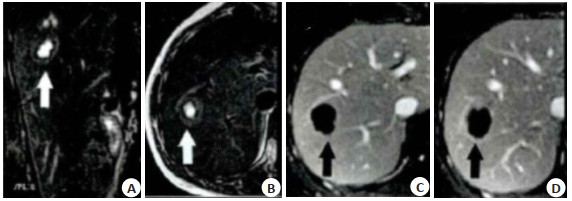
Diagnostic value of MRI and CT in liver solitary necrotic nodule
-
摘要:
目的 探讨肝脏孤立性坏死结节(SNN)的MRI、CT影像学表现及诊断价值。 方法 选取2014年1月~2020年6月在我院就诊的肝脏SNN患者40例,其中接受MRI检查的22例患者作为MRI组,CT检查的18例患者作为CT组,分析MRI、CT诊断肝脏SNN的价值,同时分析单纯凝固性坏死型、伴液化性坏死型和多结节融合型病灶的MRI、CT影像学表现差异。 结果 MRI诊断肝脏SNN准确率为95.45%,明显高于CT组(P < 0.05);CT组,单纯凝固性坏死型、伴液化性坏死型和多结节融合型病灶CT平扫及增强扫描表现差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),单纯凝固性坏死型、伴液化性坏死型和多结节融合型病灶CT平扫主要呈低密度影,分别占83.33%、42.86%和40.00%,3种病灶均无强化,其中分别有83.33%、57.14%和80.00%病灶包膜延迟强化;MRI组,伴液化性坏死型T2WI序列低信号比例高于单纯凝固性坏死型和多结节融合型(P < 0.05),多结节融合型T2WI序列稍高信号比例高于伴液化性坏死型(P < 0.05),单纯凝固性坏死型、伴液化性坏死型和多结节融合型病灶T1WI序列低信号比例均为100.00%,T2WI序列低信号鉴别伴液化性坏死型SNN的敏感度为100.00%,特异性为78.57%,准确率为86.36%,阳性预测值为72.73%,阴性预测值为100.00%;T2WI序列序列稍高信号鉴别伴液化性坏死型鉴别多结节融合型SNN的敏感度为100.00%,特异性为68.75%,准确率为77.27%,阳性预测值为54.55%,阴性预测值为100.00%,单纯凝固性坏死型、伴液化性坏死型和多结节融合型动脉期、门脉期和延迟期病灶无强化比例均为100.00%,但延迟期所有病灶边缘有强化。 结论 MRI和CT在肝脏SNN诊断中有一定应用价值,其中MRI诊断价值较好。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the MRI and CT findings and diagnostic value of solitary necrotic nodule (SNN) of the liver. Methods Forty cases of liver SNN patients in our hospital from January 2014 to June 2020 were selected, including 22 cases of MRI examination (MRI group) and 18 cases of CT examination (CT group). The value of MRI and CT in the diagnosis of liver SNN were analyzed. The differences of MRI and CT images of simple coagulative necrosis type, liquefying necrosis type and multi nodule fusion type were analyzed. Results The accuracy of MRI in diagnosing liver SNN was 95.45%, which was significantly higher than that in CT group (P < 0.05). In the CT group, there was no significant difference in the plain and enhanced CT findings of the simple coagulation necrosis type, liquefaction necrosis type and multi nodule fusion type (P> 0.05). The lesions of simple coagulation necrosis, liquefaction necrosis and multi nodule fusion showed low density on plain CT scan, accounting for 83.33%, 42.86% and 40.00%. There was no enhancement in the three types of lesions, including 83.33%, 57.14% and 80.00% of the capsule of lesions had delayed enhancement. In MRI group, the low signal ratio of T2WI in liquefying necrosis was significantly higher than that of coagulation necrosis and multi nodule fusion (P < 0.05). The proportion of slightly high signal in T2WI of multi nodule fusion type was significantly higher than that of liquefaction necrosis type (P < 0.05). The low signal ratio of T1WI sequence in the single coagulable necrosis type, liquefaction necrosis type and multi-nodule fusion type lesions was 100.00%. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of T2WI sequence low signal for the identification of SNN with liquefaction necrosis were 100.00%, 78.57%, 86.36%, 72.73% and 100.00% respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of slightly higher signal of T2WI sequence identifies SNNs with multi-nodular fusion were 100.00%, 68.75%, 77.27%, 54.55% and 100.00%, respectively for the identification of SNN with liquefaction necrosis. The proportion of lesions of the necrotic type, liquefactive necrosis type and multi-tuberculous fusion without enhancement at the arterial, portal and delayed stages was 100.00%, but there was enhancement in the edge of all lesions at the delayed stage. Conclusion MRI and CT have certain application value in the diagnosis of liver SNN, among which MRI has better diagnostic value. -
Key words:
- liver /
- solitary necrotic nodule /
- magnetic resonance imaging /
- CT /
- diagnostic value
-
表 1 MRI组和CT组一般资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of general data between MRI group and CT group (Mean±SD)
组別 MRI组(n=22) CT组(n=18) t/χ2 P 男/女(n) 15/7 14/4 0.103 0.749 年龄(岁) 50.16±5.66 52.34±7.10 -1.081 0.286 BMI(kg/m2) 22.09±6.82 22.54±7.10 -0.204 0.840 ALT (U/L) 25.01±5.51 24.16±6.06 0.464 0.645 AST(U/L) 22.51±6.60 22.18±7.10 0.152 0.880 ALB(g/L) 48.03±10.12 47.11±12.20 0.261 0.796 STB(mmol/L) 8.32±1.95 8.51±1.81 -0.317 0.753 类型[n(%)] 0.044 0.978 单纯凝固性坏死型 8(36.36) 6(33.33) 伴液化性坏死型 8(36.36) 7(38.89) 多结节融合型 6(27.27) 5(27.78) 表 2 CT组平扫及增强扫描结果
Table 2. Results of plain scan and enhanced scan in CT group[n(%)]
类型 病灶呈低密度 病灶呈等密度 病灶呈高密度 病灶无强化 包膜延迟强化 单纯凝固性坏死型(n=6) 5(83.33) (16.67) 0(0.00) 6(100.00) 5(83.33) 伴液化性坏死型(n=7) 3(42.86) 4(57.14) 0(0.00) 7(100.00) 4(57.14) 多结节融合型(n=5) 2(40.00) (20.00) 2(40.00) 2(100.00) 4(80.00) χ2 2.738 2.621 3.953 - 1.279 P 0.292 0.319 0.065 - 0.669 表 3 MRI组平扫结果
Table 3. Plain scan results of MRI group
类型 T1WI序列低信号 T2WI序列低信号 TTWI序列稍高信号 单纯凝固件坏死型(n=8) 8(100.00) 3(37.50) 5(62.50) 伴液化件坏死型(n=8) 8(100.00) 8(l00.00)ab 0(0.00)b 多结节融合型(n=6) 6(100.00) 0(0.00) 6(100.00) χ2 - 15.120 < 0.001 P - 15.120 < 0.001 aP < 0.05 vs单纯凝固性坏死型;bP < 0.05 vs多结节融合型. 表 4 MRI组增强扫描结果
Table 4. Enhanced scan results of MRI group[n(%)]
类型 动脉期病灶无强化 fj脉期病灶无强化 延迟期病灶无强化 延迟期病灶边缘强化 单纯凝固件坏死型(n=8) 8(100.00) 8(100.00) 8(100.00) 8(100.00) 伴液化件坏死型(n=8) 8(100.00) 8(100.00) 8(100.00) 8(100.00) 多结节融合型(n=6) 6(100.00) 6(100.00) 6(100.00) 6(100.00) -
[1] Zhao K, Sun GC, Wang Q, et al. The diagnostic value of conventional MRI and CT features in the identification of the IDH1-mutant and 1p/19q Co-deletion in WHO grade Ⅱ gliomas[J]. Acad Radiol, 2021, 28(7): e189-98. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.03.008 [2] 史芳芳, 胡海东, 郑增, 等. 肝脏孤立性坏死结节的MRI表现[J]. 肝脏, 2018, 23(7): 580-2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2018.07.008 [3] Lebert P, Adens-Fauquembergue M, Azahaf M, et al. MRI for characterization of benign hepatocellular tumors on hepatobiliary phase: the added value of in-phase imaging and lesion-to-liver visual signal intensity ratio[J]. Eur Radiol, 2019, 29(11): 5742-51. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06210-y [4] 何平, 杨学俊, 李原, 等. MRI和CT诊断及鉴别诊断肝脏孤立性结节临床分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21(S2): 173-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX2018S2066.htm [5] 刘荣伟, 徐小虎, 刘月军, 等. 肝硬化背景下肝脏良恶性结节的MRI及CT诊断价值[J]. 癌症进展, 2018, 16(6): 790-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AZJZ201806036.htm [6] D'Angelo T, Vogl TJ, Wichmann JL. From low-dose to no-dose: thin-section magnetic resonance imaging for evaluation of pulmonary nodules[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2018, 10(Suppl 9): S1055-7. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Julian_Wichmann/publication/324722934_From_low-dose_to_no-dose_thin-section_magnetic_resonance_imaging_for_evaluation_of_pulmonary_nodules/links/5ae08a7c0f7e9b2859470997/From-low-dose-to-no-dose-thin-section-magnetic-resonance-imaging-for-evaluation-of-pulmonary-nodules.pdf [7] Millischer AE, Marcellin L, Santulli P, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging presentation of deep infiltrating endometriosis nodules before and after pregnancy: a case series[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14 (10): e0223330. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223330 [8] 周鹏, 王烁, 郑玉明. MRI增强扫描在阜新地区肝脏坏死结节鉴别诊断中的应用价值[J]. 解放军预防医学杂志, 2018, 36(10): 1271-3, 1276. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYYX201810013.htm [9] 雒大健, 全艳, 张志勇. 超声造影与彩色多普勒超声在肝实质性肿块诊断中的对比研究[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2018, 34(8): 701-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2018.08.009 [10] Saitoh T, Sato S, Yazaki T, et al. Progression of hepatic hypovascular nodules with hypointensity in the hepatobiliary phase of Gd-EOBDTPA-enhanced MRI in hepatocellular carcinoma cases[J]. Intern Med, 2018, 57(2): 165-71. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8801-16 [11] Kim HI, Jang JK, Lim J, et al. Hepatocyte-specific magnetic resonance imaging-based assessment of indeterminate hepatic nodules in the liver transplant evaluation of patients with cirrhosis [J]. Liver Transpl, 2020, 26(3): 359-69. doi: 10.1002/lt.25684 [12] Horvat N, Rocha MS, Chagas AL, et al. Multimodality screening of hepatic nodules in patients with congenital heart disease after fontan procedure: role of ultrasound, ARFI elastography, CT, and MRI[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2018, 211(6): 1212-20. doi: 10.2214/AJR.18.19762 [13] 周文华, 徐大伟, 王立军, 等. 多层螺旋CT及动态增强磁共振成像血流参数在肝良恶性结节鉴别诊断中应用价值探究[J]. 中华生物医学工程杂志, 2019, 5(5): 518-22. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1927.2019.05.002 [14] 张尧评, 程瑞洪, 王海军, 等. 超声结合X线指导原发性肝内胆管结石患者手术的价值[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2020, 43(3): 495-9. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2020.03.26 [15] 张见增, 胡海东, 郑增, 等. 肝脾手术及上消化道出血后肝脏缺血/坏死灶CT和MR特征[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志, 2019, 25(12): 915-20. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-8118.2019.12.008 [16] 李王佳, 吕发金, 张艳, 等. 有恶性肿瘤病史的患者孤立性肺结节的CT诊断研究[J]. 中华胸心血管外科杂志, 2019(7): 390-5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-4497.2019.07.002 [17] 张晓明. 多排螺旋CT对肝脏孤立性坏死结节的诊断价值[J]. 中国医药指南, 2016, 14(26): 71-2. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYXK201626063.htm [18] 崔金超. 肝脏孤立性坏死结节鉴别诊断中磁共振成像长时间延迟增强扫描的应用价值[J]. 实用医学影像杂志, 2019, 20(5): 524-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXY201905054.htm [19] 方家杨, 于德新, 马祥兴, 等. MRI长时间延迟增强扫描在肝脏孤立性坏死结节诊断和鉴别诊断中的应用价值[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2017, 36(4): 511-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS201704019.htm [20] 李鹏, 刘小丽, 喻奇志. MRI对肝孤立性坏死结节诊断及鉴别诊断价值研究[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2019, 22(1): 129-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2019.01.034 [21] 回瑾, 张卓, 邱建星. 腹部磁共振增强扫描结合弥散加权成像对肝脏良恶性肿瘤的鉴别诊断价值[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2021, 44(1): 163-6. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2021.01.33 -







 下载:
下载: