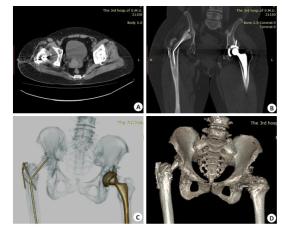
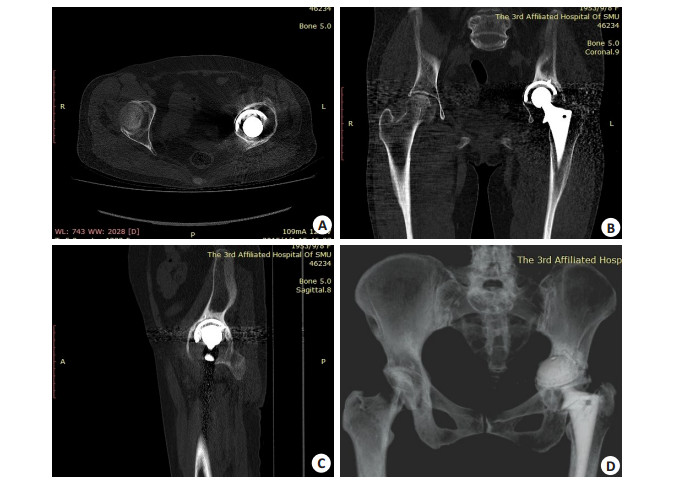
| [1] |
Hsiue PP, Chen CJ, Villalpando C, et al. Trends and patient factors associated with technology-assisted total hip arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2014[J]. Arthroplast Today, 2020, 6(1):112-7. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2019.12.009
|
| [2] |
Esposito CI, Miller TT, Lipman JD, et al. Biplanar low-dose radiography is accurate for measuring combined anteversion after total hip arthroplasty[J]. HSS J, 2020, 16(1): 23-9. doi: 10.1007/s11420-018-09659-7
|
| [3] |
Colombi A, Schena D, Castelli CC. Total hip arthroplasty planning [J]. EFORT Open Rev, 2019, 4(11): 626-32. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.4.180075
|
| [4] |
Plate JF, Shields JS, Langfitt MK, et al. Utility of radiographs, computed tomography, and three dimensional computed tomography pelvis reconstruction for identification of acetabular defects in residency training[J]. Hip Pelvis, 2017, 29(4): 247-52. doi: 10.5371/hp.2017.29.4.247
|
| [5] |
DelSole EM, Mercuri JJ. Utility of upright weight-bearing imaging in total hip arthroplasty[J]. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol, 2019, 23 (6): 603-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1697935
|
| [6] |
徐海永.术前规范DR片对人工髋关节置换手术的指导研究[D].南宁: 广西医科大学, 2015.
|
| [7] |
路玉峰, 许鹏, 郭万首, 等.成人正常髋关节旋转中心的X线影像测量研究[J].中华解剖与临床杂志, 2017, 22(2): 99-102. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-7041.2017.02.003
|
| [8] |
Iwamoto M, Fujii M, Komiyama K, et al. Is lateral acetabular rotation sufficient to correct anterolateral deficiency in periacetabular reorientation osteotomy? A CT-Based simulation study[J]. J Orthop Sci, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.jos.2019.12.014.
|
| [9] |
Graulich T, Graeff P, Nicolaides S, et al. Acetabular posterior wall morphology. A CT-based method to distinguish two acetabular posterior wall types[J]. J Orthop, 2020, 20: 160-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2020.01.027
|
| [10] |
Kobayashi H, Cech A, Kase M, et al. Pre-operative templating in THA. Part Ⅱ: a CT-based strategy to correct architectural hip deformities[J]. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2020, 140(4): 551-62. doi: 10.1007/s00402-020-03341-6
|
| [11] |
Ghanem M, Zajonz D, Heyde CE, et al. Acetabular defect classification and management: Revision arthroplasty of the acetabular cup based on 3-point fixation[J]. Orthopade, 2020. DOI: 10.1007/s00132-020-03895-8.
|
| [12] |
张先龙, 蒋垚, 陈云苏.人工髋关节外科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2009.
|
| [13] |
黄海滨, 袁长深, 寇伯龙.全髋关节翻修术现状[J].重庆医学, 2009, 38 (9): 1116-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2009.09.051
|
| [14] |
杨涛, 谢杰, 胡懿郃, 等. 354例Ribbed股骨柄假体置换术的中远期疗效分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2019, 33(9): 1116-20. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgxfcjwkzz201909011
|
| [15] |
何斌, 章淼锋, 沈跃, 等.人工髋关节置换术后初次翻修的原因分析及翻修术疗效评估[J].中华骨科杂志, 2019, 39(15): 909-17. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2352.2019.15.001
|
| [16] |
蒋梅花, 何川, 冯建民, 等. X线、CT及MRI对髋关节置换术后并发症的诊断价值[J].中国医学计算机成像杂志, 2015, 21(3): 278-82. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyxjsjcx201503018
|
| [17] |
Patel AR, Sweeney P, Ochenjele G, et al. Radiographically silent loosening of the acetabular component in hip arthroplasty[J]. Am J Orthop, 2015, 44(9): 406-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8bb77d4abbfe87238396cff24fe837c5
|
| [18] |
Bäcker HC, Steurer-Dober I, Beck M, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) versus single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT/CT) in painful total hip arthroplasty: a comparative multi- institutional analysis[J]. Br J Radiol, 2020, 93 (1105): 20190738-50. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20190738
|
| [19] |
Boomsma MF, Slouwerhof I, van Lingen C, et al. CT-based quantification of bone stock in large head metal-on-metal unilateral total hip replacements[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2016, 85(4): 760-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.01.019
|
| [20] |
汪飞, 邱麟, 佘国荣, 等.人工髋关节置换术后并发症影像学表现[J].中国医学影像技术, 2015, 31(7): 1095-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgyxyxjs201507036
|
| [21] |
Giaretta S, Momoli A, Porcelli G, et al. Diagnosis and management of periprosthetic femoral fractures after hip arthroplasty[J]. Injury, 2019, 50(Suppl 2): S29-33.
|
| [22] |
Rupp M, Kern S, Ismat A, et al. Computed tomography for managing periprosthetic femoral fractures. A retrospective analysis[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2019, 20(1): 258-67. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2632-y
|
| [23] |
Kwee RM, Broos WA, Brans B, et al. Added value of 18F-FDG PET/ CT in diagnosing infected hip prosthesis[J]. Acta Radiol, 2018, 59 (5): 569-76. doi: 10.1177/0284185117726812
|
| [24] |
Moon KH, Kang JS, Won MH, et al. The usefulness of threedimensional computed tomography as an assessment of periacetabular osteolysis in revision total hip arthroplasty[J]. Hip Pelvis, 2015, 27(2): 90-7. doi: 10.5371/hp.2015.27.2.90
|
| [25] |
Salem HS, Marchand KB, Ehiorobo JO, et al. Benefits of CT scanning for the management of hip arthritis and arthroplasty[J]. Surg Technol Int, 2020, 36(5): 1249-58.
|
| [26] |
Tang H, Yang DJ, Guo SJ, et al. Digital tomosynthesis with metal artifact reduction for assessing cementless hip arthroplasty: a diagnostic cohort study of 48 patients[J]. Skeletal Radiol, 2016, 45 (11): 1523-32. doi: 10.1007/s00256-016-2466-8
|
| [27] |
Horas K, Arnholdt J, Steinert AF, et al. Acetabular defect classification in times of 3D imaging and patient-specific treatment protocols[J]. Orthopade, 2017, 46(2): 168-78. doi: 10.1007/s00132-016-3378-y
|
| [28] |
Greffier J, Pereira F, Hamard A, et al. Effect of tin filter-based spectral shaping CT on image quality and radiation dose for routine use on ultralow-dose CT protocols: a phantom study[J]. Diagn Interv Imaging, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.diii.2020.01.002.
|
| [29] |
Trabzonlu TA, Terrazas M, Mozaffary A, et al. Application of iterative metal artifact reduction algorithm to CT urography for patients with hip prostheses[J]. Am J Roentgenol, 2020, 214(1): 137- 43. doi: 10.2214/AJR.19.21748
|






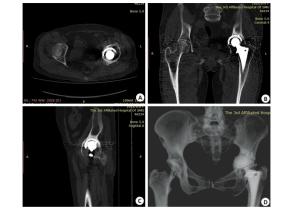
 下载:
下载: