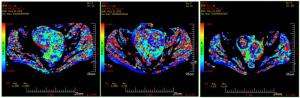
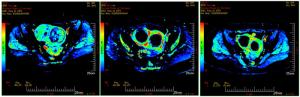
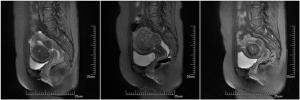
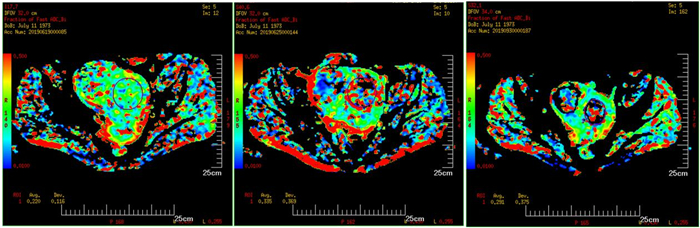
Comparison of IVIM-DWI and DCE-MRI in the treatment of uterine fibroids with high intensity focused ultrasound knife
-
摘要:
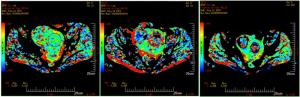
目的分析体素内不相干运动扩散加权成像(IVIM-DWI)和动态对比增强MRI(DCE-MRI)定量参数对高强度聚焦超声刀治疗子宫肌瘤疗效的比较。 方法对60例子宫肌瘤患者进行高强度聚焦超声消融术,所有患者在术前1周、术后48 h及术后3月分别行IVIM-DWI及DCE-MRI检查,通过相关参数(ADC、eADC、StandardADC、f值、D值、D*值、MSI、SER)对同一肌瘤比较IVIM-DWI与DCE-MRI在消融和未消融区域的差异,分析两种扫描参数之间是否具有相关性。 结果术后48 h、术后3月的DCE-MRI相关参数MSI、SER与IVIM-DWI相关参数D*与f值与术前差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05),IVIM-DWI相关参数f与D*值与DCE-MRI相关参数MSI、SER有显著正相关性。 结论IVIM-DWI所产生的伪彩图相较DCE-MRI对子宫肌瘤消融界限较难以区分,但IVIM-DWI相关参数仍能对子宫肌瘤HIFU术后早期病灶的血供及灌注情况提供一定的参考价值。 Abstract:ObjectiveTo compare the efficacy of IVIM-DWI and DCE-MRI in the treatment of uterine fibroids with highintensity focused ultrasound scalpel. Methods60 patients with hysteromyoma underwent high intensity focused ultrasound ablation. IVIM-DWI and DCE-MRI were performed in all patients 1 week before operation, 48 hours after operation and 3 months after operation respectively. The differences between IVIM-DWI and DCE-MRI in ablated and UN ablated areas were compared between IVIM-DWI and DCE-MRI through relevant parameters (ADC, eADC, standardABC, f value, D value, D*value, MSI, SER). The correlation between the two scanning parameters was analyzed. ResultsThe values of D* and F related with IVIM-DWI and the MSI, SER value of DCE-MRI at 48 h and 3 months after operation were significantly different from those before operation (P < 0.05). And there was a significant positive correlation between the values of F and D* of IVIMDWI and MSI and SER of DCE-MRI. ConclusionCompared with DCE-MRI, IVIM-DWI can not distinguish the ablation boundary of hysterical, but the parameters of IVIM-DWI can still provide some reference value for the blood supply and perfusion of uterine leiomyoma in the early stage after HIFU. -
Key words:
- uterine fibroids /
- high-intensity focused ultra-sound /
- IVIM-DWI /
- DCE-MRI
-
表 1 HIFU术前、术后48 h肌瘤以及术后3月IVIM各参数值及DCE-MRI各参数值差异比较
Table 1. Comparison of IVIM parameter values and DCE-MRI parameters before HIFU, 48 h after HIFU, and 3 months after HIFU
指标 Mean±SD t P eADC 术前(n=60) 0.26±0.06 - - 术后48 h(n=60) 0.25±0.06 0.77 0.44 术后3月(n=35) 0.24±0.04 -1.42 0.16 ADC(10-3 mm2/s) 术前(n=60) 1.44±0.15 - - 术后48 h(n=60) 1.41±0.15 0.89 0.38 术后3月(n=35) 1.43±0.1 -0.25 0.8 StADC(10-3 mm2/s) 术前(n=60) 1.27±0.32 - - 术后48 h(n=60) 1.35±0.35 -1.20 0.20 术后3月(n=35) 1.38±0.29 1.64 0.11 D(10-3 mm2/s) 术前(n=60) 1.31±0.15 - - 术后48 h(n=60) 1.33±0.27 0.42 0.67 术后3月(n=35) 1.35±0.16 1.13 0.26 f(%) 术前(n=60) 0.29±0.1 - - 术后48 h(n=60) 0.18±0.09 6.29 <0.05 术后3月(n=35) 0.17±0.1 -5.64 <0.05 D* 术前(n=60) 0.1±0.02 - - 术后48 h(n=60) 0.07±0.03 6.52 <0.05 术后3月(n=35) 0.07±0.01 -8.91 <0.05 MSI 术前(n=60) 306.75±122.32 - - 术后48 h(n=60) 71.43±31.62 14.54 <0.05 术后3月(n=35) 160.86±49.74 -6.73 <0.05 SER 术前(n=60) 43.21±13.49 - - 术后48 h(n=60) 12.07±2.92 17.39 <0.05 术后3月(n=35) 22.81±4.71 -8.63 <0.05 D: True diffusion value; D*: Pseudo diffusion value; f: Perfusion fraction; ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient; St ADC: Standard apparent diffusion coefficient; EADC: Exponential apparent diffusion coefficient; MSI: Maximum slop of increase; SER: Signal enhancement rate. 表 2 IVIM-DWI与DCE-DWI术后各相关参数相关性比较(n=155)
Table 2. Correlation comparison between iVIm-DWI and CE-DWI after operation
指标 eADC ADC StADC D f D* MSI SER eADC r 1 0.007 -0.031 -0.032 0.031 0.061 0.143 -0.068 P - 0.932 0.702 0.693 0.704 0.448 0.075 0.398 ADC r 0.007 1 0.013 0.085 0.062 -0.014 -0.005 -0.082 P 0.932 - 0.869 0.293 0.447 0.865 0.951 0.313 StADC r -0.031 0.013 1 -0.060 -0.151 0.027 -0.079 0.066 P 0.702 0.869 - 0.459 0.061 0.737 0.327 0.412 D r -0.032 0.085 -0.060 1 -0.011 -0.071 -0.022 0.035 P 0.693 0.293 0.293 - 0.897 0.379 0.786 0.662 f r 0.031 0.062 -0.151 -0.011 1 0.236 0.452 0.509 P 0.704 0.447 0.061 0.897 - 0.003 0.000 0.000 D* r 0.061 -0.014 0.027 -0.071 0.236 1 0.377 0.422 P 0.448 0.865 0.737 0.379 0.003 - 0.000 0.000 MSI r 0.143 -0.005 -0.079 -0.022 0.452 0.377 1 0.650 P 0.075 0.951 0.327 0.786 0.000 0.000 - 0.000 SER r -0.068 -0.082 0.066 0.035 0.509 0.422 0.650 1 P 0.398 0.313 0.412 0.662 0.000 0.000 0.000 - -
[1] Wang FL, Tang LD, Wang L, et al. Ultrasound-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound vs laparoscopic myomectomy for symptomatic uterine myomas[J]. J Minim Invasive Gynecol, 2014, 21(2): 279-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2013.09.004 [2] Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, et al. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging[J]. Radiology, 1988, 168(2): 497-505. doi: 10.1148/radiology.168.2.3393671 [3] Lee JT, Liau J, Murphy P, et al. Cross-sectional investigation of correlation between hepatic steatosis and IVIM perfusion on MR imaging[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2012, 30(4): 572-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2011.12.013 [4] Zhang YD, Wang Q, Wu CJ, et al. The histogram analysis of diffusion-weighted intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging for differentiating the gleason grade of prostate cancer[J]. Eur Radiol, 2015, 25(4): 994-1004. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3511-4 [5] Barnes SL, Whisenant JG, XiaLi, et al. Techniques and applications of dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in cancer[J].Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc, 2014, 2014: 4264-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25570934/ [6] Van VDP,Becker AS,Ciritsis A, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion analysis of abdominal organs[J].Investig Radiol, 2018,53(3):179-85. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000426 [7] Stojanov D, Aracki- Trenkic A, Benedeto-Stojanov D. Gadolinium deposition within the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus after repeated administrations of gadolinium-based contrast agentscurrent status[J]. Neuroradiology, 2016, 58(5): 433-41. doi: 10.1007/s00234-016-1658-1 [8] 卢瑞沾, 张俊成, 杨振华, 等. IVIM-DWI评价高强度聚焦超声治疗子宫肌瘤早期疗效的价值[J].临床放射学杂志, 2017, 36(5): 692-6. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92832X/201705/672380318.html [9] 符孔, 郑桦, 黄素静.不同b值的弥散加权成像评价子宫肌瘤高能聚焦超声术后消融疗效的效果观察[J].中国性科学, 2018, 27(11): 52-5. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zgxkx201811017 [10] 王素青, 田静. DWI和CE-MRI评价高强度聚焦超声刀治疗子宫肌瘤术后早期的疗效价值比较[J].中国药物与临床, 2018, 18(5): 727-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YWLC201805027.htm [11] 卢瑞沾, 张俊成, 杨振华, 等. DCE-MRI对评价高强度聚焦超声刀治疗子宫肌瘤早期疗效的价值[J].磁共振成像, 2013, 4(4): 271-5. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cgzcx201304011 [12] Lee HJ, Rha SY, Chung YE, et al. Tumor perfusion-related parameter of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: correlation with histological microvessel density[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2014, 71(4): 1554-8. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24810 [13] Ikink ME, Voogt MJ, van den Bosch MA, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging using different b-value combinations for the evaluation of treatment results after volumetric MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of uterine fibroids[J]. Eur Radiol, 2014, 24(9): 2118-27. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3274-y [14] 辛建英, 邵显敏, 高珊珊, 等.良性前列腺增生ESWAN成像与临床指标的对照研究[J].临床放射学杂志, 2016, 35(2): 238-42. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lcfsxzz201602022 [15] 田士峰, 刘爱连, 郭维亚, 等. R2*值预估肝细胞癌病理分级的可行性[J].中国医学影像技术, 2016, 32(11): 1693-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZYXX201611021.htm [16] 孙成凤, 韩雨, 吴准, 等. ESWAN评估子宫肌瘤高强度聚焦超声消融术的应用研究[J].实用医学杂志, 2017, 33(16): 2761-4. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93362X/201716/672890541.html [17] 马良. 3.0T场强磁共振应用MRA血管成像与3D-ASL脑灌注成像技术在诊断缺血性脑血管疾病中的应用比较[J].中国医疗器械信息, 2019, 25(14): 136-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGQX201914069.htm [18] 王习, 吴准, 王宗英, 等.联合DCE-MRI及FAIR评价子宫肌瘤高强度聚集超声刀治疗前后的应用价值[J].中国医学计算机成像杂志, 2018, 24(3): 258-61. [19] 杨笛, 朱雅馨, 王雪, 等.不同病理类型子宫肌瘤3.0T磁共振扩散加权成像观察[J].中华医学杂志, 2016, 96(15): 1155-9. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=668628219 -






 下载:
下载: