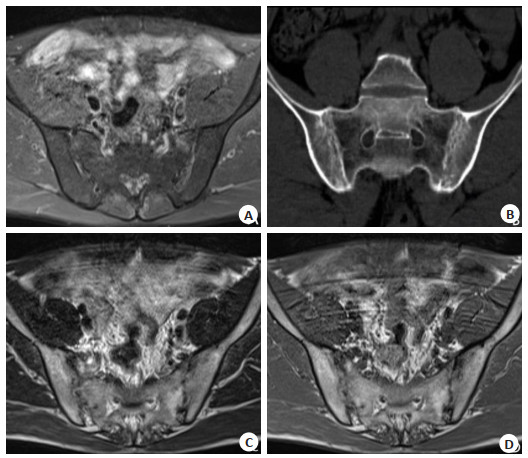
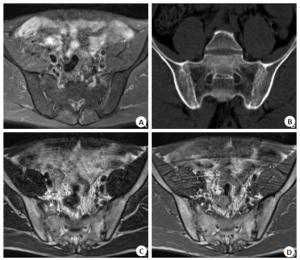
Imaging features of CT and MRI diagnosis of sacroiliac joint lesions in early ankylosing spondylitis
-
摘要:
目的观察CT和MRI诊断早期强直性脊柱炎(AS)骶髂关节病变的影像特点。 方法选取2018年11月~2019年11月本院收治的60例早期AS骶髂关节病变患者为研究对象,其中男36例,女24例,年龄20~60岁(37.28±6.33岁),病程4月~10年(4.80± 1.17年)。所有患者均经CT和MRI检查,比较两种检测方法影像学特点和敏感性。 结果MRI检查Ⅰ级AS骶髂关节病变敏感性高于CT检查(P < 0.05);CT、MRI检查0级、Ⅱ级、Ⅲ级及Ⅳ级AS骶髂关节病变敏感性比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);MRI检查关节面骨质囊变、关节面侵蚀的检出率高于CT(P < 0.05),两组在关节间隙变宽和变窄、关键面下骨质硬化及关节软骨肿胀的检出率比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。CT检查显示,关节面骨质示锯齿状,且见多发小囊变,关节间隙变窄、模糊,受累部位多在关节中下部,MRI检查显示,关节积液呈长T1、T2信号,关节软骨炎性水肿T1呈信号,T2呈高信号;关节软骨破坏T1呈低信号,T2呈高信号,且强度不均匀。 结论MRI可清晰显示早期AS骶髂关节病变情况,且异常检出率和早期诊断率均高于CT,适用于早期诊断。 Abstract:ObjectiveTo observe the imaging features of CT and MRI in the diagnosis of sacroiliac joint lesions in early ankylosing spondylitis. MethodsFrom November 2018 to November 2019, 60 patients with early as sacroiliac joint disease in our hospital were selected, including 36 males and 24 females, with the age from 20 to 60 years old (37.28±6.33 years old). The course of disease was from 4 months to 10 years (4.80±1.17 years). All patients were examined by CT and MRI. The imaging characteristics and sensitivity of the two detection methods were compared. ResultsThe sensitivity of level Ⅰ as sacroiliac joint lesions in MRI was higher than that in CT (P < 0.05). The difference of the sensitivity of level 0, level Ⅱ, level Ⅲ and level Ⅳ as sacroiliac joint lesions in CT and MRI was not significant (P > 0.05). The detection rate of articular surface osteocystic degeneration and articular surface erosion in MRI was higher than that in CT (P < 0.05). The two groups had widened and narrowed joint space, osteosclerosis and osteosclerosis under key surfaces. There was no significant difference in the detection rate of articular cartilage swelling(P > 0.05). CT examination showed that the articular surface was serrated, with multiple small cysts, narrowed and blurred joint space. The most of the affected parts were in the middle and lower part of the joint. The joint effusion showed long T1 and T2 signals, the arthritic edema T1 showed signals, T2 showed high signals. The destruction of articular soft bone T1 showed low signals, T2 showed high signals, and the intensity was uneven. ConclusionMRI can clearly show the early as sacroiliac joint lesions. The abnormal detection rate and early diagnosis rate are higher than CT. -
Key words:
- ankylosing /
- spondylitis /
- sacroiliac joint /
- CT /
- MRI /
- imaging features
-
表 1 CT、MRI检查分级情况比较[n (%), n=60]
Table 1. Comparison of CT and MRI grading
组别 0级 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅲ级 Ⅳ级 CT 3 (5.00) 11 (18.33) 22 (36.67) 23 (38.33) 1 (1.67) MRI 0 (0.00) 21 (35.00) 21 (35.00) 16 (26.67) 2 (3.33) χ2 3.077 4.261 0.036 1.861 0.342 P 0.079 0.039 0.849 0.172 0.559 表 2 CT、MRI影像学表现分析[n (%), n=60]
Table 2. CT and MRI imaging analysis
组别 关节面侵蚀 骨质囊变 关节间隙变宽 关节间隙变窄 关键面下骨质硬化 关节软骨肿胀 CT 50 (83.33) 42 (70.00) 39 (65.00) 20 (33.33) 42 (70.00) 4 (6.67) MRI 57 (95.00) 52 (86.67) 41 (68.00) 20 (33.33) 44 (73.33) 7 (11.67) χ2 4.227 4.910 0.150 0.000 0.164 0.901 P 0.040 0.027 0.699 1.000 0.685 0.343 -
[1] Soroush M, Mominzadeh M, Ghelich Y, et al. Investigation of cardiac complications and their incidence in patients with ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Med Arch, 2016, 70(1): 35-8. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2016.70.35-38 [2] 赵英华, 孙尔维, 韩新爱, 等.扩散加权成像与对比增强MRI评估强直性脊柱炎活动性的对比研究[J].中华放射学杂志, 2015, (9): 665-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2015.09.006 [3] de Hooge M, van den Berg R, Navarro-Compán V, et al. Patients with chronic back pain of short duration from the SPACE cohort: which MRI structural lesions in the sacroiliac joints and inflammatory and structural lesions in the spine are most specific for axial spondyloarthritis[J].Ann Rheum Dis, 2016, 75(7): 1308-14. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207823 [4] 蔡长寿, 冯丰坔, 邱波, 等. CT和MRI在早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变中的诊断价值[J].医学影像学杂志, 2016, 26(6): 1132-5. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yxyxxzz201606052 [5] 曲哲, 钱邦平, 邱勇. MRI在强直性脊柱炎诊疗中的应用进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2016, 26(9): 850-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-406X.2016.09.13 [6] 崔保刚.比较与分析不同影像学检测方法用于诊断强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变效果[J].中国CT和MRI杂志, 2015, 13(5): 25-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2015.05.009 [7] 董晓强, 杨勇, 张凌志, 等.螺旋CT低剂量扫描和MRI检查在强直性骶髂关节炎中的诊断价值研究[J].检验医学与临床, 2015, 12(6): 812-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2015.06.038 [8] Sipko T, Paluszak A, Siudy A. Effect of sacroiliac joint mobilization on the level of soft tissue pain threshold in asymptomatic women[J]. J Manipulative Physiol Ther, 2018, 41(3): 258-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jmpt.2017.09.004 [9] 陈芳妮, 李绍林, 张晓东, 等.强直性脊柱炎骨盆骨髓脂肪沉积的磁共振成像分析[J].南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(2): 256-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dyjydxxb201402023 [10] 徐启兰, 洪国斌, 刘强, 等. 3D T1-VIBE序列用于评价强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节软骨的初步研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志, 2015, 13(3): 101-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2015.03.30 [11] Bellini M, Barbieri M. Single strip lesions radiofrequency denervation for treatment of sacroiliac joint pain: two years' results[J].Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther, 2016, 48(1): 19-22. doi: 10.5603/AIT.2016.0004 [12] 王警建, 王龙龙, 高延忠, 等. MRI与CT在诊断早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变中的效果比较[J].实用临床医药杂志, 2018, 22(19): 57-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jslcyxzz201819016 [13] 刘志飞, 李亮洁. X线、CT和MRI在早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变诊断中的应用价值对比[J].中国急救医学, 2017, 37(1): 192-3. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgjjyx2017z1147 [14] 杨林根, 彭晋, 吴贵华, 等. 320排CT容积扫描结合MRI诊断早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变的临床价值[J].医疗卫生装备, 2012, 33 (12): 63-4, 67. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ylwszb201212024 [15] Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Lenaerts J, et al. Partial remission in ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in treatment with infliximab plus naproxen or naproxen alone: associations between partial remission and baseline disease characteristics[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2016, 55(11): 1946-53. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew230 [16] 高岱, 李坤鹏, 文琼芳, 等.低剂量斜冠状位骶髂关节CT检查诊断强直性脊柱炎的研究初探[J].中华内科杂志, 2016, 55(5): 355-60. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2016.05.005 [17] Choi SH, Kim SY, Park SH, et al. Diagnostic performance of CT, gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI, and PET/CT for the diagnosis of colorectal liver metastasis: Systematic review and meta- analysis[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2018, 47(5): 1237-50. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25852 [18] 雷扬.强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变应用MRI与CT诊断价值研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志, 2015, 13(4): 111-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2015.04.35 [19] 王雨, 毛明伟, 陈家飞.磁共振在强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变诊断中的价值[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2015, 24(36): 4085-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2015.36.037 [20] 梁佐堂, 李继峰, 董乐, 等.对比分析X线、CT和MRI在早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变诊断中应用的价值[J].中国CT和MRI杂志, 2015, 13(2): 84-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2015.02.27 [21] Guo W, Hao B, Chen HJ, et al. PET/CT-guided percutaneous biopsy of FDG-avid metastatic bone lesions in patients with advanced lung cancer: a safe and effective technique[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2017, 44(1): 25-32. doi: 10.1007/s00259-016-3455-9 [22] 金明花, 马湘乔, 胡冰. CT与MRI检查强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变的临床分析[J].医学影像学杂志, 2016, 26(11): 2089-91. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yxyxxzz201611042 [23] 周萍丽.早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变应用X线、CT和MRI的诊断价值研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志, 2016, 14(10): 117-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2016.10.037 [24] 钟浩博, 刘伟乐, 孙春汉, 等. 3D打印技术在肘关节恐怖三联征治疗中的应用效果评估[J].分子影像学杂志, 2020, 43(1): 162-6. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1674-4500.2020.01.34 [25] Soker G, Bozkirli ED, Soker E, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of shoulder joint in patients with early stage of ankylosing spondylitis: a case-control study[J]. Diagn Interv Imaging, 2016, 97(4): 419-24. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2015.10.003 -






 下载:
下载: