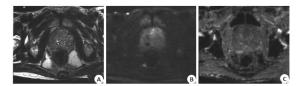
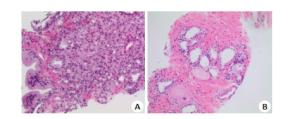
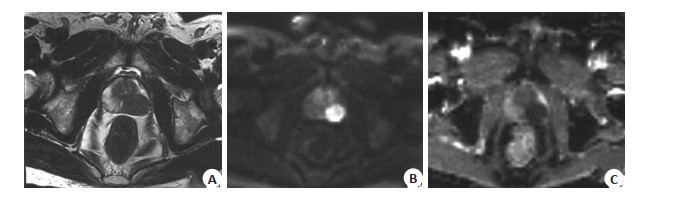
Value of 1.5 T MR DWI in the evaluation of benign and malignant prostate lesions
-
摘要:
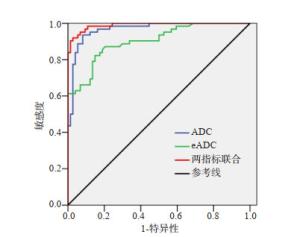
目的探究前列腺良恶性病变采用1.5 T磁共振扩散加权成像(MR DWI)检查应用价值。 方法对2017年10月~2020年8月我院收治136例前列腺病变患者相关资料进行回顾性分析,患者均接受MR DWI检查。分析DWI对于前列腺良恶性病变诊断价值,比较前列腺良恶性病变患者ADC值、eADC值及其对前列腺良恶性病变诊断价值,比较前列腺良恶性病变患者DWI半定量分级分布情况。 结果以病理检查作为金标准,DWI诊断前列腺恶性病变敏感度、特异性及准确度分别为95.16%、98.65%、97.06%,Kappa值为0.941;恶性病变患者ADC值显著低于良性病变,eADC值显著高于良性病变(P < 0.05);ROC曲线显示,ADC值、eADC值及两指标联合诊断前列腺良恶性病变ADC值分别为0.902、0.967、0.990;恶性病变患者DWI半定量分级主要为4~5级,良性病变患者DWI半定量分级主要为1~3级,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论1.5 T MR DWI用于评估前列腺良恶性病变价值优异,值得临床推广应用。 Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the application value of 1.5 T magnetic resonance diffusion weighted imaging (MR DWI) in evaluating benign and malignant prostate lesions. MethodsThe relevant data of 136 patients with prostate lesions admitted to the hospital from October 2017 to August 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. All patients were subjected to MR DWI examination, and the diagnostic value of DWI in benign and malignant prostate lesions was analyzed. The ADC value, eADC value, and DWI semi-quantitative classification of patients with benign and malignant prostate lesions were compared. ResultsTaking pathological examination as the golden standard, the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of DWI for diagnosing malignant prostate lesions were 95.16%, 98.65%, and 97.06%, and the Kappa value was 0.941. The ADC value of malignant lesions was significantly lower than that of benign lesions, and the eADC value was significantly higher than that of benign lesions (P < 0.05). ROC curve showed that the AUC values of ADC value, eADC value and combination of the two for diagnosing benign and malignant prostate lesions were 0.902, 0.967, and 0.990, respectively. DWI semi-quantitative classification of patients with malignant lesions was dominated by grade 4-5, which of patients with benign lesions was dominated by grade 1-3 (P < 0.05). Conclusion1.5 T MR DWI is of great value in evaluating benign and malignant prostate lesions. -
Key words:
- MR /
- DWI /
- benign and malignant prostate lesions /
- evaluation value
-
表 1 DWI对于前列腺良恶性病变诊断价值分析
Table 1. Diagnostic value of DWI for benign and malignant prostate lesions
DWI 病理检查 合计 恶性 良性 恶性 59 1 60 良性 3 73 76 合计 62 74 136 表 2 前列腺良恶性病变患者ADC值与eADC值比较
Table 2. Comparison of ADC value and eADC value between patients with benign and malignant prostate lesions (Mean±SD)
组别 ADC值(×10-3 mm2/s) eADC值 恶性病变(n=62) 0.97±0.26 0.57±0.15 良性病变(n=74) 1.82±0.38 0.33±0.09 t 16.557 11.515 P < 0.001 < 0.001 表 3 ADC值与eADC值对于前列腺良恶性病变诊断价值分析
Table 3. Diagnostic value of ADC value and eADC value for benign and malignant prostate lesions
指标 截断值 AUC 敏感度(%) 特异性(%) 95%CI P ADC值 1.25×10-3 mm2/s 0.902 85.3 79.6 0.851~0.952 < 0.001 eADC值 0.46 0.967 94.5 89.5 0.940~0.994 < 0.001 两指标联合 0.990 96.4 92.3 0.977~1.000 < 0.001 表 4 前列腺良恶性病变患者DWI半定量分级分布情况比较
Table 4. Comparison of DWI semi- quantitative classification of patients with benign and malignant prostate lesions [n(%)]
组别 1~3级 4~5级 恶性病变(n=62) 18(29.03) 44(70.97) 良性病变(n=74) 45(60.81) 29(39.19) t 13.702 P < 0.001 -
[1] Komura K, Sweeney CJ, Inamoto T, et al. Current treatment strategies for advanced prostate cancer[J]. Int J Urol, 2018, 25(3): 220-31. doi: 10.1111/iju.13512 [2] de Nunzio C, Presicce F, Giacinti S, et al. Castration-resistance prostate cancer: what is in the pipeline?[J]. Italian J Urol Nephrol, 2018, 70(1): 22-41. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28707844 [3] Tucci M, Leone G, Buttigliero C, et al. Hormonal treatment and quality of life of prostate cancer patients: new evidence[J]. Italian J Urol Nephrol, 2018, 70(2): 144-51. [4] Schiavina R, Bianchi L, Borghesi M, et al. MRI displays the prostatic cancer anatomy and improves the bundles management before robotassisted radical prostatectomy[J]. J Endourol, 2018, 32(4): 315-21. doi: 10.1089/end.2017.0701 [5] Jendoubi S, Wagner M, Montagne S, et al. MRI for prostate cancer: can computed high b-value DWI replace native acquisitions?[J]. Eur Radiol, 2019, 29(10): 5197-204. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06085-z [6] Bajgiran AM, Mirak SA, Sung K, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) ratio versus conventional ADC for detecting clinically significant prostate cancer with 3-T MRI[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2019, 213(3): W134-W142. doi: 10.2214/AJR.19.21365 [7] Barentsz JO, Richenberg J, Clements R, et al. ESUR prostate MR guidelines 2012[J]. Eur Radiol, 2012, 22(4): 746-57. doi: 10.1007/s00330-011-2377-y [8] Wang XY, Liu Y, Wang W, et al. The applied research of simultaneous image acquisition of T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in the assessment of patients with prostate cancer[J]. Asian JAndrol, 2019, 21(2): 177. doi: 10.4103/aja.aja_82_18 [9] Scialpi M, D'Andrea A, Martorana E, et al. Biparametric MRI of the prostate[J]. Turk J Urol, 2017, 43(4): 401-9. doi: 10.5152/tud.2017.06978 [10] Alabousi M, Salameh JP, Gusenbauer K, et al. Biparametric vs multiparametric prostate magnetic resonance imaging for the detection of prostate cancer in treatment-naïve patients: a diagnostic test accuracy systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BJU Int, 2019, 124(2): 209-20. doi: 10.1111/bju.14759 [11] de Perrot T, Rager O, Scheffler M, et al. Potential of hybrid ¹Ffluorocholine PET/MRI for prostate cancer imaging[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2014, 41(9): 1744-55. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2786-7 [12] Petrylak DP, Vogelzang NJ, Chatta K, et al. PSMA ADC monotherapy in patients with progressive metastatic castration- resistant prostate cancer following abiraterone and/or enzalutamide: Efficacy and safety in open-label single-arm phase 2 study[J]. Prostate, 2020, 80(1): 99-108. doi: 10.1002/pros.23922 [13] 宋振强, 时宇鹏, 陈淑宽, 等. MRI弥散加权成像在前列腺增生和前列腺癌诊断鉴别中的应用[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2020, 18(5): 31-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2020.05.010 [14] 杨雪融, 刘晓航, 周良平. 前列腺局限性病变良恶性鉴别诊断: 弥散加权成像图与表观弥散系数值比较[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2014, 24(3): 212-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3969.2014.03.010 [15] 冯智超, 颜智敏, 罗慕晴, 等. 前列腺影像报告和数据系统联合表观扩散系数图像定量分析对外周带前列腺癌的诊断价值[J]. 中南大学学报: 医学版, 2019, 44(3): 277-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYD201903010.htm [16] 陈轶, 李华, 郭宝琴. 早期前列腺外周带癌与炎症的MRI鉴别诊断[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2018, 34(7): 1066-8, 1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2018.07.021 [17] Kim CK, Park JJ, Park BK. Prostate diffusion-weighted imaging at 3T: effect of intravenous gadobutrol administration[J]. Eur Radiol, 2016, 26(5): 1450-6. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3942-6 [18] 单连强, 瞿色华, 蒋旭, 等. 磁共振DWI联合PI-RADS评分对前列腺癌的筛查价值[J]. 中国医药导报, 2019, 16(25): 142-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY201925035.htm [19] Park H, Kim SH, Lee Y, et al. Comparison of diagnostic performance between diffusion kurtosis imaging parameters and monoexponential ADC for determination of clinically significant cancer in patients with prostate cancer[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2020, 45 (12): 4235-43. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02776-0 [20] Sprinkart AM, Marx C, Träber F, et al. Evaluation of exponential ADC (eADC) and computed DWI (cDWI) for the detection of prostate cancer[J]. Rofo, 2018, 190(8): 758-66. doi: 10.1055/a-0637-9980 [21] 张丽君, 邢伟, 邢士军. 3.0T磁共振扩散峰度成像联合扩散加权成像评估侵袭性前列腺癌[J]. 分子影像学杂志, 2020, 43(1): 76-81. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2020.01.16 -






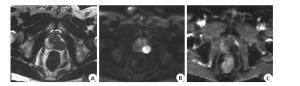
 下载:
下载: