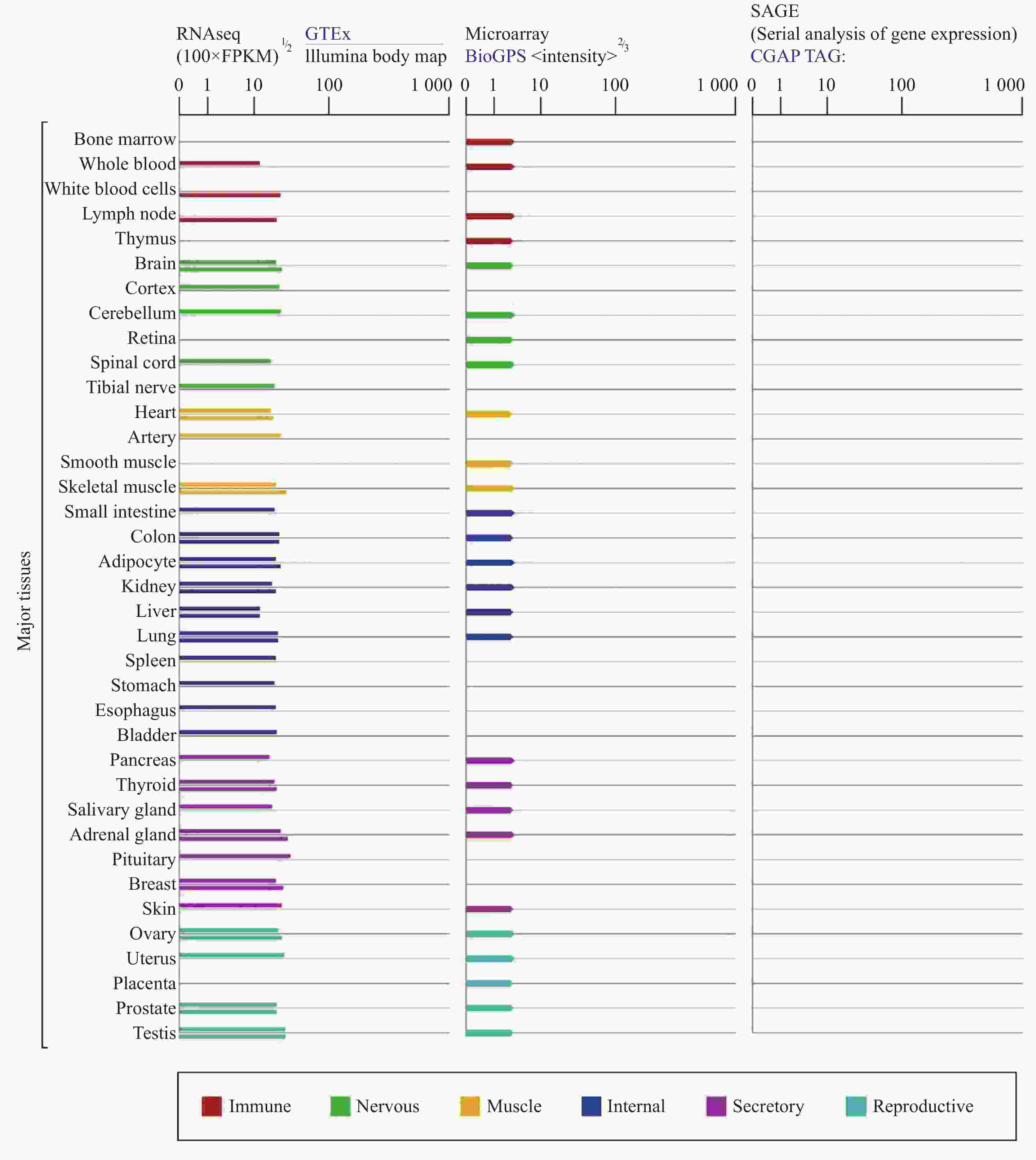
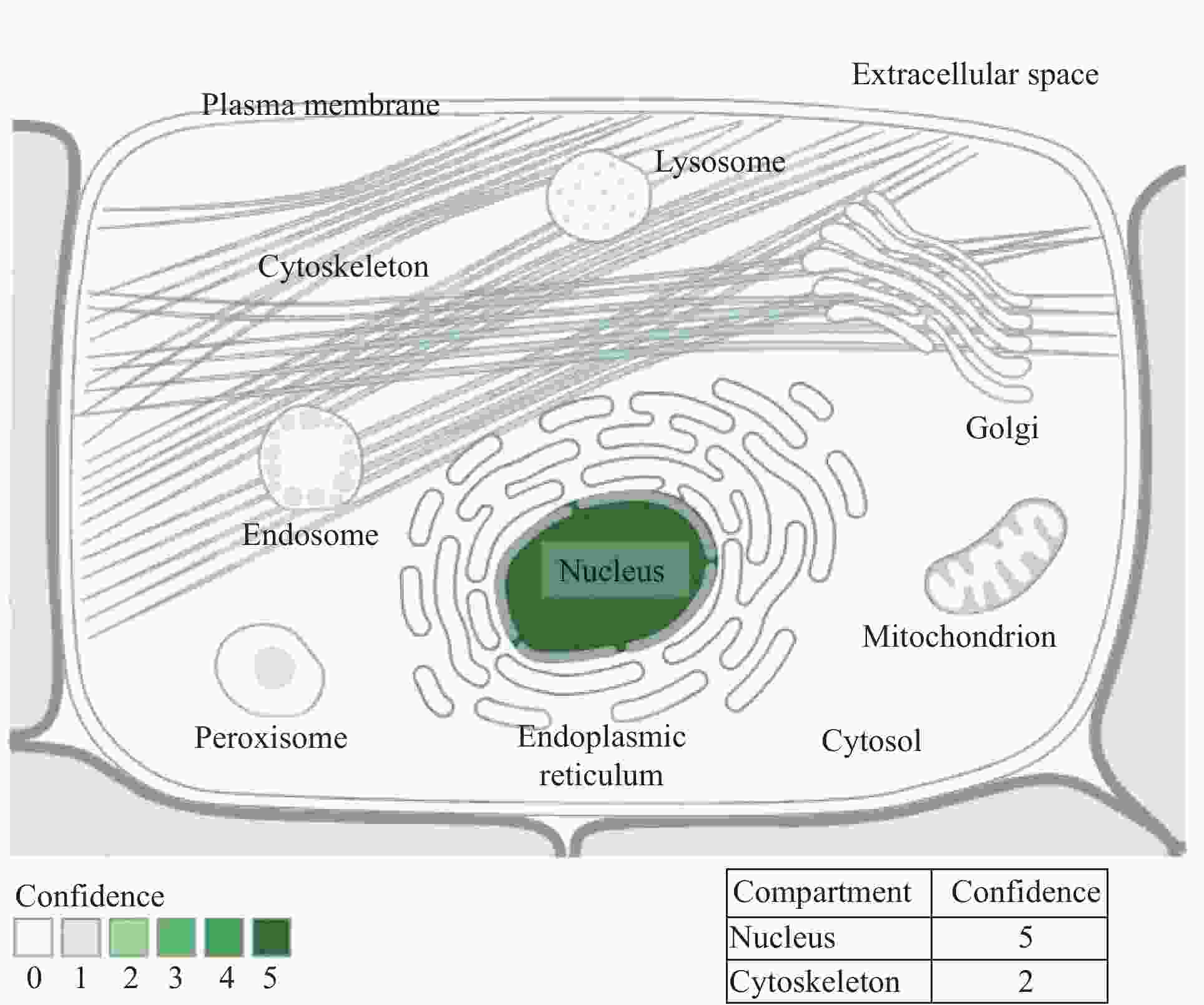
Biological characteristics of FOXK1 and its research progress in various tumors
-
摘要: 叉头框K1(FOXK1)是近年来广受研究关注的FOX转录因子家族成员之一。越来越多的研究表明,FOXK1与生殖、神经和消化等多种系统的肿瘤密切相关,FOXK1可通过调节细胞周期、细胞自噬以及介导信号转导通路,参与各个系统肿瘤的发生发展,影响肿瘤侵袭、转移及患者的预后。FOXK1在各个系统肿瘤组织中的特异性表达及其作用机制的研究,为肿瘤的诊治提供了新方向。本文就FOXK1的基因特征、生物学功能及其与各系统肿瘤的关系进行综述并作展望。
-
关键词:
- FOXK1基因 /
- Wnt/β-catenin信号通路 /
- 肿瘤
Abstract: Fork head box 1 (FOXK1) is one of the members of the FOX transcription factors family that has attracted increasing attention in recent years. More and more studies have shown that FOXK1 is closely related to various tumors such as cancer of reproductive, nervous and digestive systems. Through regulating cell cycle, autophagy and mediating signal pathway, FOXK1 influences tumor invasion and metastasis. It affecting the prognosis of patients. The research of expression of FOXK1 in various tumor tissues and its mechanism provide a new direction for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors.-
Key words:
- FOXK1 gene /
- Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway /
- neoplasms
-
表 1 FOXK1在各种肿瘤中的表达及可能机制
肿瘤类型 FOXK1表达水平 可能的调节机制 参考文献 食管癌 上调 尚未阐明 [25] 卵巢癌 上调 抑制p21转录促进细胞增殖 [16] 弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤 上调 靶向miR-17 [18] 乳腺癌 下调 抑制Twist和VEGF转录 [24] 前列腺癌 上调 正向调控Wnt/β-catenin通路 [19] 神经胶质瘤 上调 激活Wnt/β-catenin通路 [20] 下调 ZRANB2-SNHG20-FOXK1通路 [21] 胶质母细胞瘤 上调 激活Snail转录促进EMT [23] 肺癌 上调 circMAN2B2/miR-1275/FOXK1通路 [17] 肝细胞性肝癌 上调 TGF-β- FOXK1 - Wnt信号通路 [26] 通过Akt/mTOR通路抑制糖酵解 [27] 胃癌 上调 c-jun-FOXK1通路 [28] miR-646通过下调FOXK1抑制Bcl-2/Akt通路 [24] LINC02163-miR-593-3p/FOXK1通路 [29] 与波形蛋白相互作用促进EMT [30] 结直肠癌 上调 FOXK1- RUFY3通路 [35, 36] 与FHL2共表达诱导EMT [33] FOXK1-Cyr61-Snail通路 [37] LINC01503/miR-4492/FOXK1通路 [38] -
[1] Huang JT, Lee V. Identification and characterization of a novel human FOXK1 gene in silico[J]. Int J Oncol, 2004, 25(3): 751-7. [2] Weigel D, Jackle H. The fork head domain:a novel DNA binding motif of eukaryotic transcription factors[J]. Cell, 1990, 63(3): 455-6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90439-L [3] Katoh M. Human Fox gene family(Review)[J]. Int J Oncol, 2004, 25(5): 1495-500. [4] 曹冬梅, 卢 建. 叉头框(Fox)转录因子家族的结构与功能[J]. 生命科学, 2006, 18(5): 491-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0374.2006.05.018 [5] Grant GD, Gamsby J, Martyanov V, et al. Live-cell monitoring of periodic gene expression in synchronous human cells identifies Forkhead genes involved in cell cycle control[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2012, 23(16): 3079-93. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e11-02-0170 [6] Hawke TJ, Jiang N, Garry DJ. Absence of p21CIP rescues myogenic progenitor cell proliferative and regenerative capacity in Foxk1 null mice[J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(6): 4015-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209200200 [7] Shi X, Wallis AM, Gerard RD, et al. Foxk1 promotes cell proliferation and represses myogenic differentiation by regulating Foxo4 and Mef2[J]. J Cell Sci, 2012, 125(22): 5329-37. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105239 [8] Wu Y, Xie R, Liu X, et al. Knockdown of FOXK1 alone or in combination with apoptosis-inducing 5-FU inhibits cell growth in colorectal cancer[J]. Oncol Rep, 2016, 36(4): 2151-5. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5041 [9] Ramkumar P, Lee CM, Moradian A, et al. JNK associated leucine zipper protein functions as a docking platform for Polo like kinase 1 and regulation of the associating transcription factor Forkhead box protein K1[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290(49): 29617-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.664649 [10] Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling,disease,and emerging therapeutic modalities[J]. Cell, 2017, 169(6): 985-99. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.016 [11] Yang K, Wang X, Zhang HM, et al. The evolving roles of canonical WNT signaling in stem cells and tumorigenesis:implications in targeted cancer therapies[J]. Lab Invest, 2016, 96(2): 116-36. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.144 [12] Wang W, Li X, Lee M, et al. FOXKs promote Wnt/β-Catenin signaling by translocating DVL into the nucleus[J]. Dev Cell, 2015, 32(6): 707-18. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.01.031 [13] Zhang P, Tang WM, Zhang H, et al. MiR-646 inhibited cell proliferation and EMT-induced metastasis by targeting FOXK1 in gastric cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2017, 117(4): 525-36. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.181 [14] Casas-Tinto S, Gomez-Velazquez M, Granadino B, et al. FoxK mediates TGF-beta signalling during midgut differentiation in flies[J]. J Cell Biol, 2008, 183(6): 1049-60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200808149 [15] Li L, Miao G, Yu Z, et al. FOXK1 facilitates cell proliferation through regulating the expression of p21,and promotes metastasis in ovarian cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(41): 70441-51. [16] Ma XM, Yang XD, Bao WH, et al. Circular RNA circMAN2B2 facilitates lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion via miR-1275/FOXK1 axis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 498(4): 1009-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.105 [17] Luo X, Shi F, Qiu H, et al. Identification of potential key genes associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma based on microarray gene expression profiling[J]. Neoplasma, 2017, 64(6): 824-33. doi: 10.4149/neo_2017_603 [18] Chen F, Xiong W, Dou K, et al. Knockdown of FOXK1 suppresses proliferation,migration,and invasion in prostate cancer cells[J]. Oncol Res, 2017, 25(8): 1261-7. doi: 10.3727/096504017X14871164924588 [19] Ji ZG, Jiang HT, Zhang PS. FOXK1 promotes cell growth through activating wnt/beta-catenin pathway and emerges as a novel target of miR-137 in glioma[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2018, 10(6): 1784-92. [20] Li X, Xue Y, Liu X, et al. ZRANB2/SNHG20/FOXK1 axis regulates vasculogenic mimicry formation in glioma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 68-79. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1073-7 [21] Karginova EA, Pentz ES, Kazakova IG, et al. Zis:a developmentally regulated gene expressed in juxtaglomerular cells[J]. Am J Physiol, 1997, 273(5): F731-42. [22] Xu H, Huang S, Zhu X, et al. FOXK1 promotes glioblastoma proliferation and metastasis through activation of snail transcription[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 15(3): 3108-16. [23] Sun T, Wang H, Li Q, et al. Forkhead box protein k1 recruits TET1 to act as a tumor suppressor and is associated with MRI detection[J]. Jpn J Clin Oncol, 2016, 46(3): 209-21. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv185 [24] Chen D, Wang K, Li X, et al. FOXK1 plays an oncogenic role in the development of esophageal cancer[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017, 494(1/2): 37-49. [25] Li P, Yu Z, He L, et al. Knockdown of FOXK1 inhibited the proliferation,migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Retour Au Numéro, 2017, (13): 270-81. [26] Cui H, Gao Q, Zhang L, et al. Knockdown of FOXK1 suppresses liver cancer cell viability by inhibiting glycolysis[J]. Life Sci, 2018, 213(2): 66-73. [27] Peng Y, Zhang P, Huang X, et al. Direct regulation of FOXK1 by C-jun promotes proliferation,invasion and metastasis in gastric cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2016, 7(11): e2480-91. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.225 [28] Dong L, Hong H, Chen X, et al. LINC02163 regulates growth and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotype via miR-593-3p/FOXK1 axis in gastric cancer cells[J]. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2018, 46(9): 607-15. [29] Wu Y, Peng Y, Wu M, et al. Oncogene FOXK1 enhances invasion of colorectal carcinoma by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(32): 51150-62. [30] Cao CY, Mok WF, Cheng WS, et al. The FHL2 regulation in the transcriptional circuitry of human cancers[J]. Gene, 2015, 572(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.07.043 [31] Wu M, Wang J, Tang W, et al. FOXK1 interaction with FHL2 promotes proliferation,invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer[J]. Oncogenesis, 2016, 5(11): e271-82. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2016.68 [32] Xie R, Wang J, Liu X, et al. RUFY3 interaction with FOXK1 promotes invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 3709-20. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04011-1 [33] Huang X, Xiang L, Li Y, et al. Snail/FOXK1/Cyr61 signaling axis regulates the Epithelial-Mesenchymal transition and metastasis in colorectal cancer[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 47(2): 590-603. doi: 10.1159/000490015 [34] Lu SR, Li Q, Lu JL, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC01503 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating miR-4492/FOXK1 signaling[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 16(6): 4879-85. -






 下载:
下载: