Expression of serum miR-31 for the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer
-
摘要:
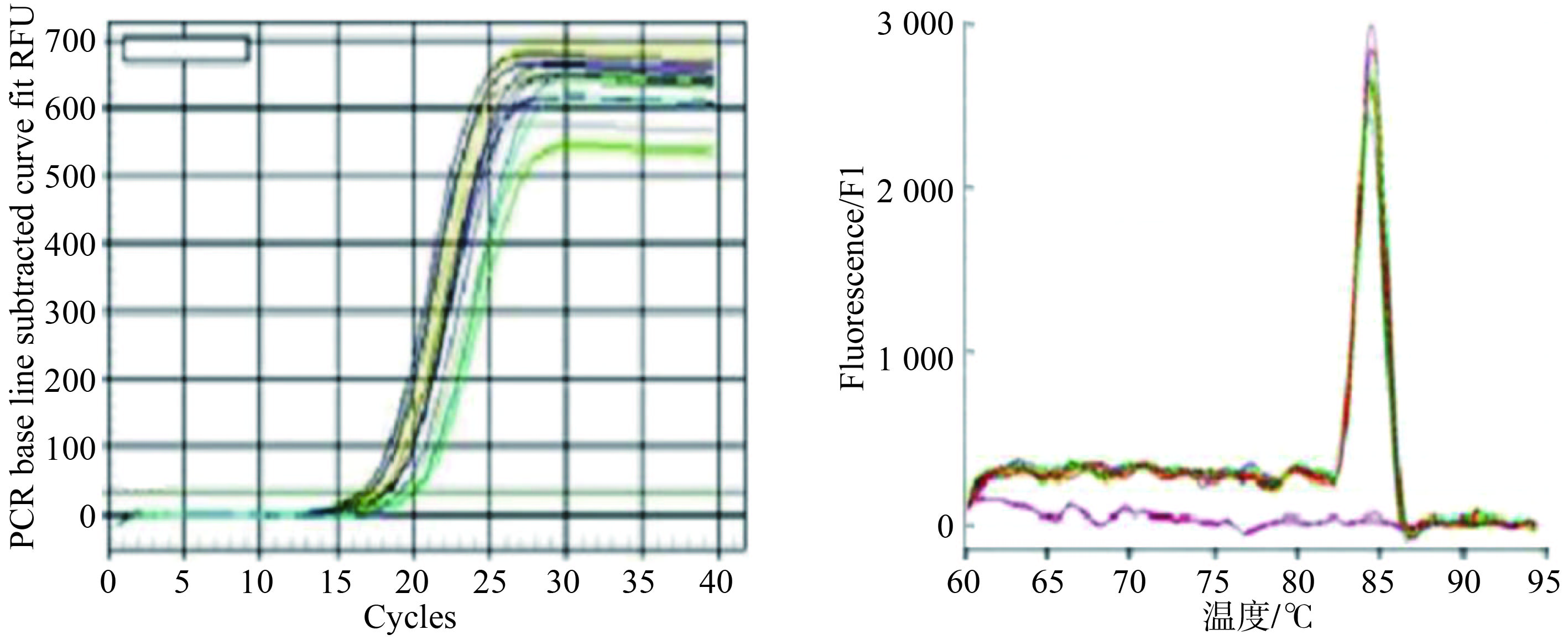
目的研究血清miR-31对非小细胞型肺癌的诊断价值。 方法选取非小细胞型肺癌患者42名为研究对象,收集患者的肺癌组织、癌旁组织、血清,和正常人40例的血清,检测miR-31的表达水平。 结果非小细胞型肺癌组织miR-31显著高于癌旁组织(P< 0.05),临床分期、是否存在淋巴结转移是影响miR-31表达水平的独立性危险因素(P< 0.05)。患者血清miRNA水平显著高于正常人血清(P< 0.05)。ROC曲线表明miRNA诊断非小细胞型肺癌的敏感性0.829,特异性0.763。 结论miRNA可以作为非小细胞型细胞新的分子标志物。 Abstract:ObjectiveTo exlpore the diagnostic value of serum miR-31 in non-small cell lung cancer. MethodsA total of 42 patients with non-small cell lung cancer were enrolled. The serum of 40 patients with lung cancer, paracancerous tissues, serum, and normal subjects were collected to detect the expression level of miR-31. ResultsmiR-31 in non-small cell lung cancer tissues was significantly higher than that of paracancerous tissues(P< 0.05). Clinical stage and lymph node metastasis were independent risk factors affecting the expression level of miR-31. The serum miRNA levels of patients were significantly higher than that of normal human serum(P< 0.05). The ROC curve indicates that the miRNA had a sensitivity of 0.829 and a specificity of 0.763 for the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. ConclusionmiRNA can be used as a new molecular marker for non-small cell lung cancer. -
Key words:
- non-small cell lung cancer /
- microRNA /
- molecular markers
-
表 1 NSCLC组织中miR-31表达与临床特征的单因素分析(Mean±SD)
参数 例数 miR-31表达量 t/F P 年龄(岁) 0.802 0.427 <45 19 5.99±9.07 ≥45 23 5.35±3.92 临床分期 −2.935 0.005 I期 18 4.24±2454 II期 14 5.38±3.19 III期 10 6.89±2.67 病理类型 1.087 0.355 鳞癌 15 5.43±4.11 腺癌 17 5.78±7.09 大细胞癌 10 5.81±8.96 病理分级 0.062 0.951 低分化 22 5.67±6.63 高分化 20 5.61±6.57 淋巴结转移 −2.783 0.006 无 24 4.76±7.41 有 18 6.87±8.34 表 2 NSCLC组织中miR-31表达与临床特征的多因素分析
参数 标准误 Wald df 95% CI P 临床分期 0.579 5.553 1 0.335-3.238 0.019 淋巴结转移 0.961 4.026 1 0.091-3.920 0.037 -
[1] Chen X, Zhao J, Guan YH, et al. Prognostic value of 2-{[}F-18]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake as measured by PET scan in patients with non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2008, 1(6): 889-93. [2] Lin K, Xu T, He BS, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles predict progression and clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2016, 9(12): 5679-92. [3] Gallardo E, Navarro A, Vinolas N, et al. miR-34a as a prognostic marker of relapse in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2009, 30(11): 1903-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp219 [4] Zhao YF, He J, Yang L, et al. Histone deacetylase-3 modification of MicroRNA-31 promotes cell proliferation and aerobic glycolysis in breast cancer and is predictive of poor prognosis[J]. J Breast Cancer, 2018, 21(2): 112-23. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2018.21.2.112 [5] Liu ZY, Bai J, Zhang LY, et al. Conditional knockout of microRNA-31 promotes the development of colitis associated cancer[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017, 490(1): 62-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.012 [6] Wang CJ, Zhou ZG, Wang L, et al. Clinicopathological significance of microRNA-31, -143 and -145 expression in colorectal cancer[J]. Dis Markers, 2009, 26(1): 27-34. doi: 10.1155/2009/921907 [7] Li P, Wang QA, Wang HN. MicroRNA-204 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of human lung cancer cells by targeting PCNA-1 and inhibits tumor growth in vivo[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2019, 43(3): 1149-56. [8] Ma Y, Li XE, Chen S, et al. MicroRNA-4458 suppresses migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via targeting HMGA1 in non-small-cell lung cancer cells[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2019, 11(7): 637-49. [9] Amin NP, Mohindra P, Jabbour SK. Serum microRNA guiding personalized radiation therapy in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2018, 10(33): S4108-12. [10] Hou S, Cheng Z, Wang W, et al. Ailanthone exerts an antitumor function on the development of human lung cancer by upregulating microRNA-195[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 37(4): 380-93. [11] Li W, Jia MX, Deng J, et al. Down-regulation of microRNA-200b is a potential prognostic marker of lung cancer in southern-central Chinese population[J]. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2019, 26(1): 173-7. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.08.023 [12] Zhou Y, Zheng X, Chen LJ, et al. microRNA-181b suppresses the metastasis of lung cancer cells by targeting sex determining region y-related high mobility group-box 6(Sox6)[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2019, 215(2): 335-42. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.12.009 [13] Stepicheva NA, Song JL. Function and regulation of MicroRNA-31 in development and disease[J]. Mol Reprod Dev, 2016, 83(8): 654-74. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22678 [14] Yamagishi M, Nakano K, Miyake A, et al. Polycomb-Mediated loss of miR-31 activates NIK-Dependent NF-kappa B pathway in adult T cell leukemia and other cancers[J]. Cancer Cell, 2012, 21(1): 121-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.12.015 [15] Vire E, Curtis C, Davalos V, et al. The breast cancer oncogene EMSY represses transcription of antimetastatic microRNA miR-31[J]. Mol Cell, 2014, 53(5): 806-18. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.01.029 [16] Liu X, Sempere LF, Ouyang H, et al. MicroRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in mouse and human lung cancer cells by repressing specific tumor suppressors[J]. J Clin Invest, 2010, 120(4): 1298-309. doi: 10.1172/JCI39566 [17] Edmonds MD, Boyd KL, Moyo T, et al. MicroRNA-31 initiates lung tumorigenesis and promotes mutant KRAS-driven lung cancer[J]. J Clin Invest, 2016, 126(1): 349-64. [18] Vishnubalaji R, Hamam R, Abdulla MH, et al. Genome-wide mRNA and miRNA expression profiling reveal multiple regulatory networks in colorectal cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2015, 6(10): e1614-26. [19] 王 昆, 胡早秀, 赵铁荣, 等. miRNA-31基因谱与宣威女性肺癌的相关性研究[J]. 云南医药, 2016, 28(1): 4-8. [20] 侯春英. MET-PI3K-Akt信号通路介导miRNA--31调控肺腺癌肿瘤干细胞功能[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2016. -







 下载:
下载: