性浓聚占90.20%(46/51), 混合型病灶占7.84%(4/51),放射性稀疏病变1.96%(1/51), 且主要为多发骨转移病变, 占84.62%(11/13)。 结论 99mTc-MDP全身骨显像及SPECT/CT融合显像对乳腺癌的早期诊断有重要价值,TNBC骨转移好发与脊柱、肋骨、胸骨,以多发性、放射性浓聚病变为主。 -
关键词:
- 三阴性乳腺癌 /
- 骨转移 /
- 骨显像 /
- 单光子发射计算机断层扫描
Abstract:Objective To investigate the characteristics of bone metastasis of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) with 99mTc-MDP whole-body bone imaging and SPECT/CT bone fusion imaging. Methods Clinical records of 46 untreated patients with confirmed bone metastases of breast cancer by pathology or clinical follow-up were collected. All cases had received 99mTc-MDP whole-body bone imaging before treatment, and SPECT/CT bone fusion imaging was performed on sites of suspected bone metastasis or bone pain of unknown reason. Results A total of 46 patients with 204 lesions were detected. The spine was found to be the most common site for bone metastases (62, 30.39%), followed by ribs (57, 27.94%), thoracic bones (31, 15.20%), pelvic bones (28, d13.73%), craniofacial bones (15, 7.35%) and limb bones (11, 5.39%). No significant differences were found in lesion distribution in the spine, ribs, thoracic bones, pelvic bones, craniofacial bones and limb bones between TNBC and non-TNBC and their bone metastases(X2=0.591, P=0.988). The bone metastasis of TNBC accounted for 28.26% (13/46) of the whole breast cancer bone metastasis. There were 51 bone metastases in 13 cases of TNBC. Totally 90.20% (46/51) of metastatic lesion had high radioactivity concentration, 7.84% (4/51) were mixed lesions, 1.96% (1/51) had low radioactivity concentration, and most of lesions were multiple bone metastases, accounting for 84.26% (11/13). Conclusion 99m Tc-MDP bone imaging and SPECT/CT bone fusion imaging are of great value in the early diagnosis of TNBC. Bone metastasis of TNBC often occurs in the spine, ribs and thoracic bones, and it is mainly caused by multiple and strong radioactivity concentration. -
表 1 乳腺癌骨转移病灶分布及转移率分布
骨转移
部位非TNBC骨转移
病灶(n)百分比(%) TNBC骨转移
病灶(n)百分比(%) 合计病灶
(n, %)胸部骨 22 14.38 9 17.35 31(15.20) 肋骨 43 28.10 14 27.45 57(27.94) 脊柱骨 47 30.72 15 29.41 62(30.39) 骨盆骨 21 13.73 7 13.73 28(13.73) 颅面骨 11 7.12 4 7.84 15(7.35 四肢骨 9 5.88 2 3.92 11(5.39) 合计 153 100 51 100 204(100) -
[1] Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65(2): 87-108. [2] Zuo TT, Zheng RS, Zeng HM, et al. Female breast cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2013[J]. Thoracic Cancer, 2017, 8(3): 214-8. [3] Fontanella C, Fanotto V, Rihawi K, et al. Skeletal metastases from breast cancer: pathogenesis of bone tropism and treatment strategy[J]. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2015, 32(8): 819-33. [4] Gerratana L, Fanotto V, Bonotto M, et al. Pattern of metastasis and outcome in patients with breast cancer[J]. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2015, 32(2): 125-33. [5] Cleeland C, von Moos R, Walker MS, et al. Burden of symptoms associated with development of metastatic bone disease in patients with breast cancer[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2016, 24(8): 3557-65. [6] Hayashi N, Yamauchi H, Nakamura S. Management of bone metastases from breast cancer[J]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho, 2012, 39(8): 1174-7. [7] Haraldsen A, Bluhme H, Røhl L, et al. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and SPECT/low-dose computerized tomography did not increase sensitivity or specificity compared to planar bone scintigraphy for detection of bone metastases in advanced breast cancer[J]. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging, 2016, 36(1): 40-6. [8] Abikhzer G, Gourevich K, Kagna O, et al. Whole-body bone SPECT in breast cancer patients: the future bone scan protocol[J]. Nucl Med Commun, 2016, 37(3): 247-53. [9] Kingsley LA, Fournier PG, Chirgwin JM, et al. Molecular biology of bone metastasis[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2007, 6(10): 2609-17. [10] Hagberg KW, Taylor A, Hernandez RK, et al. Incidence of bone metastases in breast cancer patients in the United Kingdom: results of a multi-database linkage study using the general practice research database[J]. Cancer Epidemiol, 2013, 37(3): 240-6. [11] 崔世恩, 储 兵, 凌飞海. 390例原发乳腺癌远处转移与分子分型关联性的10年回顾性分析[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2015, 25(10): 774-9. [12] Chikarmane SA, Tirumani SH, Howard SA, et al. Metastatic patterns of breast cancer subtypes: what radiologists should know in the era of personalized cancer medicine[J]. Clin Radiol, 2015, 70(1): 1-10. [13] Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, et al. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28(20): 3271-7. [14] Bryan BB, Schnitt SJ, Collins LC. Ductal carcinoma in situ with basal-like phenotype: a possible precursor to invasive basal-like breast cancer[J]. Mod Pathol, 2006, 19(5): 617-21. [15] Kumar P, Aggarwal R. An overview of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2016, 293(2): 247-69. [16] 景 娜, 王 玉, 王仙玲, 等. 三阴性乳腺癌的临床特征分析[J]. 肿瘤研究与临床杂志, 2015, 27(3): 201-3. [17] 吴 涛, 王淑莲, 金 晶, 等. 转移性三阴乳腺癌的临床特征和治疗结果[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2014, 23(3): 177-9. [18] 罗安琪, 韩 瑞, 吴 芳, 等. 不同分子亚型乳腺癌骨转移患者的临床特征和预后分析[J]. 西安交通大学学报: 医学版, 2017, 38(5): 740-3. [19] 周炳娟, 黄丽娟, 曹建江, 等. 成骨细胞特异性转录因子2在乳腺癌中的表达及临床意义[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2017, 37(01): 50-5. [20] Chen WZ, Shen JF, Zhou Y, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors for developing bone metastases in patients with breast cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 11325-8. [21] Piggott RP, Waters PS, Kerin MJ. The influence of breast cancer subtype on bone metastases development and survival in women with metastatic breast cancer[J]. Ir J Med Sci, 2017, 186(1): 97-102. [22] Mundy GR. Metastasis to bone: causes, Consequences and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2002, 2(8): 584-93. [23] 江泽飞, 陈佳艺, 牛晓辉, 等. 乳腺癌骨转移和骨相关疾病临床诊疗专家共识(2014版) [J]. 中华医学杂志, 2015, 95(4): 241-7. [24] 董 科, 傅健飞, 楼菁菁, 等. 分子影像SPECT/CT对乳腺癌骨转移的临床应用价值[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2015, 26(7): 465-8. [25] Harisankar CN, Agrawal K, Bhattacharya A, et al. F-18 fluoro-deoxy-glucose and F-18 Sodium fluoride cocktail PET/CT scan in patients with breast cancer having equivocal bone SPECT/CT[J]. Indian J Nucl Med, 2014, 29(2): 81-6. -







 下载:
下载: